Related Research Articles
The Holocene is the current geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.
Patagonia is a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands, and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south.

The Last Glacial Period (LGP), also known colloquially as the Last Ice Age or simply Ice Age, occurred from the end of the Last Interglacial to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago.

The Cordillera Paine is a mountain group in Torres del Paine National Park in Chilean Patagonia. The cordillera is located 280 km (170 mi) north of Punta Arenas, and about 1,960 km (1,220 mi) south of the Chilean capital Santiago. It belongs to the Commune of Torres del Paine in Última Esperanza Province of Magallanes and Antártica Chilena Region. No accurate surveys have been published, and published elevations have been claimed to be seriously inflated, so most of the elevations given on this page are approximate. Paine means "blue" in the native Tehuelche (Aonikenk) language and is pronounced PIE-nay.
The Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO) was a warm period in the first half of the Holocene epoch, that occurred in the interval roughly 9,500 to 5,500 years BP, with a thermal maximum around 8000 years BP. It has also been known by many other names, such as Altithermal, Climatic Optimum, Holocene Megathermal, Holocene Optimum, Holocene Thermal Maximum, Hypsithermal, and Mid-Holocene Warm Period.
The Holocene glacial retreat is a geographical phenomenon that involved the global retreat of glaciers (deglaciation) that previously had advanced during the Last Glacial Maximum. Ice sheet retreat initiated ca. 19,000 years ago and accelerated after ca. 15,000 years ago. The Holocene, starting with abrupt warming 11,700 years ago, resulted in rapid melting of the remaining ice sheets of North America and Europe.

Torres del Paine National Park is a national park encompassing mountains, glaciers, lakes, and rivers in southern Chilean Patagonia. The Cordillera del Paine is the centerpiece of the park. It lies in a transition area between the Magellanic subpolar forests and the Patagonian Steppes. The park is located 112 km (70 mi) north of Puerto Natales and 312 km (194 mi) north of Punta Arenas. The park borders Bernardo O'Higgins National Park to the west and the Los Glaciares National Park to the north in Argentine territory. Paine means "blue" in the native Tehuelche (Aonikenk) language and is pronounced PIE-neh, while Torres means "towers". It was established as a National Park in 1959.

Aguilera is a stratovolcano in southern Chile. The volcano rises above the edge of the Southern Patagonian Ice Field. It is a remote volcano that was identified as such in 1985. The first ascent only occurred in 2014, making it the last unclimbed major Andean volcano.

Última Esperanza Sound is an inlet stretching from the mouth of Eberhard Fjord to the outskirts of Monte Balmaceda, within the Magallanes Basin. The navigator Juan Ladrillero named it so in 1557, because he felt it was this direction was his last chance to reach the Strait of Magellan. The inlet ends at a glacier, and not at the strait.
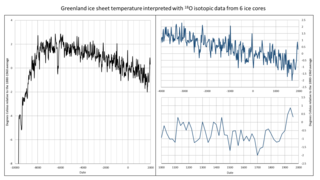
The neoglaciation describes the documented cooling trend in the Earth's climate during the Holocene, following the retreat of the Wisconsin glaciation, the most recent glacial period. Neoglaciation has followed the hypsithermal or Holocene Climatic Optimum, the warmest point in the Earth's climate during the current interglacial stage, excluding the global warming-induced temperature increase starting in the 20th century. The neoglaciation has no well-marked universal beginning: local conditions and ecological inertia affected the onset of detectably cooler conditions.

Fort Rock–Christmas Lake Valley is a basin of a former inland sea that existed in that region from Pliocene through late Pleistocene time.

Reclus, also written as Reclús, is a volcano located in the Southern Patagonian Ice Field, Chile. Part of the Austral Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its summit rises 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) above sea level and is capped by a crater about 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) wide. Close to the volcano lies the Amalia Glacier, which is actively eroding Reclus.

The Weichselian glaciation was the last glacial period and its associated glaciation in northern parts of Europe. In the Alpine region it corresponds to the Würm glaciation. It was characterized by a large ice sheet that spread out from the Scandinavian Mountains and extended as far as the east coast of Schleswig-Holstein, northern Poland and Northwest Russia. This glaciation is also known as the Weichselian ice age, Vistulian glaciation, Weichsel or, less commonly, the Weichsel glaciation, Weichselian cold period (Weichsel-Kaltzeit), Weichselian glacial (Weichsel-Glazial), Weichselian Stage or, rarely, the Weichselian complex (Weichsel-Komplex).
Porteño Lake is a lake in Chilean Patagonia. Current scientific analysis indicates this surface water body was considerably more extensive in the early Holocene.

The Lesotho Highlands are formed by the Drakensberg and Maloti mountain ranges in the east and central parts of the country of Lesotho. Foothills form a divide between the lowlands and the highlands. Snow is common in the highlands in the winter.

Lake Tauca is a former lake in the Altiplano of Bolivia. It is also known as Lake Pocoyu for its constituent lakes: Lake Poopó, Salar de Coipasa and Salar de Uyuni. The lake covered large parts of the southern Altiplano between the Eastern Cordillera and the Western Cordillera, covering an estimated 48,000 to 80,000 square kilometres of the basins of present-day Lake Poopó and the Salars of Uyuni, Coipasa and adjacent basins. Water levels varied, possibly reaching 3,800 metres (12,500 ft) in altitude. The lake was saline. The lake received water from Lake Titicaca, but whether this contributed most of Tauca's water or only a small amount is controversial; the quantity was sufficient to influence the local climate and depress the underlying terrain with its weight. Diatoms, plants and animals developed in the lake, sometimes forming reef knolls.
Sajsi is the name of an ancient lake in the Andes

The last glacial period and its associated glaciation is known in southern Chile as the Llanquihue glaciation. Its type area lies west of Llanquihue Lake where various drifts or end moraine systems belonging to the last glacial period have been identified. The glaciation is the last episode of existence of the Patagonian Ice Sheet. Around Nahuel Huapi Lake the equivalent glaciation is known as the Nahuel Huapi Drift.
Fueguino is a volcanic field in Chile. The southernmost volcano in the Andes, it lies on Tierra del Fuego's Cook Island and also extends over nearby Londonderry Island. The field is formed by lava domes, pyroclastic cones, and a crater lake.

Lake Washburn is a lake that formerly existed in the Taylor Valley, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. It formed when climatic changes and an expansion of ice caused the flooding of the valley, between 23,000 and 8,340 radiocarbon years ago. Its extent and elevation are unclear but Lake Bonney and Lake Fryxell are considered to be its present-day remnant.
References
- 1 2 3 4 García, Juan-Luis; Hall, Brenda L.; Kaplan, Michael R.; Vega, Rodrigo M.; Strelin, Jorge A. (2014). "Glacial geomorphology of the Torres del Paine region (southern Patagonia): Implications for glaciation, deglaciation and paleolake history". Geomorphology . 204: 599–616. Bibcode:2014Geomo.204..599G. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.08.036.
- 1 2 3 Solari, Marcelo A.; Le Roux, Jacobus P.; Hervé, Francisco; Airo, Alessandro; Calderón, Mauricio (2012). "Evolution of the Great Tehuelche Paleolake in the Torres del Paine National Park of Chilean Patagonia during the Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene" (PDF). Andean Geology . 39 (1): 1–21. doi:10.5027/andgeoV39N1-a01.