
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Dow Jones, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index of 30 prominent companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States.

A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often follow speculation and economic bubbles.
A market trend is a perceived tendency of the financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as secular for long time-frames, primary for medium time-frames, and secondary for short time-frames. Traders attempt to identify market trends using technical analysis, a framework which characterizes market trends as predictable price tendencies within the market when price reaches support and resistance levels, varying over time.
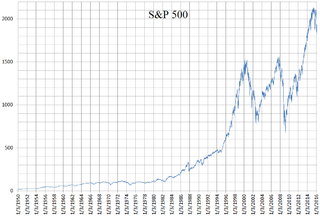
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 of the largest companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and includes approximately 80% of the total market capitalization of U.S. public companies, with an aggregate market cap of more than $43 trillion as of January 2024.
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund that is also an exchange-traded product, i.e., it is traded on stock exchanges. ETFs own financial assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, debts, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars. The list of assets that each ETF owns, as well as their weightings, is posted on the website of the issuer daily, or quarterly in the case of active non-transparent ETFs. Many ETFs provide some level of diversification compared to owning an individual stock.

MSCI Inc. is an American finance company headquartered in New York City. MSCI is a global provider of equity, fixed income, real estate indices, multi-asset portfolio analysis tools, ESG and climate products. It operates the MSCI World, MSCI All Country World Index (ACWI) and MSCI Emerging Markets Indices among others.
The S&P 100 Index is a stock market index of United States stocks maintained by Standard & Poor's.
The Nasdaq Composite is a stock market index that includes almost all stocks listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange. Along with the Dow Jones Industrial Average and S&P 500, it is one of the three most-followed stock market indices in the United States. The composition of the NASDAQ Composite is heavily weighted towards companies in the information technology sector. The Nasdaq-100, which includes 100 of the largest non-financial companies in the Nasdaq Composite, accounts for over 90% of the movement of the Nasdaq Composite.

The US bear market of 2007–2009 was a 17-month bear market that lasted from October 9, 2007 to March 9, 2009, during the financial crisis of 2007–2009. The S&P 500 lost approximately 50% of its value, but the duration of this bear market was just below average.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
The August 2011 stock markets fall was the sharp drop in stock prices in August 2011 in stock exchanges across the United States, Middle East, Europe and Asia. This was due to fears of contagion of the European sovereign debt crisis to Spain and Italy, as well as concerns over France's current AAA rating, concerns over the slow economic growth of the United States and its credit rating being downgraded. Severe volatility of stock market indexes continued for the rest of the year.
This article is a summary of the closing milestones of the S&P 500 Index, a United States stock market index.
The 2015–2016 stock market selloff was the period of decline in the value of stock prices globally that occurred between June 2015 to June 2016. It included the 2015–2016 Chinese stock market turbulence, in which the SSE Composite Index fell 43% in just over two months between June 2015 and August 2015, which culminated in the devaluation of the yuan. Investors sold shares globally as a result of slowing growth in the GDP of China, a fall in petroleum prices, the Greek debt default in June 2015, the effects of the end of quantitative easing in the United States in October 2014, a sharp rise in bond yields in early 2016, and finally, in June 2016, the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, in which Brexit was voted upon.
Since the beginning of the Bombay stock exchange, stock markets in India, particularly the Bombay Stock Exchange and National Stock Exchange of India have seen a number of booms as well as crashes.

On 20 February 2020, stock markets across the world suddenly crashed after growing instability due to the COVID-19 pandemic. It ended on 7 April 2020.

Economic turmoil associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has had wide-ranging and severe impacts upon financial markets, including stock, bond, and commodity markets. Major events included a described Russia–Saudi Arabia oil price war, which after failing to reach an OPEC+ agreement resulted in a collapse of crude oil prices and a stock market crash in March 2020. The effects upon markets are part of the COVID-19 recession and are among the many economic impacts of the pandemic.
The COVID-19 recession, also known as the Great Lockdown, was a global economic recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. The recession began in most countries in February 2020. After a year of global economic slowdown that saw stagnation of economic growth and consumer activity, the COVID-19 lockdowns and other precautions taken in early 2020 drove the global economy into crisis. Within seven months, every advanced economy had fallen to recession.

The expression "everything bubble" refers to the correlated impact of monetary easing by the Federal Reserve on asset prices in most asset classes, namely equities, housing, bonds, many commodities, and even exotic assets such as cryptocurrencies and SPACs. The policy itself and the techniques of direct and indirect methods of quantitative easing used to execute it are sometimes referred to as the Fed put. Modern monetary theory advocates the use of such tools, even in non-crisis periods, to create economic growth through asset price inflation. The term "everything bubble" first came in use during the chair of Janet Yellen, but it is most associated with the subsequent chair of Jerome Powell, and the 2020–2021 period of the coronavirus pandemic.











