Related Research Articles

The 34th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from March 4, 1855, to March 4, 1857, during the last two years of Franklin Pierce's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1850 United States census. The Whig Party, one of the two major parties of the era, had largely collapsed, although many former Whigs ran as Republicans or as members of the "Opposition Party." The Senate had a Democratic majority, and the House was controlled by a coalition of Representatives led by Nathaniel P. Banks, a member of the American Party.

The 1854–55 United States House of Representatives elections were held during President Franklin Pierce's term at various dates in different states from August 1854 to November 1855.

The 1852–53 United States Senate elections were elections which had the Democratic Party gain two seats in the United States Senate, and which coincided with the 1852 presidential election. Only six of the twenty senators up for election were re-elected.
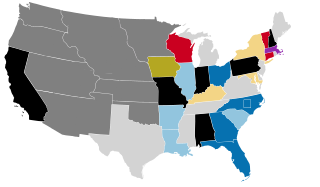
The 1854–55 United States Senate elections were elections which saw the final decline of the Whig Party and the maintained majority of the Democrats. Those Whigs in the South who were opposed to secession ran on the "Opposition Party" ticket, and were elected to a minority. Along with the Whigs, the Senate roster also included Free Soilers, Know Nothings, and a new party: the Republicans. Only five of the twenty-one senators up for election were re-elected.

The 1916 United States elections elected the members of the 65th United States Congress. The election occurred during the Fourth Party System, six months before the United States entered World War I. Unlike 1912, the Democrats did not benefit from a split in the Republican Party, but the Democrats still retained the Presidency and the majority in the Senate. Democrats lost the majority in the House, but retained control of the chamber.
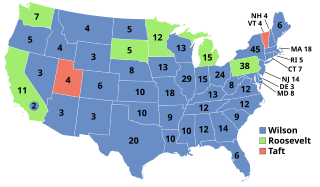
The 1912 United States elections elected the members of the 63rd United States Congress, occurring during the Fourth Party System. Amidst a division between incumbent Republican President William Howard Taft and former Republican President Theodore Roosevelt, the Democratic Party won the Presidency and both chambers of Congress, the first time they accomplished that feat since the 1892 election.
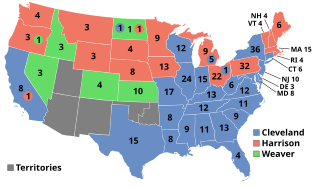
The 1892 United States elections was held on November 8, electing member to the 53rd United States Congress, taking place during the Third Party System. Democrats retained the House and won control of the Presidency and the Senate. Following the election, Democrats controlled the Presidency and a majority in both chambers of Congress for the first time since the 1858 elections.

The 1884 United States elections was held on November 4, electing the members of the 49th United States Congress. The election took place during the Third Party System.

The 1860 United States elections elected the members of the 37th United States Congress. The election marked the start of the Third Party System and precipitated the Civil War. The Republican Party won control of the Presidency and both houses of Congress, making it the fifth party to accomplish such a feat. The election is widely considered to be a realigning election.
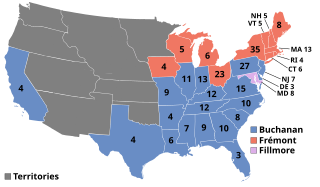
The 1856 United States elections elected the members of the 35th United States Congress and the President to serve from 1857 until 1861. The elections took place during a major national debate over slavery, with the issue of "Bleeding Kansas" taking center stage. Along with the 1854 elections, these elections occurred during the transitional period immediately preceding the Third Party System. Old party lines were broken; new party alignments along sectional lines were in the process of formation. The Republican Party absorbed the Northern anti-slavery representatives who had been elected in 1854 under the "Opposition Party" ticket as the second-most powerful party in Congress. Minnesota and Oregon joined the union before the next election, and elected their respective Congressional delegations to the 35th Congress.

The 1852 United States elections elected the members of the 33rd United States Congress. The election marked the end of the Second Party System, as the Whig Party ceased to function as a national party following this election. Democrats won the presidency and retained control of both houses of Congress.

