Related Research Articles
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the forms of decisions. Understanding in this context means the transformation of visual images into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory.
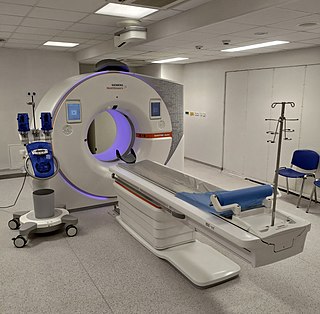
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.
Pattern recognition is the automated recognition of patterns and regularities in data. It has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power. These activities can be viewed as two facets of the same field of application, and they have undergone substantial development over the past few decades.
Computer science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. One well known subject classification system for computer science is the ACM Computing Classification System devised by the Association for Computing Machinery.
Medical physics deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been included as a health profession according to International Standard Classification of Occupation of the International Labour Organization.

Machine learning (ML) is a field devoted to understanding and building methods that let machines "learn" – that is, methods that leverage data to improve computer performance on some set of tasks.

Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, Endoscopy, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.
The image fusion process is defined as gathering all the important information from multiple images, and their inclusion into fewer images, usually a single one. This single image is more informative and accurate than any single source image, and it consists of all the necessary information. The purpose of image fusion is not only to reduce the amount of data but also to construct images that are more appropriate and understandable for the human and machine perception. In computer vision, multisensor image fusion is the process of combining relevant information from two or more images into a single image. The resulting image will be more informative than any of the input images.
Informatics is the study of computational systems. According to the ACM Europe Council and Informatics Europe, informatics is synonymous with computer science and computing as a profession, in which the central notion is transformation of information. In other countries, the term "informatics" is used with a different meaning in the context of library science, in which case it is synonymous with data storage and retrieval.
William Eric Leifur Grimson is a Canadian-born computer scientist and professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he served as Chancellor from 2011 to 2014. An expert in computer vision, he headed MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from 2005 to 2011 and currently serves as its Chancellor for Academic Advancement.
Cognitive computing refers to technology platforms that, broadly speaking, are based on the scientific disciplines of artificial intelligence and signal processing. These platforms encompass machine learning, reasoning, natural language processing, speech recognition and vision, human–computer interaction, dialog and narrative generation, among other technologies.

Ferenc Andras Jolesz was a Hungarian-American physician and scientist best known for his research on image guided therapy, the process by which information derived from diagnostic imaging is used to improve the localization and targeting of diseased tissue to monitor and control treatment during surgical and interventional procedures. He pioneered the field of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-guided interventions and introduced of a variety of new medical procedures based on novel combinations of imaging and therapy delivery.
In the field of medicine, radiomics is a method that extracts a large number of features from medical images using data-characterisation algorithms. These features, termed radiomic features, have the potential to uncover tumoral patterns and characteristics that fail to be appreciated by the naked eye. The hypothesis of radiomics is that the distinctive imaging features between disease forms may be useful for predicting prognosis and therapeutic response for various cancer types, thus providing valuable information for personalized therapy. Radiomics emerged from the medical fields of radiology and oncology and is the most advanced in applications within these fields. However, the technique can be applied to any medical study where a pathological process can be imaged.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to machine learning. Machine learning is a subfield of soft computing within computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. In 1959, Arthur Samuel defined machine learning as a "field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed". Machine learning explores the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms operate by building a model from an example training set of input observations in order to make data-driven predictions or decisions expressed as outputs, rather than following strictly static program instructions.
Dorin Comaniciu is a Romanian-American computer scientist. He is the Senior Vice President of Artificial Intelligence and Digital Innovation at Siemens Healthcare.

René Vidal is a Chilean electrical engineer and computer scientist who is known for his research in machine learning, computer vision, medical image computing, robotics, and control theory. He is the Herschel L. Seder Professor of the Johns Hopkins Department of Biomedical Engineering, and the founding director of the Mathematical Institute for Data Science (MINDS).
Anant Madabhushi is the Donnell Institute Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) in Cleveland, Ohio, USA and founding director of CWRU's Center for Computational Imaging and Personalized Diagnostics (CCIPD). He is also a Research Scientist at the Louis Stokes Cleveland Veterans Administration (VA) Medical Center in Cleveland, OH, USA. He holds secondary appointments in the Case Western Reserve University departments of Urology, Radiology, Pathology, Radiation Oncology, General Medical Sciences, Computer & Data Sciences, and Electrical, Computer and Systems Engineering.

Information engineering is the engineering discipline that deals with the generation, distribution, analysis, and use of information, data, and knowledge in systems. The field first became identifiable in the early 21st century.

Gregory D. Hager is the Mandell Bellmore Professor of Computer Science and founding director of the Johns Hopkins Malone Center for Engineering in Healthcare at Johns Hopkins University.
Merative, formerly IBM Watson Health, is a standalone company as of 2022. Merative offers products and services that help clients facilitate medical research, clinical research, Real world evidence, and healthcare services, through the use of artificial intelligence, data analytics, cloud computing, and other advanced information technology. Merative is owned by Francisco Partners, an American private equity firm headquartered in San Francisco, California.
References
- ↑ "Yuichi Motai - Personal". People.vcu.edu. Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ↑ Prediction and Classification of Respiratory Motion | Suk Jin Lee. Springer. 2016-10-14. Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ↑ Latency and Distortion of Electromagnetic Trackers for Augmented Reality Systems. Dl.acm.org. May 2014. ISBN 9781627055079 . Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ↑ "Data-Variant Kernel Analysis - Yuichi Motai". Wiley. Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ↑ "Predicting Vehicle Trajectory - CRC Press Book". Crcpress.com. Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ↑ "Yuichi Motai - Publication". People.vcu.edu. Retrieved 2017-02-23.
- ↑ "Yuichi Motai - Research". People.vcu.edu. Retrieved 2017-02-16.
- ↑ "Yuichi Motai - Teaching". People.vcu.edu. Retrieved 2017-02-16.