Related Research Articles
The 1810–11 United States Senate elections were elections that had the Democratic-Republican Party maintain their majority in the United States Senate. The minority Federalists had gone into the elections with such a small share of Senate seats that, had they won all of the elections, they would still not have reached a majority.

The 1930 United States elections were held on November 4, 1930, in the middle of Republican President Herbert Hoover's term. Taking place shortly after the start of the Great Depression, the Republican Party suffered substantial losses. The election was the last of the Fourth Party System, and marked the first time since 1918 that Democrats controlled either chamber of Congress.
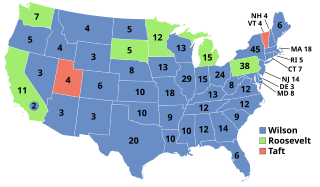
The 1912 United States elections elected the members of the 63rd United States Congress, occurring during the Fourth Party System. Amidst a division between incumbent Republican President William Howard Taft and former Republican President Theodore Roosevelt, the Democratic Party won the Presidency and both chambers of Congress, the first time they accomplished that feat since the 1892 election.
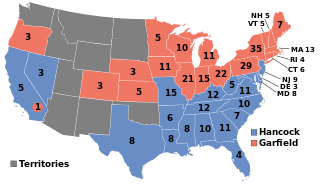
The 1880 United States elections occurred during the Third Party System, and elected the members of the 47th United States Congress. Republicans retained the Presidency and took control of the House. An unclear partisan situation prevailed in the Senate. As the first presidential election after the end of Reconstruction, this election saw the first occurrence of the Democratic Party sweeping the Southern United States; the party would carry an overwhelming majority of Southern states well into the 20th century.
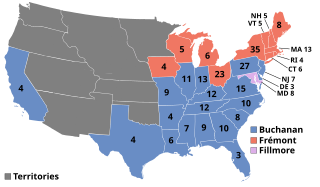
The 1856 United States elections elected the members of the 35th United States Congress and the President to serve from 1857 until 1861. The elections took place during a major national debate over slavery, with the issue of "Bleeding Kansas" taking center stage. Along with the 1854 elections, these elections occurred during the transitional period immediately preceding the Third Party System. Old party lines were broken; new party alignments along sectional lines were in the process of formation. The Republican Party absorbed the Northern anti-slavery representatives who had been elected in 1854 under the "Opposition Party" ticket as the second-most powerful party in Congress. Minnesota and Oregon joined the union before the next election, and elected their respective Congressional delegations to the 35th Congress.

The 1832 United States elections elected the members of the 23rd United States Congress. Taking place during the Second Party System and a political conflict over the re-authorization of the Second Bank of the United States, the elections were contested between Andrew Jackson's Democratic Party and opponents of Jackson, including the National Republicans. Though the Democrats retained the presidency and the House, they lost their Senate majority. The Anti-Masonic Party also fielded the first notable presidential candidacy from a third party.

The 1828 United States elections elected the members of the 21st United States Congress. It marked the beginning of the Second Party System, and the definitive split of the Democratic-Republican Party into the Democratic Party and the National Republican Party. While the Democrats cultivated strong local organizations, the National Republicans relied on a clear national platform of high tariffs and internal improvements. Political scientists such as V.O. Key, Jr. consider this election to be a realigning election, while political scientists such as James Reichley instead see the election as a continuation of the Democratic-Republican tradition. Additionally, this election saw the Anti-Masonic Party win a small number of seats in the House, becoming the first third party to gain representation in Congress.

The 1820 United States elections elected the members of the 17th United States Congress. The election took place during Era of Good Feelings and the First Party System. Despite the Panic of 1819, the Democratic-Republican Party maintained control of the presidency and both houses of Congress, while the Federalist Party provided only limited opposition. Missouri joined the union during the 17th Congress.

