
Titanosaurs were a diverse group of sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thriving at the time of the extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous. This group includes some of the largest land animals known to have ever existed, such as Patagotitan—estimated at 37 m (121 ft) long with a weight of 69 tonnes —and the comparably-sized Argentinosaurus and Puertasaurus from the same region.

Aeolosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. Like most sauropods, it would have been a quadrupedal herbivore with a long neck and tail. Aeolosaurus is well known for a titanosaur, as it is represented by the remains of several individuals belonging to at least two species. However, like most titanosaurs, no remains of the skull are known. The holotype of Aeolosaurus rionegrinus consists of a series of seven tail vertebrae, as well as parts of both forelimbs and the right hindlimb. It was discovered in the Angostura Colorada Formation in Argentina, which dates from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 83 to 74 million years ago. The species A. maximus was transferred over to the new genus Arrudatitan in 2021.

Euhelopus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived between 145 and 133 million years ago during the Berriasian and Valanginian stages of the Early Cretaceous in what is now Shandong Province in China. It was a large quadrupedal herbivore. Like sauropods such as brachiosaurs and titanosaurs, Euhelopus had longer forelegs than hind legs. This discovery was paleontologically significant because it represented the first dinosaur scientifically investigated from China: seen in 1913, rediscovered in 1922, and excavated in 1923 and studied by T'an during the same year. Unlike most sauropod specimens, it has a relatively complete skull.

Andesaurus is a genus of basal titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which existed during the middle of the Cretaceous Period in South America. Like most sauropods, belonging to one of the largest animals ever to walk the Earth, it would have had a small head on the end of a long neck and an equally long tail.

Epachthosaurus was a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. It was a basal lithostrotian titanosaur. Its fossils have been found in Central and Northern Patagonia in South America.

Pellegrinisaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period. The holotype was found in the Allen Formation, Argentina.

Maxakalisaurus is a genus of titanosaur dinosaur, found in the Adamantina Formation of Brazil, in the state of Minas Gerais in 1998. The genus name is derived from the tribe of the Maxakali; Topa is one of their divinities.

Lithostrotia is a clade of derived titanosaur sauropods that lived during the Early Cretaceous and Late Cretaceous. The group was defined by Upchurch et al. in 2004 as the most recent common ancestor of Malawisaurus and Saltasaurus and all the descendants of that ancestor. Lithostrotia is derived from the Ancient Greek lithostros, meaning "inlaid with stones", referring to the fact that many known lithostrotians are preserved with osteoderms. However, osteoderms are not a distinguishing feature of the group, as the two noted by Unchurch et al. include caudal vertebrae with strongly concave front faces (procoely), although the farthest vertebrae are not procoelous.

Diamantinasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod from Australia that lived during the early Late Cretaceous, about 94 million years ago. The type species of the genus is D. matildae, first described and named in 2009 by Scott Hocknull and colleagues based on fossil finds in the Winton Formation. Meaning "Diamantina lizard", the name is derived from the location of the nearby Diamantina River and the Greek word sauros, "lizard". The specific epithet is from the Australian song Waltzing Matilda, also the locality of the holotype and paratype. The known skeleton includes most of the forelimb, shoulder girdle, pelvis, hindlimb and ribs of the holotype, and one shoulder bone, a radius and some vertebrae of the paratype.

Paludititan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which lived in the area of present Romania during the Late Cretaceous. It existed in the island ecosystem known as Hațeg Island.

Aeolosaurini is an extinct clade of titanosaurian dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous period of Argentina and Brazil. Rodrigo M. Santucci and Antonio C. de Arruda-Campos (2011) in their cladistic analysis found Aeolosaurus, Gondwanatitan, Maxakalisaurus, Panamericansaurus and Rinconsaurus to be aeolosaurids.

Patagotitan is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Cerro Barcino Formation in Chubut Province, Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species known from at least six young adult individuals, Patagotitan mayorum, which was first announced in 2014 and then named in 2017 by José Carballido and colleagues. Preliminary studies and press releases suggested that Patagotitan was the largest known titanosaur and land animal overall, with an estimated length of 37 m (121 ft) and an estimated weight of 69 tonnes. Later research revised the length estimate down to 31 m (102 ft) and weight estimates down to approximately 50–57 tonnes, suggesting that Patagotitan was of a similar size to, if not smaller than, its closest relatives Argentinosaurus and Puertasaurus. Still, Patagotitan is one of the most-known titanosaurs, and so its interrelationships with other titanosaurs have been relatively consistent in phylogenetic analyses. This led to its use in a re-definition of the group Colossosauria by Carballido and colleagues in 2022.

Rukwatitan is a genus of titanosaur sauropod dinosaur from the Galula Formation in Tanzania. It lived around 100 million years ago, during the middle Cretaceous. The species, which shared features with another southern African species, Malawisaurus dixeyi, measured 30 feet (9.1 m) from the head to the tip of the tail, and had forelimbs that were estimated around 6.5 feet (2.0 m) long. Its fossils were found embedded in a cliff face near Lake Rukwa in the Rukwa Valley, from which it gets its name.
Lohuecotitan is an extinct genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur which lived during the Late Cretaceous in Spain. The only species known in the genus is Lohuecotitan pandafilandi, described and named in 2016.
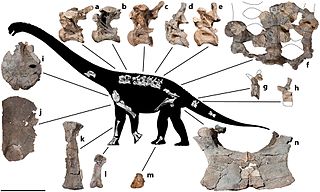
Savannasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Winton Formation of Queensland, Australia. It contains one species, Savannasaurus elliottorum, named in 2016 by Stephen Poropat and colleagues. The holotype and only known specimen, originally nicknamed "Wade", is the most complete specimen of an Australian sauropod, and is held at the Australian Age of Dinosaurs museum. Dinosaurs known from contemporary rocks include its close relative Diamantinasaurus and the theropod Australovenator; associated teeth suggest that Australovenator may have fed on the holotype specimen.
Triunfosaurus is a genus of somphospondylan sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Brazil. It contains a single species, T. leonardii, described by Carvalho et al. in 2017. As a genus, Triunfosaurus can be distinguished from all other titanosaurs by the unique proportions of its ischium. It was initially described as a basal titanosaur, making it the earliest basal titanosaur known; however, subsequent research questioned the identification of the taxon as a titanosaur, instead reassigning it to the Somphospondyli.
Shingopana is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod from the Upper Cretaceous Galula Formation of Tanzania. It is known from only the type species, S. songwensis. Gorscak & O'Connor's phylogenetic testing suggest Shingopana is more closely related to the South American titanosaur family of Aeolosaurini than any of the titanosaurs found so far in North & South Africa.

Mansourasaurus is a genus of herbivorous lithostrotian sauropod dinosaur from the Quseir Formation of Egypt. The type and only species is Mansourasaurus shahinae.
Wamweracaudia is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Tanzania, Africa, 155-145 million years ago.
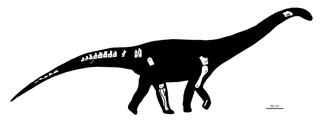
Nullotitan is a genus of lithostrotian titanosaur from the Chorrillo Formation from Santa Cruz Province in Argentina. The type and only species is Nullotitan glaciaris. It was a contemporary of the ornithopod Isasicursor which was described in the same paper.

























