Corporate haven, corporate tax haven, or multinational tax haven is used to describe a jurisdiction that multinational corporations find attractive for establishing subsidiaries or incorporation of regional or main company headquarters, mostly due to favourable tax regimes, and/or favourable secrecy laws, and/or favourable regulatory regimes.

The International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) is an area of central Dublin and part of the CBD established in the 1980s as an urban regeneration area and special economic zone (SEZ) on the derelict state-owned former port authority lands of the reclaimed North Wall and George's Dock areas of the Dublin Docklands. The term has become a metonym for the Irish financial services industry as well as being used as an address and still being classified as an SEZ.

Ireland's Corporate Tax System is a central component of Ireland's economy. In 2016–17, foreign firms paid 80% of Irish corporate tax, employed 25% of the Irish labour force, and created 57% of Irish OECD non-farm value-add. As of 2017, 25 of the top 50 Irish firms were U.S.–controlled businesses, representing 70% of the revenue of the top 50 Irish firms. By 2018, Ireland had received the most U.S. § Corporate tax inversions in history, and Apple was over one–fifth of Irish GDP. Academics rank Ireland as the largest tax haven; larger than the Caribbean tax haven system.
The Tax Justice Network (TJN) is a British advocacy group consisting of a coalition of researchers and activists with a shared concern about tax avoidance, tax competition, and tax havens.
A tax haven is a term, often used pejoratively, to describe a place with very low tax rates for non-domiciled investors, even if the official rates may be higher.

An offshore financial centre (OFC) is defined as a "country or jurisdiction that provides financial services to nonresidents on a scale that is incommensurate with the size and the financing of its domestic economy."

The Double Irish arrangement was a base erosion and profit shifting (BEPS) corporate tax avoidance tool used mostly by United States multinationals since the late 1980s to avoid corporate taxation on non-U.S. profits. It was the largest tax avoidance tool in history and by 2010 was shielding US$100 billion annually in US multinational foreign profits from taxation, and was the main tool by which US multinationals built up untaxed offshore reserves of US$1 trillion from 2004 to 2018. Traditionally, it was also used with the Dutch Sandwich BEPS tool; however, 2010 changes to tax laws in Ireland dispensed with this requirement.

Base erosion and profit shifting (BEPS) refers to corporate tax planning strategies used by multinationals to "shift" profits from higher-tax jurisdictions to lower-tax jurisdictions or no-tax locations where there is little or no economic activity, thus "eroding" the "tax-base" of the higher-tax jurisdictions using deductible payments such as interest or royalties. For the government, the tax base is a company's income or profit. Tax is levied as a percentage on this income/profit. When that income / profit is transferred to a tax haven, the tax base is eroded and the company does not pay taxes to the country that is generating the income. As a result, tax revenues are reduced and the country is disadvantaged. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) define BEPS strategies as "exploiting gaps and mismatches in tax rules". While some of the tactics are illegal, the majority are not. Because businesses that operate across borders can utilize BEPS to obtain a competitive edge over domestic businesses, it affects the righteousness and integrity of tax systems. Furthermore, it lessens deliberate compliance, when taxpayers notice multinationals legally avoiding corporate income taxes. Because developing nations rely more heavily on corporate income tax, they are disproportionately affected by BEPS.

Dutch Sandwich is a base erosion and profit shifting (BEPS) corporate tax tool, used mostly by U.S. multinationals to avoid incurring European Union withholding taxes on untaxed profits as they were being moved to non-EU tax havens. These untaxed profits could have originated from within the EU, or from outside the EU, but in most cases were routed to major EU corporate-focused tax havens, such as Ireland and Luxembourg, by the use of other BEPS tools. The Dutch Sandwich was often used with Irish BEPS tools such as the Double Irish, the Single Malt and the Capital Allowances for Intangible Assets ("CAIA") tools. In 2010, Ireland changed its tax-code to enable Irish BEPS tools to avoid such withholding taxes without needing a Dutch Sandwich.

