
The Indus River is one of the longest rivers in Asia. Originating in the Tibetan Plateau in the vicinity of Lake Manasarovar, the river runs a course through the Ladakh region of Jammu and Kashmir, towards the Gilgit-Baltistan region of Pakistan and the Hindukush ranges, and then flows in a southerly direction along the entire length of Pakistan to merge into the Arabian Sea near the port city of Karachi in Sindh. It is the longest river and national river of Pakistan.

The Himalayas, or Himalaya, form a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau.

Leh is a town in the Leh district of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. It was the capital of the Himalayan kingdom of Ladakh, the seat of which was in the Leh Palace, the former mansion of the royal family of Ladakh, built in the same style and about the same time as the Potala Palace in Tibet - the chief residence of the Dalai Lama until the 14th Dalai Lama fled to Dharamshala, India, during the 1959 Tibetan uprising. Leh is at an altitude of 3,524 metres (11,562 ft), and is connected via National Highway 1 to Srinagar in the southwest and to Manali in the south via the Leh-Manali Highway. In 2010, Leh was heavily damaged by the sudden floods caused by a cloud burst.
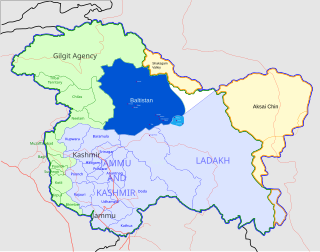
Baltistan (Urdu: بلتستان, Balti: སྦལ་ཏི་སྟཱན also known as Baltiyul or Little Tibet, is a mountainous region in Pakistan-administered Kashmir near the Karakoram mountains just south of K2. Baltistan borders Gilgit to the west, Xinjiang in the north, Ladakh on the southeast and the Kashmir Valley on the southwest. Its average altitude is over 3,350 metres.
{{Infobox river | name = Sutlej / Satluj | name_native = | name_native_lang = | name_other = ਸਤਲੁਜ / ستلُج | name_etymology = | image = 2 River Satluj Sutlej Ropar Dam and Bridge in Rupnagar Punjab India.jpg | image_size = | image_caption = River Sutlej in Rupnagar, [[Punjab, | image_caption = River Sutlej in Rupnagar, Punjab, India | map = Indus river.svg | map_size = | map_caption = The Sutlej is a tributary to the Indus | pushpin_map = | pushpin_map_size = | pushpin_map_caption= | subdivision_type1 = Country | subdivision_name1 = China, India, Pakistan | subdivision_type2 = State | subdivision_name2 = Tibet, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Punjab | subdivision_type3 = | subdivision_name3 = | subdivision_type4 = | subdivision_name4 = | subdivision_type5 = | subdivision_name5 = | length = 1,500 km (930 mi)approx. | width_min = | width_avg = | width_max = | depth_min = | depth_avg = | depth_max = | discharge1_location= Ropar | discharge1_min = | discharge1_avg = 500 m3/s (18,000 cu ft/s) | discharge1_max = | source1 = Langqên Zangbo | source1_location = [[Tibet Autonomous Region|| source1_location = Tibet | source1_coordinates= 30°50′39″N81°12′17″E | source1_elevation = 4,575 m (15,010 ft) | mouth = Confluence with Chenab to form the Panjnad River | mouth_location = Bahawalpur district, Punjab, Pakistan | mouth_coordinates = 29°23′23″N71°3′42″E | mouth_elevation = 102 m (335 ft) | progression = | river_syste| river_system = | basin_size = 395,000 km2 (153,000 sq mi)approx. | tributaries_left = Baspa | tributaries_right = Spiti, Beas | custom_label = | custom_dat| custom_data = | extra = }} The Sutlej River (Punjabi: ਸਤਲੁਜ, Sanskrit: शतद्रुम, , is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as Satadree It is addressed as Shatarudra by the Gorkhalis. It is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River.

The Indus River Delta, forms where the Indus River flows into the Arabian Sea, mostly in the Southern Sindh province of Pakistan with a small portion in the Kutch Region of the Western tip of India. The delta covers an area of about 41,440 km², and is approximately 210 km (130 mi) across where it meets the sea. The active part of the delta is 6,000 km2 in area (2,300 sq mi). The climate is arid, the region only receives between 25 and 50 centimetres of rainfall in a normal year. The delta is home to the largest arid mangrove forests in the world, as well as many birds, fish and the Indus Dolphin.

