
The woolly monkeys are the genus Lagothrix of New World monkeys, usually placed in the family Atelidae.

The insect order Zoraptera, commonly known as angel insects, contains small and soft bodied insects with two forms: winged with wings sheddable as in termites, dark and with eyes (compound) and ocelli (simple); or wingless, pale and without eyes or ocelli. They have a characteristic nine-segmented beaded (moniliform) antenna. They have mouthparts adapted for chewing and are mostly found under bark, in dry wood or in leaf litter.

Zorotypus is a genus of angel insects in the family Zorotypidae.

Sapium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is widespread across most of Latin America and the West Indies. Many Old World species were formerly included in the genus, but recent authors have redistributed all the Old World species into other genera.

The subantarctic fur seal is a species of arctocephaline found in the southern parts of the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic Oceans. It was first described by Gray in 1872 from a specimen recovered in northern Australia—hence the inappropriate specific name tropicalis.

Heterorhabditis is a genus of nematodes belonging to the order Rhabditida. All species of this genus are obligate parasites of insects, and some are used as biological control agents for the control of pest insects.
Druceiella is a genus of moths of the family Hepialidae. There are four described species, although a revision of the genus is being carried out which will add at least four new species. The current species are all found in South America.

The cinnamon dog-faced bat, is a South American bat species of the family Molossidae. It is found in northern and central South America.

The long-tailed spiny rat is a spiny rat species found in Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay.

Pholidostachys is a genus of palms found in Central America and northwestern South America.
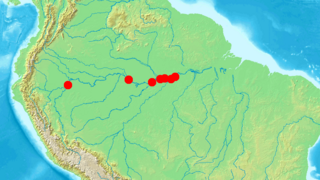
Pariosternarchus amazonensis is a little-known species of weakly electric knifefish in the family Apteronotidae, and the only member of the genus Pariosternarchus. It is found in the main channel of the Amazon River in Brazil and Peru, likely near the bottom in deep, fast-moving water. This species is characterized by a wide head with a flat bottom, and very large sensory canals along the lower jaw. Like several other knifefishes found in deep river channels, it has reduced eyes, scales, and body pigmentation.

Gracile capuchin monkeys are capuchin monkeys in the genus Cebus. At one time all capuchin monkeys were included within the genus Cebus. In 2011, Jessica Lynch Alfaro et al. proposed splitting the genus between the robust capuchin monkeys, such as the tufted capuchin, and the gracile capuchins. The gracile capuchins retain the genus name Cebus, while the robust species have been transferred to Sapajus.
Clavulina amazonensis is a species of fungus in the family Clavulinaceae. Found in South America, it was described by British mycologist E.J.H. Corner in 1970.

Mansonia mosquitoes are big, black or brown mosquitoes with sparkling on their wings and legs. They breed in ponds and lakes containing certain aquatic plants, especially the floating type like Pistia stratiotes and water hyacinth. The eggs are laid in star-shaped clusters on the undersurface of leaves of these plants. The larvae and pupae are found attached to the rootlets of these plants by their siphons. They obtain their air supply from these rootlets. When about to become adult, these pupae come to the surface of water and the fully formed adults emerge and escape. The control of Mansonia mosquitoes is easy by removal or destruction of the aquatic host plants by herbicides.
Zorotypus absonus is an extinct species of insect in the order Zoraptera that lived during the Burdigalian age of the Miocene epoch. It was described from a fossil of an alate male found in Dominican amber; the specimen is deposited in Joachim Scheven's private collection at his "Lebendige Vorwelt" museum in Hagen, Germany.

Humboldt's white-fronted capuchin is a species of gracile capuchin monkey. It is found in Colombia, Venezuela, Brazil, and potentially the island of Trinidad.
Macrostomus is a genus of flies in the family Empididae.
Sabicea amazonensis is a species of plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in tropical South America. Zemagho, et al. assign Sabicea amazonensis to their subgenus, Sabicea Aubl. subgenus Sabicea, on the basis of morphological characters.
Cazuza's saki is a species of saki monkey, a type of New World monkey. It is endemic to northwestern Brazil.
Parotocinclus amazonensis is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Amazon River basin in areas with a pH of 6.0 to 7.0 and a dH range of 5 to 15. The species reaches 2.5 cm in total length.












