Related Research Articles

The Aldrich–Vreeland Act was a United States law passed in response to the Panic of 1907 which established the National Monetary Commission.

His Majesty's Treasury, occasionally referred to as the Exchequer, or more informally the Treasury, is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy and economic policy. The Treasury maintains the Online System for Central Accounting and Reporting (OSCAR), the replacement for the Combined Online Information System (COINS), which itemises departmental spending under thousands of category headings, and from which the Whole of Government Accounts (WGA) annual financial statements are produced.

The global financial system is the worldwide framework of legal agreements, institutions, and both formal and informal economic action that together facilitate international flows of financial capital for purposes of investment and trade financing. Since emerging in the late 19th century during the first modern wave of economic globalization, its evolution is marked by the establishment of central banks, multilateral treaties, and intergovernmental organizations aimed at improving the transparency, regulation, and effectiveness of international markets. In the late 1800s, world migration and communication technology facilitated unprecedented growth in international trade and investment. At the onset of World War I, trade contracted as foreign exchange markets became paralyzed by money market illiquidity. Countries sought to defend against external shocks with protectionist policies and trade virtually halted by 1933, worsening the effects of the global Great Depression until a series of reciprocal trade agreements slowly reduced tariffs worldwide. Efforts to revamp the international monetary system after World War II improved exchange rate stability, fostering record growth in global finance.
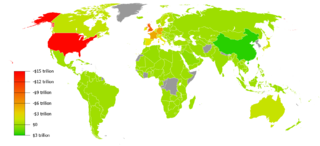
In international economics, the balance of payments of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. In other words, it is economic transactions between countries during a period of time. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services.

The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, and Australia among 44 other countries after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretton Woods system was the first example of a fully negotiated monetary order intended to govern monetary relations among independent states. The Bretton Woods system required countries to guarantee convertibility of their currencies into U.S. dollars to within 1% of fixed parity rates, with the dollar convertible to gold bullion for foreign governments and central banks at US$35 per troy ounce of fine gold. It also envisioned greater cooperation among countries in order to prevent future competitive devaluations, and thus established the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to monitor exchange rates and lend reserve currencies to nations with balance of payments deficits.

William Gibbs McAdoo Jr. was an American lawyer and statesman. McAdoo was a leader of the Progressive movement and played a major role in the administration of his father-in-law President Woodrow Wilson. A member of the Democratic Party, he also represented California in the United States Senate.
The Long Depression was a worldwide price and economic recession, beginning in 1873 and running either through March 1879, or 1896, depending on the metrics used. It was most severe in Europe and the United States, which had been experiencing strong economic growth fueled by the Second Industrial Revolution in the decade following the American Civil War. The episode was labeled the "Great Depression" at the time, and it held that designation until the Great Depression of the 1930s. Though it marked a period of general deflation and a general contraction, it did not have the severe economic retrogression of the Great Depression.
The Mexican peso crisis was a currency crisis sparked by the Mexican government's sudden devaluation of the peso against the U.S. dollar in December 1994, which became one of the first international financial crises ignited by capital flight.

Lehman Brothers Inc. was an American global financial services firm founded in 1850. Before filing for bankruptcy in 2008, Lehman was the fourth-largest investment bank in the United States, with about 25,000 employees worldwide. It was doing business in investment banking, equity, fixed-income and derivatives sales and trading, research, investment management, private equity, and private banking. Lehman was operational for 158 years from its founding in 1850 until 2008.

