Related Research Articles

The 3rd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met at Congress Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from March 4, 1793, to March 4, 1795, during the fifth and sixth years of George Washington's presidency.
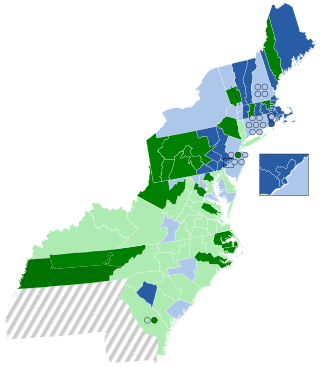
The 1794–95 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in each state between August 25, 1794, and September 5, 1795 (Kentucky). The election was held during President George Washington's second term.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections coincided with the re-election of President George Washington. While Washington ran for president as an independent, his followers formed the nation's first organized political party, the Federalist Party, whose members and sympathizers are identified as pro-Administration on this page. In response, followers of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison created the opposition Democratic-Republican Party, who are identified as anti-Administration on this page. The Federalists promoted urbanization, industrialization, mercantilism, centralized government, and a broad interpretation of the United States Constitution. In contrast, Democratic-Republicans supported the ideal of an agrarian republic made up of self-sufficient farmers and small, localized governments with limited power.

Party divisions of United States Congresses have played a central role on the organization and operations of both chambers of the United States Congress—the Senate and the House of Representatives—since its establishment as the bicameral legislature of the Federal government of the United States in 1789. Political parties had not been anticipated when the U.S. Constitution was drafted in 1787, nor did they exist at the time the first Senate elections and House elections occurred in 1788 and 1789. Organized political parties developed in the U.S. in the 1790s, but political factions—from which organized parties evolved—began to appear almost immediately after the 1st Congress convened. Those who supported the Washington administration were referred to as "pro-administration" and would eventually form the Federalist Party, while those in opposition joined the emerging Democratic-Republican Party.

The 4th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met at Congress Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from March 4, 1795, to March 4, 1797, during the last two years of George Washington's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1790 United States census. The Senate had a Federalist majority, and the House had a Democratic-Republican majority.

The 1790–91 United States Senate elections were the second series of elections of senators in the United States. In these elections, terms were up for the nine senators in Class 1. As of these elections, formal organized political parties had yet to form in the United States, but two political factions were present: The coalition of senators who supported President George Washington's administration were known as the Pro-Administration Party, and the senators against him as the Anti-Administration Party.

The 1792–93 United States Senate elections were elections of United States senators that coincided with President George Washington's unanimous re-election. In these elections, terms were up for the ten senators in class 2.

The 1794–95 United States Senate elections were elections that had the formation of organized political parties in the United States, with the Federalist Party emerging from the Pro Administration coalition, and the Democratic-Republican Party emerging from the Anti-Administration coalition.

The 1828 United States elections elected the members of the 21st United States Congress. It marked the beginning of the Second Party System, and the definitive split of the Democratic-Republican Party into the Democratic Party and the National Republican Party. While the Democrats cultivated strong local organizations, the National Republicans relied on a clear national platform of high tariffs and internal improvements. Political scientists such as V.O. Key, Jr. consider this election to be a realigning election, while political scientists such as James Reichley instead see the election as a continuation of the Democratic-Republican tradition. Additionally, this election saw the Anti-Masonic Party win a small number of seats in the House, becoming the first third party to gain representation in Congress.

The 1820 United States elections elected the members of the 17th United States Congress. The election took place during Era of Good Feelings and the First Party System. Despite the Panic of 1819, the Democratic-Republican Party maintained control of the presidency and both houses of Congress, while the Federalist Party provided only limited opposition. Missouri joined the union during the 17th Congress.

The 1816 United States elections elected the members of the 15th United States Congress. Mississippi and Illinois were admitted as states during the 15th Congress. The election took place during the First Party System. The Democratic-Republican Party controlled the Presidency and both houses of Congress, while the Federalist Party provided only limited opposition. The election marked the start of the Era of Good Feelings, as the Federalist Party became nearly irrelevant in national politics after the War of 1812 and the Hartford Convention.

The 1812 United States elections elected the members of the 13th United States Congress. The election took place during the First Party System, and shortly after the start of the War of 1812. The Federalist Party made a relatively strong showing, winning seats in both chambers while supporting a competitive challenge to the incumbent Democratic-Republican President. However, the Democratic-Republican Party continued its control of the Presidency and both houses of Congress.

The 1808 United States elections elected the members of the 11th United States Congress. The election took place during the First Party System. In the aftermath of the Embargo of 1807, the Federalists picked up Congressional seats for the first time since their defeat in the 1800 election. However, the Democratic-Republican Party maintained control of the Presidency and both houses of Congress.

The 1796 United States elections elected the members of the 5th United States Congress. The election took place during the beginning stages of the First Party System, as the Federalist Party and the Democratic-Republican Party clashed over the states' rights, the financial policies of Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton, and the recently ratified Jay Treaty. The Federalists maintained control of the Senate, and won control of the House and the presidency.

The 1792 United States elections elected the members of the 3rd United States Congress. Congress was broadly divided between a Pro-Administration faction supporting the policies of George Washington's administration and an Anti-Administration faction opposed to those policies. Due to this, the Federalist Party and the Democratic-Republican Party were starting to emerge as the distinct political parties of the First Party System. In this election, the Pro-Administration faction maintained control of the Senate, but lost its majority in the House.

The United States elections of 1788–1789 were the first federal elections in the United States following the ratification of the United States Constitution in 1788. In the elections, George Washington was elected as the first president and the members of the 1st United States Congress were selected.
The 1814 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic-Republican President James Madison's second term, during the First Party System. Members of the 14th United States Congress were chosen in this election. During the 14th Congress, Indiana joined the union. The election took place during the War of 1812.
The 1826 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic-Republican President John Quincy Adams's term. Members of the 20th United States Congress were chosen in this election. The election took place during a transitional period between the First Party System and the Second Party System. With the Federalist Party no longer active as a major political party, the major split in Congress was between supporters of Adams and supporters of Andrew Jackson, who Adams had defeated in the 1824 Presidential election.

The 1858 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President James Buchanan's term and marked the end of the transitional period between the Second Party System and the Third Party System. Members of the 36th United States Congress were chosen in this election. In the first election since the Supreme Court decided Dred Scott v. Sandford, the Republican Party won a plurality in the House, taking control of a chamber of Congress for the first time in the party's history. Although Democrats lost control of the House, they retained their majority in the Senate.
References
- ↑ Not counting special elections.
- 1 2 Congressional seat gain figures only reflect the results of the regularly-scheduled elections, and do not take special elections into account.
- 1 2 "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- 1 2 "Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present". United States Senate. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- ↑ Jenkins, Jeffrey A.; Stewart, Charles Haines (2013). Fighting for the Speakership: The House and the Rise of Party Government. p. 59. ISBN 978-0691156446 . Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- ↑ Jamison, Dennis (December 31, 2014). "George Washington's views on political parties in America". The Washington Times . Retrieved February 14, 2017.