Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula (ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride' is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.

Selenium tetrafluoride (SeF4) is an inorganic compound. It is a colourless liquid that reacts readily with water. It can be used as a fluorinating reagent in organic syntheses (fluorination of alcohols, carboxylic acids or carbonyl compounds) and has advantages over sulfur tetrafluoride in that milder conditions can be employed and it is a liquid rather than a gas.

Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.
A tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with four fluorines in its formula.

Few compounds of californium have been made and studied. The only californium ion that is stable in aqueous solutions is the californium(III) cation. The other two oxidation states are IV (strong oxidizing agents) and II (strong reducing agents). The element forms a water-soluble chloride, nitrate, perchlorate, and sulfate and is precipitated as a fluoride, oxalate or hydroxide. If problems of availability of the element could be overcome, then CfBr2 and CfI2 would likely be stable.
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogens and pnictogens to form various binary compounds. Berkelium can also form several organometallic compounds.

Germanium tetrafluoride (GeF4) is a chemical compound of germanium and fluorine. It is a colorless gas.

Hafnium tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula HfF4. It is a white solid. It adopts the same structure as zirconium tetrafluoride, with 8-coordinate Hf(IV) centers.

Chromium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF4. It has a dark greenish-black color when solid. It rapidly hydrolysizes in presence of moisture in air or directly in water.
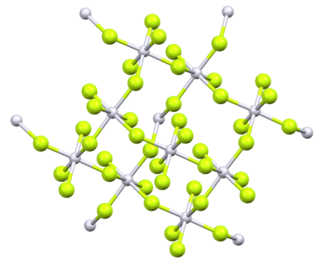
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.

Californium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula CfCl3. As in californium oxide (Cf2O3) and other californium halides, including californium(III) fluoride (CfF3) and iodide (CfI3), the californium atom has an oxidation state of +3.

Californium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound, a salt with a chemical formula CfBr3. Like in californium oxide (Cf2O3) and other californium halides, including californium(III) fluoride (CfF3), californium(III) chloride, and californium(III) iodide (CfI3), the californium atom has an oxidation state of +3.

Berkelium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and fluorine with the chemical formula BkF4.
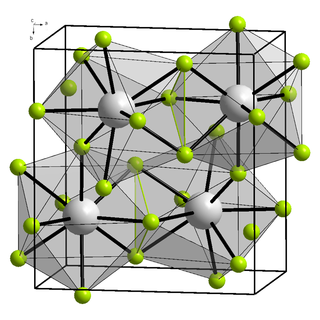
Californium(III) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of californium and fluorine with the formula CfF
3
Californium(II) iodide is a binary inorganic compound of californium and iodine with the formula CfI
2.

Curium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound, a salt of curium and fluorine with the chemical formula CmF4.

Protactinium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of protactinium metal and fluorine with the chemical formula PaF4.
Californium dichloride is a binary inorganic compound of californium metal and chlorine with the chemical formula CfCl2.












