
Ampelosaurus is a titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now France. Its type species is A. atacis, named by Le Loeuff in 1995. Its remains were found in a level dating from 71.5 million years ago representing the early Maastrichtian.
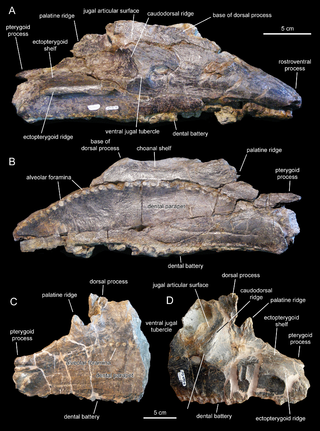
Pararhabdodon is a genus of tsintaosaurin hadrosaurid dinosaur, from the Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Tremp Group of Spain. The first remains were discovered from the Sant Romà d’Abella fossil locality and assigned to the genus Rhabdodon, and later named as the distinct species Pararhabdodon isonensis in 1993. Known material includes assorted postcranial remains, mostly vertebrae, as well as maxillae from the skull. Specimens from other sites, including remains from France, a maxilla previously considered the distinct taxon Koutalisaurus kohlerorum, an additional maxilla from another locality, the material assigned to the genera Blasisaurus and Arenysaurus, and the extensive Basturs Poble bonebed have been considered at different times to belong to the species, but all of these assignments have more recently been questioned. It was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known from the fossil record that went extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.

Lirainosaurus is a genus of titanosaur sauropod which lived in what is now Spain. The type species, Lirainosaurus astibiae, was described by Sanz, Powell, Le Loeuff, Martinez, and Pereda-Suberbiola in 1999. It was a relatively small sauropod, measuring 4 metres (13 ft) long, possibly up to 6 metres (20 ft) long for the largest individuals, and weighed about 2–4 metric tons.

Phosphatodraco is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous of what is now Morocco. In 2000, a pterosaur specimen consisting of five cervical (neck) vertebrae was discovered in the Ouled Abdoun Phosphatic Basin. The specimen was made the holotype of the new genus and species Phosphatodraco mauritanicus in 2003; the genus name means "dragon from the phosphates", and the specific name refers to the region of Mauretania. Phosphatodraco was the first Late Cretaceous pterosaur known from North Africa, and the second pterosaur genus described from Morocco. It is one of the only known azhdarchids preserving a relatively complete neck, and was one of the last known pterosaurs. Additional cervical vertebrae have since been assigned to the genus, and it has been suggested that fossils of the pterosaur Tethydraco represent wing elements of Phosphatodraco.
Argiles et Grès à Reptiles Formation also known as the Argiles Rutilantes Formation is an early Maastrichtian French geologic formation in the département of Var preserving the remains of several types of dinosaurs and other extinct organisms.

Opisthocoelicaudiinae is a subfamily of titanosaurian dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous. It was named by John McIntosh in 1990. Opisthocoelicaudiines are known from Mongolia, Argentina, and the United States. Two genera were assigned to Opisthocoelicaudiinae by Gonzalez et al. (2009): Alamosaurus and Opisthocoelicaudia, a conclusion also found by Díez Díaz et al. (2018). The hands of opisthocoelicaudiines lacked wrist bones and phalanges.

Atsinganosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which existed in what is now France during the Late Cretaceous. Well-preserved remains of Atsinganosaurus were collected from the Grès à Reptiles Formation of the Aix-en-Provence Basin. The type and only species is A. velauciensis.

Paludititan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which lived in the area of present Romania during the Late Cretaceous. It existed in the island ecosystem known as Hațeg Island.

