Related Research Articles

The economy of Spain is a highly developed social market economy. It’s the world's 15th largest by nominal GDP and the sixth-largest in Europe. Spain is a member of the European Union and the eurozone, as well as the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development and the World Trade Organization. In 2021, Spain was the twentieth-largest exporter in the world and the sixteenth-largest importer. Spain is listed 27th in the United Nations Human Development Index and 37th in GDP per capita by the World Bank. Some of the main areas of economic activity are the automotive industry, medical technology, chemicals, shipbuilding, tourism and the textile industry.

The 1997 Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided.
The Mexican peso crisis was a currency crisis sparked by the Mexican government's sudden devaluation of the peso against the U.S. dollar in December 1994, which became one of the first international financial crises ignited by capital flight.

The savings and loan crisis of the 1980s and 1990s was the failure of 32% of savings and loan associations (S&Ls) in the United States from 1986 to 1995. An S&L or "thrift" is a financial institution that accepts savings deposits and makes mortgage, car and other personal loans to individual members.
A bailout is the provision of financial help to a corporation or country which otherwise would be on the brink of bankruptcy.
Fobaproa was a contingencies fund created in 1990 by the Mexican government, led by then dominant Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) to attempt to resolve liquidity problems of the banking system. The contingencies fund was applied in 1995 during the Mexican peso crisis to protect Mexican banks. In 1998, it was replaced by Instituto para la Protección al Ahorro Bancario, Mexico's current deposit insurance agency.

"Too big to fail" (TBTF) is a theory in banking and finance that asserts that certain corporations, particularly financial institutions, are so large and so interconnected that their failure would be disastrous to the greater economic system, and therefore should be supported by government when they face potential failure. The colloquial term "too big to fail" was popularized by U.S. Congressman Stewart McKinney in a 1984 Congressional hearing, discussing the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation's intervention with Continental Illinois. The term had previously been used occasionally in the press, and similar thinking had motivated earlier bank bailouts.

The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline observed in national economies globally, i.e. a recession, that occurred in the late 2000s. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country. At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations.
The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, also known as the "bank bailout of 2008" or the "Wall Street bailout", was a United States federal law enacted during the Great Recession, which created federal programs to "bail out" failing financial institutions and banks. The bill was proposed by Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson, passed by the 110th United States Congress, and was signed into law by President George W. Bush. It became law as part of Public Law 110-343 on October 3, 2008. It created the $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP), which utilized congressionally appropriated taxpayer funds to purchase toxic assets from failing banks. The funds were mostly redirected to inject capital into banks and other financial institutions while the Treasury continued to examine the usefulness of targeted asset purchases.
In the period September 2007 to December 2009, during the events now widely known as the Global Financial Crisis, the UK government enacted a number of financial interventions in support of the UK banking sector and four UK banks in particular.

Banco de Venezuela is an international universal bank based in Caracas. It was the market leader in Venezuela until 2007, when it fell to third place, with an 11.3% market share for deposits; its major competitors are Banesco, Banco Mercantil and BBVA Banco Provincial. As of June 2008, it had 285 branches in Venezuela.
The Finnish Banking Crisis of 1990s was a deep systemic crisis of the entire Finnish financial sector that took place mainly in the years 1991–1993, after several years of debt-based economic boom in the late 1980s. Its total taxpayer cost was roughly 8% of the Finnish GNP, making it the most severe of the contemporary Nordic banking crises. The crisis has been attributed to a combination of macro-economic turbulence, weak regulation, and bank-specific problems. Governmental intervention included bank takeovers, direct monetary assistance and temporary blanket guarantees to the banks.
A bad bank is a corporate structure which isolates illiquid and high risk assets held by a bank or a financial organisation, or perhaps a group of banks or financial organisations. A bank may accumulate a large portfolio of debts or other financial instruments which unexpectedly become at risk of partial or full default. A large volume of non-performing assets usually make it difficult for the bank to raise capital, for example through sales of bonds. In these circumstances, the bank may wish to segregate its good assets from its bad assets through the creation of a bad bank. The goal of the segregation is to allow investors to assess the bank's financial health with greater certainty. A bad bank might be established by one bank or financial institution as part of a strategy to deal with a difficult financial situation, or by a government or some other official institution as part of an official response to financial problems across a number of institutions in the financial sector.