The 1816 United States elections elected the members of the 15th United States Congress. Mississippi and Illinois were admitted as states during the 15th Congress. The election took place during the First Party System. The Democratic-Republican Party controlled the Presidency and both houses of Congress, while the Federalist Party provided only limited opposition. The election marked the start of the Era of Good Feelings, as the Federalist Party became nearly irrelevant in national politics after the War of 1812 and the Hartford Convention.

The 1812 United States elections elected the members of the 13th United States Congress. The election took place during the First Party System, and shortly after the start of the War of 1812. The Federalist Party made a relatively strong showing, winning seats in both chambers while supporting a competitive challenge to the incumbent Democratic-Republican President. However, the Democratic-Republican Party continued its control of the Presidency and both houses of Congress.

The 1808 United States elections elected the members of the 11th United States Congress. The election took place during the First Party System. In the aftermath of the Embargo of 1807, the Federalists picked up Congressional seats for the first time since their defeat in the 1800 election. However, the Democratic-Republican Party maintained control of the Presidency and both houses of Congress.

The 1804 United States elections elected the members of the 9th United States Congress. The election took place during the First Party System. The Democratic-Republican Party continued its control of the Presidency and both houses of Congress.
The 1794 United States elections occurred in the middle of President George Washington's second term. Members of the 4th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Tennessee was admitted as a state during the 4th Congress. The election took place at the beginning of the First Party System, with the Democratic-Republican Party and Federalist Party emerging as political parties, succeeding the anti-administration faction and the pro-administration faction.
The 1802 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic-Republican President Thomas Jefferson's first term, during the First Party System. Members of the 8th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Democratic-Republicans picked up several seats in both chambers of Congress, solidifying their control over the House and Senate.
The 1814 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic-Republican President James Madison's second term, during the First Party System. Members of the 14th United States Congress were chosen in this election. During the 14th Congress, Indiana joined the union. The election took place during the War of 1812.
The 1818 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic-Republican President James Monroe's first term, during the First Party System and the Era of Good Feelings. Members of the 16th United States Congress were chosen in this election. During the 16th Congress, Alabama and Maine joined the union. Democratic-Republicans continued to dominate both chambers of Congress, and slightly increased their majority in both houses of Congress in this election.
The 1834 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President Andrew Jackson's second term. Members of the 24th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Taking place during the Second Party System, elections were contested between Andrew Jackson's Democratic Party and opponents of Jackson, including the remnants of the National Republican Party. During this election, the anti-Jackson faction began to transition into the Whig Party. Arkansas and Michigan joined the union during the 24th Congress. Democrats retained the majority in the House, and won control of the Senate.

The 1866 United States elections occurred in the middle of National Union/Democratic President Andrew Johnson's term, during the Third Party System and Reconstruction. Johnson had become president on April 15, 1865, upon the death of his predecessor, Abraham Lincoln. Members of the 40th United States Congress were chosen in this election. As this was the first election after the Civil War, many ex-Confederates were barred from voting, and several Southern states did not take part in the election. Delegations from Arkansas, Florida, Alabama, North Carolina, Louisiana, and South Carolina were re-admitted during the 40th Congress.

The 1874 United States elections occurred in the middle of Republican President Ulysses S. Grant's second term, during the Third Party System. Members of the 44th United States Congress were chosen in this election. The election took place during the Reconstruction Era, and many Southerners were barred from voting. Colorado joined the union during the 44th Congress. Democrats took control of a chamber of Congress for the first time since the start of the Civil War, winning a huge number of seats from House Republicans. However, the Republicans retained a majority in the Senate. The election marked the first occurrence of the six-year itch phenomenon, in which a president's party lost many Congressional seats during the president's second mid-term election.

The 1886 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President Grover Cleveland's term, during the Third Party System. Members of the 50th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Democrats retained control of the House, while Republicans retained control of the Senate.
References
- ↑ Not counting special elections.
- 1 2 Congressional seat gain figures only reflect the results of the regularly-scheduled elections, and do not take special elections into account.
- ↑ "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- ↑ "Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present". United States Senate. Retrieved 25 June 2014.