The 1996 United States presidential election was the 53rd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 5, 1996. Incumbent Democratic President Bill Clinton defeated former Senate Majority Leader Bob Dole, the Republican nominee, and Ross Perot, the Reform Party nominee.

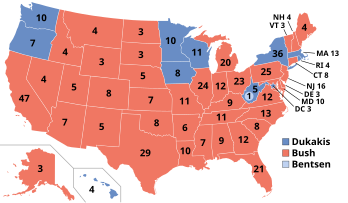
The 1988 United States presidential election was the 51st quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1988. The Republican nominee, incumbent Vice President George H. W. Bush, defeated the Democratic nominee, Governor Michael Dukakis of Massachusetts. This was the first presidential election since 1948, and the most recent to date, in which a party won a third consecutive presidential term. This also remains the most recent election in which a candidate won over 400 electoral votes, and the last time that the Republicans won the popular vote three times in a row.
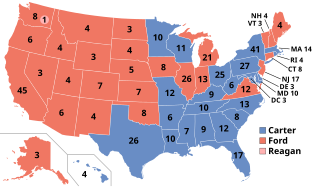
The 1976 United States presidential election was the 48th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 2, 1976. Democrat Jimmy Carter of Georgia defeated incumbent Republican President Gerald Ford from Michigan by a narrow victory of 297 electoral college votes to Ford's 240.

The 1988 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate in which, in spite of the Republican victory by George H. W. Bush in the presidential election, the Democrats gained a net of one seat in the Senate. Seven seats changed parties, with four incumbents being defeated. The Democratic majority in the Senate increased by one to 55–to–45.
The Pennsylvania Republican Party (PAGOP) is the affiliate of the Republican Party in the state of Pennsylvania. It is headquartered in Harrisburg.

The 2008 United States elections were held on November 4. Democratic Senator Barack Obama of Illinois won the presidential election, by defeating his near rival John McCain and the Democrats bolstered their majority in both Houses of Congress.
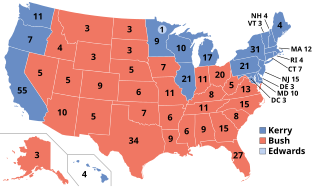
The 2004 United States elections were held on November 2. Republican President George W. Bush won re-election and Republicans retained control of Congress.

The 1980 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 4. Republican presidential nominee Ronald Reagan defeated incumbent Democratic President Jimmy Carter. Republicans also won control of the Senate, though Democrats retained a majority in the House of Representatives. The election is sometimes referred to as part of the "Reagan Revolution", a conservative realignment in U.S. politics, and marked the start of the Reagan Era.

The 2000 United States elections were held on November 7, 2000. Republican Governor George W. Bush of Texas defeated Democratic Vice President Al Gore of Tennessee in the presidential election. Republicans retained control of both houses of Congress, giving the party unified control of Congress and the presidency for the first time since the 1954 elections.

The 1996 United States elections were held on November 5. Democratic President Bill Clinton won re-election, while the Republicans maintained their majorities in both houses of the United States Congress.

The Reagan Era or Age of Reagan is a periodization of recent American history used by historians and political observers to emphasize that the conservative "Reagan Revolution" led by President Ronald Reagan in domestic and foreign policy had a lasting impact. It overlaps with what political scientists call the Sixth Party System. Definitions of the Reagan Era universally include the 1980s, while more extensive definitions may also include the late 1970s, the 1990s, the 2000s, the 2010s, and even the 2020s. In his 2008 book, The Age of Reagan: A History, 1974–2008, historian and journalist Sean Wilentz argues that Reagan dominated this stretch of American history in the same way that Franklin D. Roosevelt and his New Deal legacy dominated the four decades that preceded it.
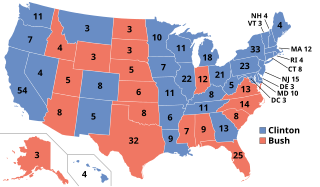
The 1992 United States elections elected state governors, the President of the United States, and members of the 103rd United States Congress. The election took place after the redistricting that resulted from the 1990 Census. Democrats won control of the presidency and both chambers of Congress for the first time since the Republican victory in the 1980 elections.

The 1976 United States elections was held on November 2, and elected the members of the 95th United States Congress. The Democratic Party won the presidential election and retained control of Congress.

The 1984 United States elections was held on November 6, and elected the members of the 99th United States Congress. Republicans won a landslide victory in the presidential election, picked up seats in the House of Representatives, and successfully defended their Senate majority.

The 1968 United States elections were held on November 5, and elected members of the 91st United States Congress. The election took place during the Vietnam War, in the same year as the Tet Offensive, the assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr., the assassination of Robert F. Kennedy, and the protests of 1968. The Republican Party won control of the presidency, and picked up seats in the House and Senate, although the Democratic Party retained control of Congress.

The 1992 United States presidential election in Illinois took place on November 3, 1992, as part of the 1992 United States presidential election. Voters chose 22 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1988 United States presidential election in Colorado took place on November 8, 1988, as part of the 1988 United States presidential election, which was held throughout all 50 states and D.C. Voters chose eight representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1988 United States Senate election in Texas was held on November 8, 1988. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Lloyd Bentsen won re-election to a fourth term, defeating Republican U.S. Representative Beau Boulter. Bentsen easily won the Democratic nomination for another term, while Boulter came through a run-off in the Republican primary defeating Wes Gilbreath. After winning renomination, Bentsen was chosen by Democratic presidential nominee Michael Dukakis as his vice-presidential running mate and therefore ran for both the Senate and the vice-presidency at the same time. Although the presidential ticket lost the general election and did not carry Texas, Bentsen was always the favorite for the Senate election and won with 59.2% of the vote, compared to 40% for Boulter.

The 1988 United States presidential election in Illinois took place on November 8, 1988. All 50 states and the District of Columbia were part of the 1988 United States presidential election. State voters chose 24 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

The 1988 United States presidential election in Wisconsin took place on November 8, 1988. All 50 states and the District of Columbia, were part of the 1988 United States presidential election. State voters chose 11 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.