Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and storage. Folate is required for the body to make DNA and RNA and metabolise amino acids necessary for cell division. As humans cannot make folate, it is required in the diet, making it an essential nutrient. It occurs naturally in many foods. The recommended adult daily intake of folate in the U.S. is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements.

Trimethoprim (TMP) is an antibiotic used mainly in the treatment of bladder infections. Other uses include for middle ear infections and travelers' diarrhea. With sulfamethoxazole or dapsone it may be used for Pneumocystis pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth.
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as para-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the para position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white solid, although commercial samples can appear gray. It is slightly soluble in water. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with amino and carboxyl groups. The compound occurs extensively in the natural world.

Sulfonamide is a functional group that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides.

Sulfamethoxazole is an antibiotic. It is used for bacterial infections such as urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and prostatitis and is effective against both gram negative and positive bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes and E. coli.
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, which is another chemical that is part of normal metabolism. Such substances are often similar in structure to the metabolite that they interfere with, such as the antifolates that interfere with the use of folic acid; thus, competitive inhibition can occur, and the presence of antimetabolites can have toxic effects on cells, such as halting cell growth and cell division, so these compounds are used as chemotherapy for cancer.

4-Aminosalicylic acid, also known as para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS) and sold under the brand name Paser among others, is an antibiotic primarily used to treat tuberculosis. Specifically it is used to treat active drug resistant tuberculosis together with other antituberculosis medications. It has also been used as a second line agent to sulfasalazine in people with inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is typically taken by mouth.

Pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Daraprim among others, is a medication used with leucovorin to treat the parasitic diseases toxoplasmosis and cystoisosporiasis. It is also used with dapsone as a second-line option to prevent Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It was previously used for malaria but is no longer recommended due to resistance. Pyrimethamine is taken by mouth.

Sulfadiazine is an antibiotic. Used together with pyrimethamine, a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, it is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis, which is caused by a protozoan parasite. It is a second-line treatment for otitis media, prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, chancroid, chlamydia, and infections by Haemophilus influenzae. It is also used as adjunct therapy for chloroquine-resistant malaria and several forms of bacterial meningitis. It is taken by mouth. Sulfadiazine is available in multiple generic tablets of 500 mg. For urinary tract infections, the usual dose is 4 to 6 grams daily in 3 to 6 divided doses.

Sulfanilamide is a sulfonamide antibacterial drug. Chemically, it is an organic compound consisting of an aniline derivatized with a sulfonamide group. Powdered sulfanilamide was used by the Allies in World War II to reduce infection rates and contributed to a dramatic reduction in mortality rates compared to previous wars. Sulfanilamide is rarely if ever used systemically due to toxicity and because more effective sulfonamides are available for this purpose. Modern antibiotics have supplanted sulfanilamide on the battlefield; however, sulfanilamide remains in use today in the form of topical preparations, primarily for treatment of vaginal yeast infections mainly vulvovaginitis which is caused by Candida albicans.
Sulfacetamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic.

Raltitrexed is an antimetabolite drug used in cancer chemotherapy. It is an inhibitor of thymidylate synthase, and is manufactured by AstraZeneca.

Dihydropteroate is an important intermediate in folate synthesis. It is a pterin created from para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) by the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase.
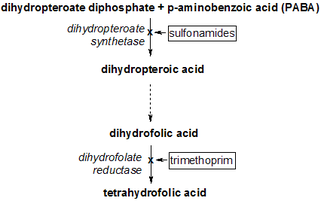
Dihydropteroate synthase is an enzyme classified under EC 2.5.1.15. It produces dihydropteroate in bacteria, but it is not expressed in most eukaryotes including humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide antibiotics, which compete with the PABA precursor.
Tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative.

Sulfadimethoxine is a long-lasting sulfonamide antimicrobial medication used in veterinary medicine. It is used to treat many infections, including respiratory, urinary tract, enteric, and soft tissue infections and can be given as a standalone or combined with ormetoprim to broaden the target range. Like all sulfamides, sulfadimethoxine inhibits bacterial synthesis of folic acid by acting as a competitive inhibitor against PABA. It is the most common drug prescribed to dogs who have coccidiosis.

Antifolates are a class of antimetabolite medications that antagonise (that is, block) the actions of folic acid (vitamin B9). Folic acid's primary function in the body is as a cofactor to various methyltransferases involved in serine, methionine, thymidine and purine biosynthesis. Consequently, antifolates inhibit cell division, DNA/RNA synthesis and repair and protein synthesis. Some such as proguanil, pyrimethamine and trimethoprim selectively inhibit folate's actions in microbial organisms such as bacteria, protozoa and fungi. The majority of antifolates work by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR).
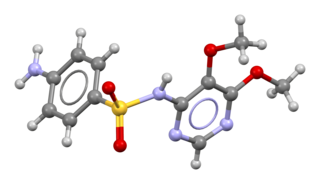
Sulfadoxine is an ultra-long-lasting sulfonamide used in combination with pyrimethamine to treat malaria.
Competitive inhibition is interruption of a chemical pathway owing to one chemical substance inhibiting the effect of another by competing with it for binding or bonding. Any metabolic or chemical messenger system can potentially be affected by this principle, but several classes of competitive inhibition are especially important in biochemistry and medicine, including the competitive form of enzyme inhibition, the competitive form of receptor antagonism, the competitive form of antimetabolite activity, and the competitive form of poisoning.

Glysobuzole is an oral antidiabetic drug, it is taken once daily by oral administration and it is water soluble to become pharmaceutically active within the gastrointestinal tract. It is a sulfonamide derivative that is similar to sulfonylureas. Glysobuzole has antihyperglycemic activity, so it is able to lower blood glucose levels by increasing the release of insulin from the pancreatic beta cells. Glysobuzole functions as a modulator in metabolic processes involving insulin and therefore it is used to treat diabetes.


