The 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis, also known as the Great Recession in Spain or the Great Spanish Depression, began in 2008 during the world 2007–2008 financial crisis. In 2012, it made Spain a late participant in the European sovereign debt crisis when the country was unable to bail out its financial sector and had to apply for a €100 billion rescue package provided by the European Stability Mechanism (ESM).

The European debt crisis, often also referred to as the eurozone crisis or the European sovereign debt crisis, was a multi-year debt crisis that took place in the European Union (EU) from 2009 until the mid to late 2010s. Several eurozone member states were unable to repay or refinance their government debt or to bail out over-indebted banks under their national supervision without the assistance of third parties like other eurozone countries, the European Central Bank (ECB), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
The 2009–2010 banking crisis occurred in Venezuela when a number of the banks of Venezuela were taken over by the government, after "the revelation that several banks owned by Hugo Chavez supporters were in financial trouble after engaging in questionable business practices. Some were seriously undercapitalized, others were apparently lending large sums of money to top executives, and at least one financier couldn't prove where he got the money to buy his banks in the first place." In November and December 2009 seven banks were taken over, accounting for around 12% of total deposits. In 2010 more banks were taken over. The government arrested at least 16 bankers and issued more than 40 corruption-related arrest warrants for others who had fled the country.
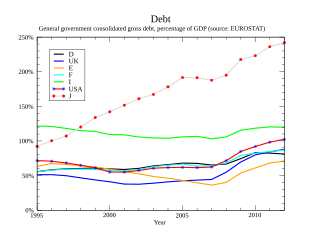
Debt crisis is a situation in which a government loses the ability of paying back its governmental debt. When the expenditures of a government are more than its tax revenues for a prolonged period, the government may enter into a debt crisis. Various forms of governments finance their expenditures primarily by raising money through taxation. When tax revenues are insufficient, the government can make up the difference by issuing debt.
Sareb is the bad bank of the Spanish government. Its purpose is to manage and disinvest high-risk assets that were transferred to it from the four nationalized Spanish financial institutions. The company was formed in 2012.
Novobanco or Novo Banco, SA is a financial institution that stands out as one of the country's main commercial banks, based in Portugal. It was established on 4 August 2014, as a result of a restructuring and recapitalisation process by the Bank of Portugal to save the good assets of the previously bankrupt Banco Espírito Santo (BES). The rescue of BES was precipitated by historic losses of 3,577 million euros. BES's toxic assets, on the other hand, were transferred to a "bad bank".
Ruth Osterreicher de Krivoy is a Venezuelan economist specialized on political, monetary and fiscal dynamics. During the early 1970s, she had been vice president of research at the Central Bank of Venezuela, where she played an active role in strengthening economic research as a major instrument of support for monetary policy. In 1992, two months after an attempted coup d'état by Hugo Chavez, she became president of the Central Bank of Venezuela. Her appointment seemed a natural choice, given both her extensive experience and her firm belief in Central Bank independence. She resigned in 1994, amid the Venezuelan banking crisis. De Krivoy wrote a book about the crisis, and has continued to voice concerns about the loss of political independence of the Central Bank's governors.
References
- 1 2 Escobar, Gabriel (1994-06-27). "VENEZUELAN ECONOMY IN CRISIS". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286 . Retrieved 2023-03-16.
- 1 2 3 Molano, 1997. Financial reverberations: the Latin American banking system during the mid-1990s. SBC Warburg Working Paper, Social Science Research Network (1997).
- ↑ "Veneuela (sic) Announces Bank Rescue Package". New York Times . August 10, 1994. Retrieved 2009-01-13.
- ↑ Molina, C.A. (2002), "Predicting bank failures using a hazard model: the Venezuelan banking crisis", Emerging Markets Review, Volume 3, Issue 1, 1 March 2002, Pages 31-50
- ↑ Maxfield, Sylvia (2003), "When do voters matter more than cronies in developing countries? The politics of bank crisis resolution", in Critical issues in international financial reform (R. Albert Berry, Gustavo Indart, eds.), Transaction Publishers, p272
- ↑ Da Costa, Mercedes (2001), Collapse: The Venezuelan Banking Crisis of '94, Finance & Development, 1 March 2001

