
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride or vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C5H5)2. The molecule is a complex consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C5H5)+2. Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and Fc+ respectively.
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. It is often abbreviated CpH because the cyclopentadienyl anion is abbreviated Cp−.

Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure.

Nickelocene is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(η5-C5H5)2. Also known as bis(cyclopentadienyl)nickel or NiCp2, this bright green paramagnetic solid is of enduring academic interest, although it does not yet have any known practical applications.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

In coordination chemistry, hapticity is the coordination of a ligand to a metal center via an uninterrupted and contiguous series of atoms. The hapticity of a ligand is described with the Greek letter η ('eta'). For example, η2 describes a ligand that coordinates through 2 contiguous atoms. In general the η-notation only applies when multiple atoms are coordinated. In addition, if the ligand coordinates through multiple atoms that are not contiguous then this is considered denticity, and the κ-notation is used once again. When naming complexes care should be taken not to confuse η with μ ('mu'), which relates to bridging ligands.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

Metal nitrosyl complexes are complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal. Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand.

Dicarbonylbis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium is the chemical compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2Ti(CO)2, abbreviated Cp2Ti(CO)2. This maroon-coloured, air-sensitive species is soluble in aliphatic and aromatic solvents. It has been used for the deoxygenation of sulfoxides, reductive coupling of aromatic aldehydes and reduction of aldehydes.

Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process.
Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 is the 2005 version of Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. It is a collection of rules for naming inorganic compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).

Sodium cyclopentadienide is an organosodium compound with the formula C5H5Na. The compound is often abbreviated as NaCp, where Cp− is the cyclopentadienide anion. Sodium cyclopentadienide is a colorless solid, although samples often are pink owing to traces of oxidized impurities.
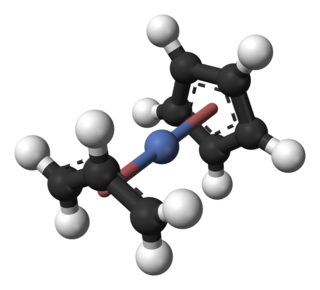
Cyclopentadienyl allyl palladium is an organopalladium compound with formula (C5H5)Pd(C3H5). This reddish solid is volatile with an unpleasant odor. It is soluble in common organic solvents. The molecule consists of a Pd centre sandwiched between a Cp and allyl ligands.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.
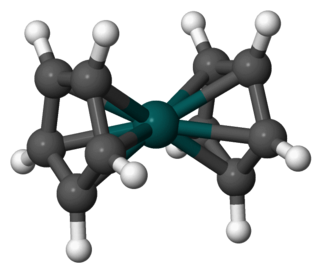
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.
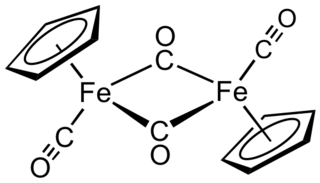
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(η5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2]2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, [CpFe(CO)2]2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below).
Nickel compounds are chemical compounds containing the element nickel which is a member of the group 10 of the periodic table. Most compounds in the group have an oxidation state of +2. Nickel is classified as a transition metal with nickel(II) having much chemical behaviour in common with iron(II) and cobalt(II). Many salts of nickel(II) are isomorphous with salts of magnesium due to the ionic radii of the cations being almost the same. Nickel forms many coordination complexes. Nickel tetracarbonyl was the first pure metal carbonyl produced, and is unusual in its volatility. Metalloproteins containing nickel are found in biological systems.



















