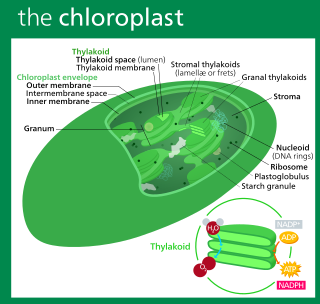
A chloroplast is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, much amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like Arabidopsis and wheat.

Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in the mesosomes of cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words χλωρός, khloros and φύλλον, phyllon ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light.

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek phōs, "light", and sunthesis, "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.
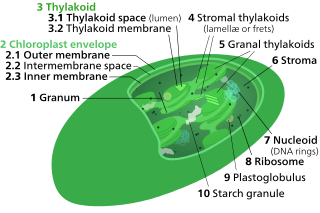
Thylakoids are membrane-bound compartments inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana. Grana are connected by intergranal/stromal thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.

Photosystems are functional and structural units of protein complexes involved in photosynthesis. Together they carry out the primary photochemistry of photosynthesis: the absorption of light and the transfer of energy and electrons. Photosystems are found in the thylakoid membranes of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. These membranes are located inside the chloroplasts of plants and algae, and in the cytoplasmic membrane of photosynthetic bacteria. There are two kinds of photosystems: PSI and PSII.

Photosystem II is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Within the photosystem, enzymes capture photons of light to energize electrons that are then transferred through a variety of coenzymes and cofactors to reduce plastoquinone to plastoquinol. The energized electrons are replaced by oxidizing water to form hydrogen ions and molecular oxygen.

Photosystem I is one of two photosystems in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and cyanobacteria. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex that uses light energy to catalyze the transfer of electrons across the thylakoid membrane from plastocyanin to ferredoxin. Ultimately, the electrons that are transferred by Photosystem I are used to produce the moderate-energy hydrogen carrier NADPH. The photon energy absorbed by Photosystem I also produces a proton-motive force that is used to generate ATP. PSI is composed of more than 110 cofactors, significantly more than Photosystem II.
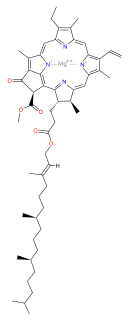
Chlorophyll a is a specific form of chlorophyll used in oxygenic photosynthesis. It absorbs most energy from wavelengths of violet-blue and orange-red light, and it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Chlorophyll does not reflect light but chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light, diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls, becomes enriched in the reflected light. This photosynthetic pigment is essential for photosynthesis in eukaryotes, cyanobacteria and prochlorophytes because of its role as primary electron donor in the electron transport chain. Chlorophyll a also transfers resonance energy in the antenna complex, ending in the reaction center where specific chlorophylls P680 and P700 are located.
The oxygen-evolving complex (OEC), also known as the water-splitting complex, is the portion of photosystem II where photo-oxidation of water occurs during the light reactions of photosynthesis. The OEC is surrounded by four core protein subunits of photosystem II at the membrane-lumen interface.

The cytochrome b6f complex is an enzyme found in the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts of plants, cyanobacteria, and green algae, that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin. The reaction is analogous to the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome bc1 of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. During photosynthesis, the cytochrome b6f complex is one step along the chain that transfers electrons from Photosystem II to Photosystem I, and at the same time pumps protons into the thylakoid space, contributing to the generation of an electrochemical (energy) gradient that is later used to synthesize ATP from ADP.
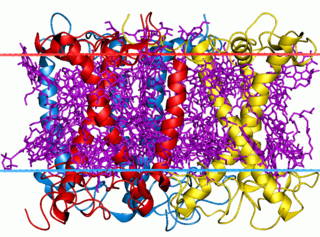
The light-harvesting complex is an array of protein and chlorophyll molecules embedded in the thylakoid membrane of plants and cyanobacteria, which transfer light energy to one chlorophyll a molecule at the reaction center of a photosystem.

A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or transferred as excitation energy via light-harvesting antenna systems, give rise to electron transfer reactions along the path of a series of protein-bound co-factors. These co-factors are light-absorbing molecules (also named chromophores or pigments) such as chlorophyll and pheophytin, as well as quinones. The energy of the photon is used to excite an electron of a pigment. The free energy created is then used, via a chain of nearby electron acceptors, for a transfer of hydrogen atoms (as protons and electrons) from H2O or hydrogen sulfide towards carbon dioxide, eventually producing glucose. These electron transfer steps ultimately result in the conversion of the energy of photons to chemical energy.

Photoinhibition is light-induced reduction in the photosynthetic capacity of a plant, alga, or cyanobacterium. Photosystem II (PSII) is more sensitive to light than the rest of the photosynthetic machinery, and most researchers define the term as light-induced damage to PSII. In living organisms, photoinhibited PSII centres are continuously repaired via degradation and synthesis of the D1 protein of the photosynthetic reaction center of PSII. Photoinhibition is also used in a wider sense, as dynamic photoinhibition, to describe all reactions that decrease the efficiency of photosynthesis when plants are exposed to light.

Photosynthetic reaction centre proteins are main protein components of photosynthetic reaction centres (RCs) of bacteria and plants. They are transmembrane proteins embedded in the chloroplast thylakoid or bacterial cell membrane.
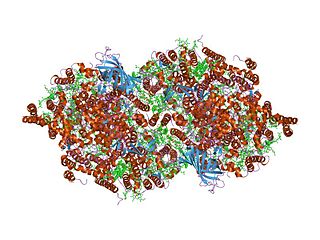
Cytochrome b559 is an important component of Photosystem II.

Photosystem II light-harvesting proteins are the intrinsic transmembrane proteins CP43 (PsbC) and CP47 (PsbB) occurring in the reaction centre of photosystem II (PSII). These polypeptides bind to chlorophyll a and β-Carotene and pass the excitation energy on to the reaction centre.

In photosynthesis, the light-dependent reactions take place on the thylakoid membranes. The inside of the thylakoid membrane is called the lumen, and outside the thylakoid membrane is the stroma, where the light-independent reactions take place. The thylakoid membrane contains some integral membrane protein complexes that catalyze the light reactions. There are four major protein complexes in the thylakoid membrane: Photosystem II (PSII), cytochrome b6f complex, Photosystem I (PSI), and ATP synthase. These four complexes work together to ultimately produce ATP and NADPH.

Bacterial anoxygenic photosynthesis differs from the better known oxygenic photosynthesis in plants by the reductant used and the byproduct generated.
Plastid terminal oxidase or plastoquinol terminal oxidase (PTOX) is an enzyme that resides on the thylakoid membranes of plant and algae chloroplasts and on the membranes of cyanobacteria. The enzyme was hypothesized to exist as a photosynthetic oxidase in 1982 and was verified by sequence similarity to the mitochondrial alternative oxidase (AOX). The two oxidases evolved from a common ancestral protein in prokaryotes, and they are so functionally and structurally similar that a thylakoid-localized AOX can restore the function of a PTOX knockout.
Photoautotrophs are organisms that use light energy and inorganic carbon to produce organic materials. Eukaryotic photoautotrophs absorb energy through the chlorophyll molecules in their chloroplasts while prokaryotic photoautotrophs use chlorophylls and bacteriochlorophylls present in their cytoplasm. All known photoautotrophs perform photosynthesis. Examples include plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.














