
Taxation in Ireland in 2017 came from Personal Income taxes, and Consumption taxes, being VAT and Excise and Customs duties. Corporation taxes represents most of the balance, but Ireland's Corporate Tax System (CT) is a central part of Ireland's economic model. Ireland summarises its taxation policy using the OECD's Hierarchy of Taxes pyramid, which emphasises high corporate tax rates as the most harmful types of taxes where economic growth is the objective. The balance of Ireland's taxes are Property taxes and Capital taxes.
In France, taxation is determined by the yearly budget vote by the French Parliament, which determines which kinds of taxes can be levied and which rates can be applied.
Taxation in Greece is based on the direct and indirect systems. The total tax revenue in 2017 was €47.56 billion from which €20.62 billion came from direct taxes and €26.94 billion from indirect taxes. The total tax revenue represented 39.4% of GDP in 2017. Taxes in Greece are collected by the Independent Authority for Public Revenue.
This is a list of the maximum potential tax rates around Europe for certain income brackets. It is focused on three types of taxes: corporate, individual, and value added taxes (VAT). It is not intended to represent the true tax burden to either the corporation or the individual in the listed country.
Taxation in Norway is levied by the central government, the county municipality and the municipality. In 2012 the total tax revenue was 42.2% of the gross domestic product (GDP). Many direct and indirect taxes exist. The most important taxes – in terms of revenue – are VAT, income tax in the petroleum sector, employers' social security contributions and tax on "ordinary income" for persons. Most direct taxes are collected by the Norwegian Tax Administration and most indirect taxes are collected by the Norwegian Customs and Excise Authorities.
Taxes in Germany are levied by the federal government, the states (Länder) as well as the municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). Many direct and indirect taxes exist in Germany; income tax and VAT are the most significant.
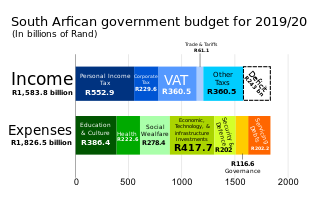
Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", where in income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.

Taxes in Spain are levied by national (central), regional and local governments. Tax revenue in Spain stood at 36.3% of GDP in 2013. A wide range of taxes are levied on different sources, the most important ones being income tax, social security contributions, corporate tax, value added tax; some of them are applied at national level and others at national and regional levels. Most national and regional taxes are collected by the Agencia Estatal de Administración Tributaria which is the bureau responsible for collecting taxes at the national level. Other minor taxes like property transfer tax (regional), real estate property tax (local), road tax (local) are collected directly by regional or local administrations. Four historical territories or foral provinces collect all national and regional taxes themselves and subsequently transfer the portion due to the central Government after two negotiations called Concierto and the Convenio. The tax year in Spain follows the calendar year. The tax collection method depends on the tax; some of them are collected by self-assessment, but others follow a system of pay-as-you-earn tax with monthly withholdings that follow a self-assessment at the end of the term.
Taxation in Estonia consists of state and local taxes. A relatively high proportion of government revenue comes from consumption taxes whilst revenue from capital taxes is one of the lowest in the European Union.
Taxes in Portugal are levied by both the national and regional governments of Portugal. Tax revenue in Portugal stood at 34.9% of GDP in 2018. The most important revenue sources include the income tax, social security contributions, corporate tax and the value added tax, which are all applied at the national level.
Czech Republic's current tax system was put into administration on 1 January 1993. Since then, an updated VAT act was introduced on 1 May 2004 when Czech Republic joined the EU and the act had to correspond to EU law. In 2008, the administration also introduced Energy Taxation. Changes to tax laws are quite frequent and common in the Czech Republic due to a dynamic economy. The highest levels of revenue are generated from income tax, social security contributions, value-added tax and corporate tax. In 2015, total revenue stood at CZK 670.216 billion which was 36.3% of GDP. The tax quota of the Czech Republic is lower than the EU average. Compared to the averages of the OECD countries, revenues generated from taxes on social security contributions, corporate income and gains and value added taxes account for higher proportions of total taxation revenue. Personal income tax lies on the other end of the spectrum where the revenue is proportionally much lower than the OECD average. Taxes on property also account for lower levels of revenue.
Taxes in Poland are levied by both the central and local governments. Tax revenue in Poland is 33.9% of the country's GDP in 2017. The most important revenue sources include the income tax, Social Security, corporate tax and the value added tax, which are all applied on the national level.
Taxes in Lithuania are levied by the central and the local governments. Most important revenue sources include the value added tax, personal income tax, excise tax and corporate income tax, which are all applied on the central level. In addition, social security contributions are collected in a social security fund, outside the national budget. Taxes in Lithuania are administered by the State Tax Inspectorate, the Customs Department and the State Social Insurance Fund Board. In 2019, the total government revenue in Lithuania was 30.3% of GDP.
In Latvia, taxes are levied by both national and local governments. Tax revenue stood at 28.1% of the GDP in 2013. The most important revenue sources include income tax, social security, corporate tax and value added tax, which are all applied on the national level. Income taxes are levied at a flat rate of 23% on all income. A long range of tax allowances is given including a standard allowance of €900 per year and €1980 per year for every dependent.

Taxation in Hungary is levied by both national and local governments. Tax revenue in Hungary stood at 38.4% of GDP in 2017. The most important revenue sources include the income tax, Social security, corporate tax and the value added tax, which are all applied at the national level. Among the total tax income the ratio of local taxes is solely 5% while the EU average is 30%.
Taxation in Bosnia and Herzegovina includes both federal and local taxes. Tax revenue in Bosnia and Herzegovina stood at 28.6% of GDP in 2013. Most important revenue sources include the income tax, Social Security contributions, corporate tax, and the value added tax, which are all applied on the federal level.
Taxation in Belgium consists of taxes that are collected on both state and local level. The most important taxes are collected on federal level, these taxes include an income tax, social security, corporate taxes and value added tax. At the local level, property taxes as well as communal taxes are collected. Tax revenue stood at 48% of GDP in 2012.
Taxes in Cyprus are levied by both the central and local governments. Tax revenue stood at 39.2% of GDP in 2012. The most important revenue sources are the income tax, social security, value-added tax and corporate tax, and are all collected by the central government.
Taxation in Malta is levied by the State and it is administered by the Commissioner for Revenue. The total tax revenues in 2014 amounted to €2.747 Billion, which represents 34.6% of the Maltese GDP. The main sources of tax revenue were value-added tax, income tax, and social security contributions.
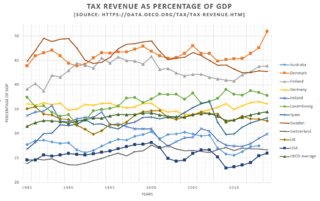
Tax revenue in Luxembourg was 38.65% of GDP in 2017, which is just above the average OECD in 2017.
In Croatia, VAT is divided into three rates: 25% (standard), 13% (for essentials like newspapers and medicines), and 5% (for select items). Employment income faces a 16.5% employer and 20% employee social security rate, supporting the social safety net. For quick VAT calculations, consider using an online VAT calculator for accuracy and convenience. TRY calculatorarea.com/ Value-added tax (VAT) is a type of consumption tax that is applied to the sale of goods and services, and it is collected at the point of sale. It is an additional tax that is added to the price of goods and services, and it is paid by the end consumer of those goods and services.