Zarafasaura is an extinct genus of elasmosaurid known from the Ouled Abdoun Basin of Morocco. As a relatively small elasmosaur, it would have measured around 3–4 metres (9.8–13.1 ft) long and weighed about 100 kilograms (220 lb).
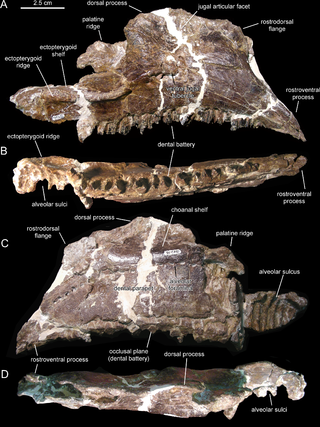
Canardia is an extinct genus of lambeosaurine dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Marnes d'Auzas Formation of Haute-Garonne department, in Occitanie region, southwestern France. The type species Canardia garonnensis was first described and named by Albert Prieto-Márquez, Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia, Rodrigo Gaete and Àngel Galobart in 2013. It is only known from juvenile specimens. The name of the genus comes from “canard”, the French word for “duck”, an allusion to the fact that this animal belongs to the hadrosaurids which are also known as duck-billed dinosaurs. The specific epithet garonnensis refers to the Haute-Garonne department where this dinosaur has been found. Although universally recognized as a lambeosaurine, its precise position within them is debated. Some authors consider it as a close relative of the genus Aralosaurus from Central Asia with which it would form the tribe Aralosaurini, while others include it in a more derived clade, the Arenysaurini in which all lambeosaurines from Europe and North Africa are placed. Canardia was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs and lived between 67,5 and 66 my on the former Ibero-Armorican Island, which included much of France and Spain.

Aralosaurini is a proposed tribe of hadrosaurid dinosaurs belonging to the subfamily Lambeosaurinae. The members of this group lived in Asia and Europe during the end of the Late Cretaceous about 83.6 to 66.0 million years ago. The clade may not be monophyletic, with Canardia and Aralosaurus potentially instead being unrelated primitive members of the subfamily.
Lohuecotitan is an extinct genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which lived during the Late Cretaceous in Spain. The only species known in the genus is Lohuecotitan pandafilandi, described and named in 2016.

Chenanisaurus is a genus of predatory abelisaurid dinosaur, with a single known species C. barbaricus. It comes from the upper Maastrichtian phosphates of the Ouled Abdoun Basin in Morocco, North Africa. The animal is known from a holotype, consisting of a partial jaw bone, and several isolated teeth found in the same beds. Chenanisaurus is one of the largest members of the Abelisauridae, and one of the last, being a contemporary of the North American Tyrannosaurus. It would have been among the dinosaur species wiped out by the Chicxulub asteroid impact and the Cretaceous-Paleogene mass extinction that followed.

Matheronodon is a genus of rhabdodontid ornithopod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of the Grès à Reptiles Formation in France. The genus contains a single species, M. provincialis, which is known from a single maxilla and associated teeth. It was named by Pascal Godefroit and colleagues in 2017. The teeth of Matheronodon are large but few in number. The teeth are also in an unusual arrangement, emerging alternatingly from one of a pair of fused tooth sockets in its mouth. In life, the teeth would have functioned like a pair of scissors, allowing Matheronodon to feed on the tough leaves of monocot plants.

Mistralazhdarcho is a genus of azhdarchid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of France. The type and only species is Mistralazhdarcho maggii.

Lirainosaurinae is a subfamily of lithostrotian titanosaur sauropods from the Late Cretaceous of France, Spain, and Romania.

Saltasaurini is a tribe of titanosaur sauropods known from the Late Cretaceous of Patagonia, Argentina. The clade was named in 2007 by Leonardo Salgado and José Bonaparte as the "least inclusive clade comprising Neuquensaurus and Saltasaurus", which is equivalent to the use of Saltasaurinae in Salgado et al. (1997). Found only in the Campanian to Maastrichtian sediments of the Neuquén Basin, Salgado & Bonaparte (2007) decided a more restrictive clade was needed because of the expansion of Saltasaurinae as defined to include far more taxa than it originally encompassed. Saltasaurini includes the original core of Saltasaurinae: Neuquensaurus, Saltasaurus, Rocasaurus and Bonatitan, although some studies exclude Bonatitan from the clade.

Ajnabia is a genus of lambeosaurine hadrosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Morocco. It is the first definitive hadrosaur from Africa, and is thought to be related to European dinosaurs like Arenysaurus. The discovery of Ajnabia came as a surprise to the paleontologists who found it, because Africa was isolated by water from the rest of the world during the Cretaceous, such that hadrosaurs were assumed to have been unable to reach the continent. Ajnabia is relatively small and similar in size to its contemporary relative Minqaria, which is estimated to have reached 3.5 metres (11 ft) in total body length. Assuming that the holotype represents an adult, Ajnabia would be one of the smallest if not the smallest known hadrosaurids.

Minqaria is a genus of arenysaurinin lambeosaurine hadrosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Ouled Abdoun Basin of Morocco. The genus contains a single species, M. bata, known from a partial skull.


























