Hypselosaurus is a dubious genus of titanosaurian sauropod that lived in southern France during the Late Cretaceous, approximately 70 million years ago in the early Maastrichtian. Hypselosaurus was first described in 1846, but was not formally named until 1869, when Phillip Matheron named it under the binomial Hypselosaurus priscus. The holotype specimen includes a partial hindlimb and a pair of caudal vertebrae, and two eggshell fragments were found alongside these bones. Because of the proximity of these eggshells to the fossil remains, many later authors, including Matheron and Paul Gervais, have assigned several eggs from the same region of France all to Hypselosaurus, although the variation and differences between these eggs suggest that they do not all belong to the same taxon. Hypselosaurus has been found in the same formation as the dromaeosaurids Variraptor and Pyroraptor, the ornithopod Rhabdodon, and the ankylosaurian Rhodanosaurus, as well as indeterminate bones from other groups.

Ampelosaurus is a titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now France. Its type species is A. atacis, named by Le Loeuff in 1995. Its remains were found in a level dating from 71.5 million years ago representing the early Maastrichtian.
Bonatitan is a genus of titanosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Allen Formation of Argentina. It was named in 2004.
Mendozasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur. It was a member of Titanosauria, which were massive sauropods that were common on the southern landmasses during the Cretaceous. It is represented by several partial skeletons from a single locality within the Coniacian Sierra Barrosa Formation in the south of Mendoza Province, northern Neuquén Basin, Argentina. The type species, Mendozasaurus neguyelap, was described by Argentine paleontologist Bernardo Javier González Riga in 2003. Mendozasaurus is the first dinosaur named from Mendoza Province, Argentina, for which it was named.

Lirainosaurus is a genus of titanosaur sauropod which lived in what is now Spain. The type species, Lirainosaurus astibiae, was described by Sanz, Powell, Le Loeuff, Martinez, and Pereda-Suberbiola in 1999. It was a relatively small sauropod, measuring 4 metres (13 ft) long, possibly up to 6 metres (20 ft) long for the largest individuals, and weighed about 2–4 metric tons.
Argiles et Grès à Reptiles Formation also known as the Argiles Rutilantes Formation is an early Maastrichtian French geologic formation in the département of Var preserving the remains of several types of dinosaurs and other extinct organisms.
The Marnes d’Auzas Formation is a geological Formation in southwestern France whose strata date back to the Late Maastrichtian. It is about 100 metres thick and consists primarily of marls with some interbeds of sandstones. It corresponds to sediments whose depositional environment evolved from the paralic domain at the base of the formation, towards a more continental domain in its upper part. The Marnes d’Auzas Formation was deposited in the west coast of the former Ibero-Armorican Island, which included much of France and Spain.

Opisthocoelicaudiinae is a subfamily of titanosaurian dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous. It was named by John McIntosh in 1990. Opisthocoelicaudiines are known from Mongolia, Argentina, and the United States. Two genera were assigned to Opisthocoelicaudiinae by Gonzalez et al. (2009): Alamosaurus and Opisthocoelicaudia, a conclusion also found by Díez Díaz et al. (2018). The hands of opisthocoelicaudiines lacked wrist bones and phalanges.

Paludititan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which lived in the area of present Romania during the Late Cretaceous. It existed in the island ecosystem known as Hațeg Island.

Aeolosaurini is an extinct clade of titanosaurian dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous period of Argentina and Brazil. Rodrigo M. Santucci and Antonio C. de Arruda-Campos (2011) in their cladistic analysis found Aeolosaurus, Gondwanatitan, Maxakalisaurus, Panamericansaurus and Rinconsaurus to be aeolosaurids.
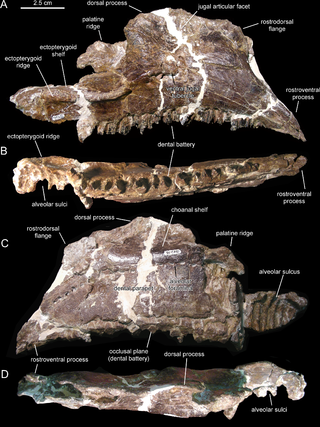
Canardia is an extinct genus of lambeosaurine dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Marnes d'Auzas Formation of Haute-Garonne department, in Occitanie region, southwestern France. The type species Canardia garonnensis was first described and named by Albert Prieto-Márquez, Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia, Rodrigo Gaete and Àngel Galobart in 2013. It is only known from juvenile specimens. The name of the genus comes from “canard”, the French word for “duck”, an allusion to the fact that this animal belongs to the hadrosaurids which are also known as duck-billed dinosaurs. The specific epithet garonnensis refers to the Haute-Garonne department where this dinosaur has been found. Although universally recognized as a lambeosaurine, its precise position within them is debated. Some authors consider it as a close relative of the genus Aralosaurus from Central Asia with which it would form the tribe Aralosaurini, while others include it in a more derived clade, the Arenysaurini in which all lambeosaurines from Europe and North Africa are placed. Canardia was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs and lived between 67,5 and 66 my on the former Ibero-Armorican Island, which included much of France and Spain.
Brasilotitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Adamantina Formation of Brazil. The type species is Brasilotitan nemophagus. Brasilotitan was a small titanosaur with a squared-off snout, and may be closely related to another Brazilian titanosaur, Uberabatitan.
Lohuecotitan is an extinct genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which lived during the Late Cretaceous in Spain. The only species known in the genus is Lohuecotitan pandafilandi, described and named in 2016.

Matheronodon is a genus of rhabdodontid ornithopod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of the Grès à Reptiles Formation in France. The genus contains a single species, M. provincialis, which is known from a single maxilla and associated teeth. It was named by Pascal Godefroit and colleagues in 2017. The teeth of Matheronodon are large but few in number. The teeth are also in an unusual arrangement, emerging alternatingly from one of a pair of fused tooth sockets in its mouth. In life, the teeth would have functioned like a pair of scissors, allowing Matheronodon to feed on the tough leaves of monocot plants.

Mistralazhdarcho is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of France. The type and only species is Mistralazhdarcho maggii.

Lirainosaurinae is a subfamily of lithostrotian titanosaur sauropods from the Late Cretaceous of France, Spain, and Romania.

Saltasaurini is a tribe of titanosaur sauropods known from the Late Cretaceous of Patagonia, Argentina. The clade was named in 2007 by Leonardo Salgado and José Bonaparte as the "least inclusive clade comprising Neuquensaurus and Saltasaurus", which is equivalent to the use of Saltasaurinae in Salgado et al. (1997). Found only in the Campanian to Maastrichtian sediments of the Neuquén Basin, Salgado & Bonaparte (2007) decided a more restrictive clade was needed because of the expansion of Saltasaurinae as defined to include far more taxa than it originally encompassed. Saltasaurini includes the original core of Saltasaurinae: Neuquensaurus, Saltasaurus, Rocasaurus and Bonatitan, although some studies exclude Bonatitan from the clade.
Garrigatitan is a genus of titanosaurian dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of the Grès à Reptiles Formation in France. The genus contains a single species, Garrigatitan meridionalis.






