The Ladakh Range is a mountain range in central Ladakh in the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir with its northern tip extending into Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan. It lies between the Indus and Shyok river valleys, stretching to 230 miles (370 km). Leh, the capital city of Ladakh, is on the foot of Ladakh Range in the Indus river valley.

Upshi is a village and road junction on the Leh-Manali Highway in Ladakh region of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. It is located 47 km (29 mi) to the southeast of Leh along the Indus river valley and Tanglang La on the Leh-Manali highway. Gya is also to the south.

Zhongba County is a county of Xigazê Prefecture in China's Tibet Autonomous Region. Located in western Tibet, it is the largest county in the prefecture.
Alice Albinia is an English journalist and author whose first book, Empires of the Indus, won several awards.
Olangchung Gola is a village development committee in the Himalayas of Taplejung District in the Mechi Zone of north-eastern Nepal. It is located to the north of Tamor River in the mountainous area in the northwest of Taplejung District bordering Tibet, China. Lately the river flowing next to the village is gradually expanding towards the village posing a serious threat of submerging the village.

Indus Vallis is a vallis (valley) in the Arabia quadrangle of Mars, located at 19.3° North and 321.3° West. It is 307 km long and was named for the Indus River in Pakistan. The westernmost part of the valley is in the vicinity of Cassini Crater.

Ngari Gunsa Airport is a dual-use military and civil airport serving the town of Shiquanhe in Ngari Prefecture, in the southwest of China's Tibet Autonomous Region near the Indian border. It started operations on 1 July 2010, becoming the fourth civil airport in Tibet after Lhasa, Nyingchi, and Qamdo airports.

Darchen,Tarchan or Taqin is a small village in Purang County of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It was previously known as Lhara and still signposted as such. It was previously an important sheep station for nomads and their flocks and had only two permanent buildings; only one of which survived the Cultural Revolution and is now used to house Tibetan pilgrims.

Empires of the Indus: The Story of a River is a non-fiction book by Alice Albinia that covers the writer's journey from Karachi to Tibet, which is the natural course of the Indus River. The book gives an insight into the communities as well as the history and political framework of the countries through which the Indus flows. Empires of the Indus was awarded the Jerwood Award by the Royal Society of Literature in 2005.
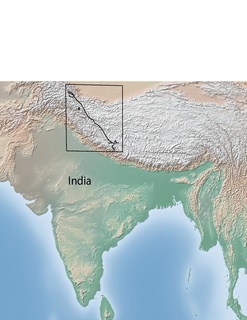
The Karakoram fault is an oblique-slip fault system in the Himalayan region across India and Asia. The slip along the fault accommodates radial expansion of the Himalayan arc, northward indentation of the Pamir Mountains, and eastward lateral extrusion of the Tibetan plateau. Current plate motions suggest that the convergence between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate is around 44±5 mm per year in the western Himalaya-Pamir region and approximately 50±2 mm per year in the eastern Himalayan region.

Demchok, also spelled Demjok, is a village and military encampment in the Leh district of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It is administered as part of the Leh tehsil, in the Indian-administered part of the disputed Demchok sector south of Aksai Chin. The Line of Actual Control (LAC) passes along the southeast side of the village, following a wadi just upstream from the nearby Indus River. Across the wadi, less than a kilometer away, is a Chinese-administered village, called Dêmqog, which was once part of Demchok.

The Shrine of Lal Shabaz Qalandar is a Sufi shrine dedicated to the 13th century Islamic mystic, Lal Shahbaz Qalandar. The shrine is located in Sehwan Sharif, in the Pakistani province of Sindh. The shrine is one of the most important in Pakistan, and attracts up to one million visitors annually.

The Shrine at Odero Lal, also spelt Udero Lal, is a joint Muslim-Hindu shrine located in the village of Odero Lal, near the city of Tando Adam Khan in the Pakistani province of Sindh. The shrine is notable as it is jointly used for worship by members of both faiths, while both communities also display reverence for the nearby Indus River at the shrine.





