Bermuda black hole refers to base erosion and profit shifting (BEPS) tax avoidance schemes in which untaxed global profits end up in Bermuda, which is considered a tax haven. The term was most associated with US technology multinationals such as Apple and Google who used Bermuda as the "terminus" for their Double Irish arrangement tax structure.
In 2010, the United States implemented the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act; the law required financial firms around the world to report accounts held by US citizens to the Internal Revenue Service. The US on the other hand refused the Common Reporting Standard set up by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, alongside Vanuatu and Bahrain.
The Republic of Panama is one of the oldest and best-known tax havens in the Caribbean, as well as one of the most established in the region. Panama has had a reputation for tax avoidance since the early 20th century, and Panama has been cited repeatedly in recent years as a jurisdiction which does not cooperate with international tax transparency initiatives.

Leprechaun economics was a term coined by economist Paul Krugman to describe the 26.3 per cent rise in Irish 2015 GDP, later revised to 34.4 per cent, in a 12 July 2016 publication by the Irish Central Statistics Office (CSO), restating 2015 Irish national accounts. At that point, the distortion of Irish economic data by tax-driven accounting flows reached a climax. In 2020, Krugman said the term was a feature of all tax havens.
The OECD G20 Base Erosion and Profit Shifting Project is an OECD/G20 project to set up an international framework to combat tax avoidance by multinational enterprises ("MNEs") using base erosion and profit shifting tools. The project, led by the OECD's Committee on Fiscal Affairs, began in 2013 with OECD and G20 countries, in a context of financial crisis and tax affairs. Currently, after the BEPS report has been delivered in 2015, the project is now in its implementation phase, 116 countries are involved including a majority of developing countries. During two years, the package was developed by participating members on an equal footing, as well as widespread consultations with jurisdictions and stakeholders, including business, academics and civil society. And since 2016, the OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on BEPS provides for its 140 members a platform to work on an equal footing to tackle BEPS, including through peer review of the BEPS minimum standards, and monitoring of implementation of the BEPS package as a whole.
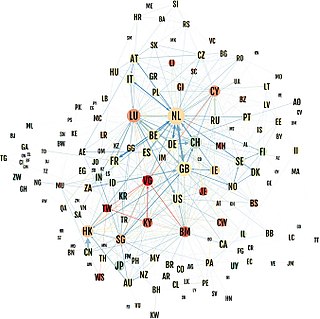
Conduit OFC and sink OFC is an empirical quantitative method of classifying corporate tax havens, offshore financial centres (OFCs) and tax havens.

Apple's EU tax dispute refers to an investigation by the European Commission into tax arrangements between Apple and Ireland, which allowed the company to pay close to zero corporate tax over 10 years.

Modified gross national income is a metric used by the Central Statistics Office (Ireland) to measure the Irish economy rather than GNI or GDP. GNI* is GNI minus the depreciation on Intellectual Property, depreciation on leased aircraft and the net factor income of redomiciled PLCs.

Feargal O'Rourke is an Irish accountant and corporate tax expert, who was the managing partner of PwC in Ireland. He is considered the architect of the Double Irish tax scheme used by U.S. firms such as Apple, Google and Facebook in Ireland, and a leader in the development of corporate tax planning tools, and tax legislation, for U.S. multinationals in Ireland.

Ireland has been labelled as a tax haven or corporate tax haven in multiple financial reports, an allegation which the state has rejected in response. Ireland is on all academic "tax haven lists", including the § Leaders in tax haven research, and tax NGOs. Ireland does not meet the 1998 OECD definition of a tax haven, but no OECD member, including Switzerland, ever met this definition; only Trinidad & Tobago met it in 2017. Similarly, no EU–28 country is amongst the 64 listed in the 2017 EU tax haven blacklist and greylist. In September 2016, Brazil became the first G20 country to "blacklist" Ireland as a tax haven.
James R. Hines Jr. is an American economist and a founder of academic research into corporate-focused tax havens, and the effect of U.S. corporate tax policy on the behaviors of U.S. multinationals. His papers were some of the first to analyse profit shifting, and to establish quantitative features of tax havens. Hines showed that being a tax haven could be a prosperous strategy for a jurisdiction, and controversially, that tax havens can promote economic growth. Hines showed that use of tax havens by U.S. multinationals had maximized long-term U.S. exchequer tax receipts, at the expense of other jurisdictions. Hines is the most cited author on the research of tax havens, and his work on tax havens was relied upon by the CEA when drafting the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017.













