
Granite is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers.

Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.

Schist is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as micas, talc, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz.

Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic rock. Foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering, but instead is in planes perpendicular to the direction of metamorphic compression.

Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.

Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculpture using stone as the primary material. Stonemasonry is the craft of shaping and arranging stones, often together with mortar and even the ancient lime mortar, to wall or cover formed structures.

Quartzite is a hard, non-foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone. Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals.

Flagstone (flag) is a generic flat stone, sometimes cut in regular rectangular or square shape and usually used for paving slabs or walkways, patios, flooring, fences and roofing. It may be used for memorials, headstones, facades and other construction. The name derives from Middle English flagge meaning turf, perhaps from Old Norse flaga meaning slab or chip.

Arkose or arkosic sandstone is a detrital sedimentary rock, specifically a type of sandstone containing at least 25% feldspar. Arkosic sand is sand that is similarly rich in feldspar, and thus the potential precursor of arkose.

Dimension stone is natural stone or rock that has been selected and finished to specific sizes or shapes. Color, texture and pattern, and surface finish of the stone are also normal requirements. Another important selection criterion is durability: the time measure of the ability of dimension stone to endure and to maintain its essential and distinctive characteristics of strength, resistance to decay, and appearance.

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic to refer to sedimentary rocks and particles in sediment transport, whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.

The Roxbury Conglomerate, also informally known as Roxbury puddingstone, is a name for a rock formation that forms the bedrock underlying most of Roxbury, Massachusetts, now part of the city of Boston. The bedrock formation extends well beyond the limits of Roxbury, underlying part or all of Quincy, Canton, Milton, Dorchester, Dedham, Jamaica Plain, Brighton, Brookline, Newton, Needham, and Dover. It is named for exposures in Roxbury, Boston area. It is the Rock of the Commonwealth in Massachusetts.

Oakley stone is the trade name of a building stone that occurs in the mountains of southern Idaho in the western United States. It is more properly known as Rocky Mountain quartzite or Idaho quartzite, a metamorphic rock. The stone is quarried south of the city of Oakley in Cassia County, northeast of the three-state border with Nevada and Utah. The quarries are located on the west slope of Middle Mountain in the Albion Mountains, northwest of the City of Rocks National Reserve.
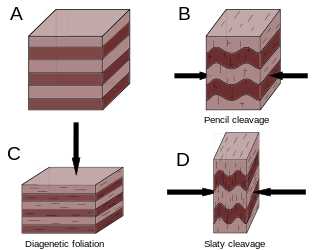
Cleavage, in structural geology and petrology, describes a type of planar rock feature that develops as a result of deformation and metamorphism. The degree of deformation and metamorphism along with rock type determines the kind of cleavage feature that develops. Generally, these structures are formed in fine grained rocks composed of minerals affected by pressure solution.
This glossary of geology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to geology, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. For other terms related to the Earth sciences, see Glossary of geography terms.

Cape Town lies at the south-western corner of the continent of Africa. It is bounded to the south and west by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the north and east by various other municipalities in the Western Cape province of South Africa.

The Catoctin Formation is a geologic formation that expands through Virginia, Maryland, and Pennsylvania. It dates back to the Precambrian and is closely associated with the Harpers Formation, Weverton Formation, and the Loudoun Formation. The Catoctin Formation lies over the a granite basement rock and below the Chilhowee Group making it only exposed on the outer parts of the Blue Ridge. The Catoctin Formation contains metabasalt, metarhyolite, and porphyritic rocks, columnar jointing, low-dipping primary joints, amygdules, sedimentary dikes, and flow breccias. Evidence for past volcanic activity includes columnar basalts and greenstone dikes.

The geology of Ghana is primarily very ancient crystalline basement rock, volcanic belts and sedimentary basins, affected by periods of igneous activity and two major orogeny mountain building events. Aside from modern sediments and some rocks formed within the past 541 million years of the Phanerozoic Eon, along the coast, many of the rocks in Ghana formed close to one billion years ago or older leading to five different types of gold deposit formation, which gave the region its former name Gold Coast.

The Schevenhütte quarry is a former slate quarry in Stolberg-Schevenhütte. Unique Schevenhütte natural stone was quarried here presumably from the Middle Ages until 2008. In the 20th century until it was closed down, the quarry was called "Kaspar Müller I Quarry". It is located on the northern edge of the Eifel at the southern end of Schevenhütte. Geologically, it is part of the outermost foothills of the Venn saddle, where very old rocks from the latest Ordovician period are exposed. These rocks are the oldest in North Rhine-Westphalia. As a special feature, the so-called "Schevenhütter Schichten" dip very straight in the quarry area and were thus worth mining. "Schevenhütter Naturstein" was quarried mainly in two varieties, a greenish and a red variety. Basically, the stone from the middle and upper Wehebach layers was roughly processed and sold on site. The "Schevenhütter Schiefer" was used in a variety of ways throughout the region, including as ornamental and rough building material, but also as walking slabs and as gravestones.





