The 1848 United States elections elected the members of the 31st United States Congress and the 12th president of the United States. The election took place during the Second Party System, nine months after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ended the Mexican–American War. With the issue of slavery dividing the nation, the Free Soil Party established itself as the third most powerful party in Congress. California joined the union before the next election, and elected its first Congressional delegation to the 31st Congress. Whigs won the presidency, but Democrats won a plurality in the House and retained control of the Senate.

The 1844 United States elections elected the members of the 29th United States Congress, and took place during the Second Party System in the midst of the debate over whether to annex Texas. Texas and Iowa joined the union during the 29th Congress. Democrats retained control of the House and took back control of the Presidency and the Senate, re-establishing the dominant position the party had lost in the 1840 election.
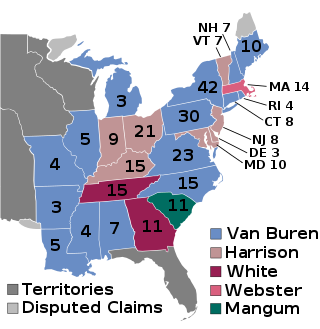
The 1836 United States elections elected the members of the 25th United States Congress. The election saw the emergence of the Whig Party, which succeeded the National Republican Party in the Second Party System as the primary opposition to the Democratic Party. The Whigs chose their name in symbolic defiance to the leader of the Democratic Party, "King" Andrew Jackson, and supported a national bank and the American System. Despite the emergence of the Whigs as a durable political party, Democrats retained the presidency and a majority in both houses of Congress.
The 1834 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President Andrew Jackson's second term. Members of the 24th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Taking place during the Second Party System, elections were contested between Andrew Jackson's Democratic Party and opponents of Jackson, including the remnants of the National Republican Party. During this election, the anti-Jackson faction began to transition into the Whig Party. Arkansas and Michigan joined the union during the 24th Congress. Democrats retained the majority in the House, and won control of the Senate.
The 1842 United States elections occurred in the middle of President John Tyler's term, during the Second Party System. Tyler had become president on April 4, 1841, upon the death of his predecessor, William Henry Harrison. Elected as vice president on the Whig ticket with Harrison in 1840, Tyler was expelled from the party in September 1841. Members of the 28th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Florida joined the union during the 28th Congress. Whigs kept control of the Senate, but lost control of the House.
The 1846 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President James Polk's term, during the Second Party System. The election took place during the Mexican–American War. Members of the 30th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Wisconsin joined the union during the 30th Congress. Democrats kept control of the Senate, but lost control of the House.
The 1850 United States elections occurred part way through Whig President Millard Fillmore's term, during the Second Party System. Fillmore had become president on July 9, 1850, upon the death of his predecessor, Zachary Taylor. Members of the 32nd United States Congress were chosen in this election. Democrats kept control of both houses of Congress.

The 1858 United States elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President James Buchanan's term and marked the end of the transitional period between the Second Party System and the Third Party System. Members of the 36th United States Congress were chosen in this election. In the first election since the Supreme Court decided Dred Scott v. Sandford, the Republican Party won a plurality in the House, taking control of a chamber of Congress for the first time in the party's history. Although Democrats lost control of the House, they retained their majority in the Senate.

The 1878 United States elections occurred in the middle of Republican President Rutherford B. Hayes's term, during the Third Party System. It was the first election following the end of the Reconstruction Era, and Redeemers had gained back control of most Southern governments following the Compromise of 1877. Members of the 46th United States Congress were chosen in this election. Democrats won control of the Senate for the first time since the start of the Civil War. Democrats lost a majority in the House, but retained a plurality and control of the chamber.
References
- ↑ Not counting special elections.
- 1 2 Congressional seat gain figures only reflect the results of the regularly-scheduled elections, and do not take special elections into account.
- 1 2 "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- ↑ Glass, Andrew (3 December 2012). "The House speaker bog-down, Dec. 3, 1855". Politico. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ↑ "Party Division in the Senate, 1789-Present". United States Senate. Retrieved 25 June 2014.