The Shanghai Stock Exchange is a stock exchange based in the city of Shanghai, China. It is one of the three stock exchanges operating independently in mainland China, the others being the Beijing Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. The Shanghai Stock Exchange is the world's third largest stock market by market capitalization. It is also Asia's biggest stock exchange. Unlike the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, the Shanghai Stock Exchange is still not entirely open to foreign investors and often affected by the decisions of the central government, due to capital account controls exercised by the Chinese mainland authorities.
The Panic of 1825 was a stock market crash that started in the Bank of England, arising in part out of speculative investments in Latin America, including the imaginary country of Poyais. The crisis was felt most acutely in Britain, where it led to the closure of twelve banks. It was also manifest in the markets of Europe, Latin America and the United States. Nationwide gold and silver confiscation ensued and an infusion of gold reserves from the Banque de France saved the Bank of England from collapse. The panic has been called the first modern economic crisis not attributable to an external event, such as a war, and so the start of modern economic cycles. The Napoleonic Wars had been highly profitable for all sectors of the British financial system, and the expansionist monetary actions taken during transition from war to peace brought a surge of prosperity and speculative ventures. The stock market boom became a bubble and banks caught in the euphoria made risky loans.
In the period September 2007 to December 2009, during the events now widely known as the Global Financial Crisis, the UK government enacted a number of financial interventions in support of the UK banking sector and four UK banks in particular.
The subprime mortgage crisis reached a critical stage during the first week of September 2008, characterized by severely contracted liquidity in the global credit markets and insolvency threats to investment banks and other institutions.
Philadelphia financier Jay Cooke established the first modern American investment bank during the Civil War era. However, private banks had been providing investment banking functions since the beginning of the 19th century and many of these evolved into investment banks in the post-bellum era. However, the evolution of firms into investment banks did not follow a single trajectory. For example, some currency brokers such as Prime, Ward & King and John E. Thayer and Brother moved from foreign exchange operations to become private banks, taking on some investment bank functions. Other investment banks evolved from mercantile firms such as Thomas Biddle and Co. and Alexander Brothers.
This article details the history of banking in the United States. Banking in the United States is regulated by both the federal and state governments.
The August 2011 stock markets fall was the sharp drop in stock prices in August 2011 in stock exchanges across the United States, Middle East, Europe and Asia. This was due to fears of contagion of the European sovereign debt crisis to Spain and Italy, as well as concerns over France's current AAA rating, concerns over the slow economic growth of the United States and its credit rating being downgraded. Severe volatility of stock market indexes continued for the rest of the year.
The 1994 bond market crisis, or Great Bond Massacre, was a sudden drop in bond market prices across the developed world. It began in Japan and the United States (US), and spread through the rest of the world. After the recession of the early 1990s, historically low interest rates in many industrialized nations preceded an unexpectedly volatile year for bond investors, including those that held on to mortgage debts. Over 1994, a rise in rates, along with the relatively quick spread of bond market volatility across international borders, resulted in a mass sell-off of bonds and debt funds as yields rose beyond expectations. This was especially the case for instruments with comparatively longer maturities attached. Some financial observers argued that the plummet in bond prices was triggered by the Federal Reserve's decision to raise rates by 25 basis points in February, in a move to counter inflation. At about $1.5 trillion in lost market value across the globe, the crash has been described as the worst financial event for bond investors since 1927.

On 20 February 2020, stock markets across the world suddenly crashed after growing instability due to the COVID-19 pandemic. It ended on 7 April 2020.

Economic turmoil associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has had wide-ranging and severe impacts upon financial markets, including stock, bond, and commodity markets. Major events included a described Russia–Saudi Arabia oil price war, which after failing to reach an OPEC+ agreement resulted in a collapse of crude oil prices and a stock market crash in March 2020. The effects upon markets are part of the COVID-19 recession and are among the many economic impacts of the pandemic.
References
- ↑ Van Der Pijl, Kees (2014). The Making of an Atlantic Ruling Class. Verso Books. ISBN 9781844679362.
- ↑ Wilkins, Mira (2004). The History of Foreign Investment in the United States, 1914-1945. Harvard University Press. p. 4.
- ↑ Silber, William L. (2007). When Washington Shut Down Wall Street: The Great Financial Crisis of 1915 and the Origins of America's Monetary Supremacy. Princeton University Press.