A guild (or ecological guild) is any group of species that exploit the same resources, or that exploit different resources in related ways. [1] [2] [3] It is not necessary that the species within a guild occupy the same, or even similar, ecological niches. [lower-alpha 1]
Guilds are defined according to the locations, attributes, or activities of their component species. For example, the mode of acquiring nutrients, the mobility, and the habitat zones that the species occupy or exploit can be used to define a guild. The number of guilds occupying an ecosystem is termed its disparity. [5] Members of a guild within a given ecosystem could be competing for resources, such as space or light, while cooperating in resisting wind stresses, attracting pollinators, or detecting predators, such as happens among savannah-dwelling antelope and zebra.
A guild does not typically have strict, or even clearly defined boundaries, nor does it need to be taxonomically cohesive. A broadly defined guild will almost always have constituent guilds; for example, grazing guilds will have some species that concentrate on coarse, plentiful forage, while others concentrate on low-growing, finer plants. Each of those two sub-guilds may be regarded as guilds in appropriate contexts, and they might, in turn, have sub-guilds in more closely selective contexts. Some authorities even speak of guilds in terms of a fractal resource model. [6] This concept arises in several related contexts, such as the metabolic theory of ecology, the scaling pattern of occupancy, and spatial analysis in ecology, all of which are fundamental concepts in defining guilds.
An ecological guild is not to be confused with a taxocene, a group of phylogenetically related organisms in a community that do not necessarily share the same or similar niches (for example, "the insect community"). Nor is a guild the same as a trophic species, which is a functional group of taxa sharing the same set of predators and prey within a food web. [7]
Some authors have used the term guild to analyze microbial communities. However, precisely because of the pointed lack of concretion in the original definition, it has been used with different connotations. Recently, some effort has been made to address this issue. [8] Some authors have proposed a formal definition for guilds that avoids this inherent ambiguity of niche exploitation, and a quantification method considering the problems arising from degeneracy in protein functions. [9] According to the authors, any organism that performs a function, regardless of its phylogenetic lineage, its environmental preferences or how it carries it out, would be regarded as a representative member of the guild. This contrasts with the definitions used for the study of macro organisms, where membership demanded that the different forms of exploitation of the resource were related or similar.
The term guild is a broad term to describe the relationship between different species using the same resource. Since it is difficult to classify a guild it can be broken down into two more specific categories, alpha guilds and beta guilds.
Alpha guild is specifically related to species that share a resource used within the same community. [10] Species in an alpha guild do not typically coexist in the same area, as the competitive exclusion principle prevents this. If species are grouped into an alpha guild together one of them will need to change the way they use this resource or change the resources they use to survive.
Beta guild is specifically related to species that are found in the same environmental conditions. [10] Species in a beta guild are typically found in the same space and time together, as their environmental range is the same. Species grouped into the same beta guild still may use the same resources but not competitively.

Ecology is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history.

An ecosystem is a system that environments and their organisms form through their interaction. The biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.

Mutualism describes the ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction. Prominent examples are:

In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors and how it in turn alters those same factors. "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts".

In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species, or of different species. These effects may be short-term, or long-term, both often strongly influence the adaptation and evolution of the species involved. Biological interactions range from mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition, harmful to both partners. Interactions can be direct when physical contact is established or indirect, through intermediaries such as shared resources, territories, ecological services, metabolic waste, toxins or growth inhibitors. This type of relationship can be shown by net effect based on individual effects on both organisms arising out of relationship.
This glossary of ecology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts in ecology and related fields. For more specific definitions from other glossaries related to ecology, see Glossary of biology, Glossary of evolutionary biology, and Glossary of environmental science.

In ecology, the competitive exclusion principle, sometimes referred to as Gause's law, is a proposition that two species which compete for the same limited resource cannot coexist at constant population values. When one species has even the slightest advantage over another, the one with the advantage will dominate in the long term. This leads either to the extinction of the weaker competitor or to an evolutionary or behavioral shift toward a different ecological niche. The principle has been paraphrased in the maxim "complete competitors cannot coexist".

Character displacement is the phenomenon where differences among similar species whose distributions overlap geographically are accentuated in regions where the species co-occur, but are minimized or lost where the species' distributions do not overlap. This pattern results from evolutionary change driven by biological competition among species for a limited resource. The rationale for character displacement stems from the competitive exclusion principle, also called Gause's Law, which contends that to coexist in a stable environment two competing species must differ in their respective ecological niche; without differentiation, one species will eliminate or exclude the other through competition.
A functional group is merely a set of species, or collection of organisms, that share alike characteristics within a community. Ideally, the lifeforms would perform equivalent tasks based on domain forces, rather than a common ancestor or evolutionary relationship. This could potentially lead to analogous structures that overrule the possibility of homology. More specifically, these beings produce resembling effects to external factors of an inhabiting system. Due to the fact that a majority of these creatures share an ecological niche, it is practical to assume they require similar structures in order to achieve the greatest amount of fitness. This refers to such as the ability to successfully reproduce to create offspring, and furthermore sustain life by avoiding alike predators and sharing meals.
A generalist species is able to thrive in a wide variety of environmental conditions and can make use of a variety of different resources. A specialist species can thrive only in a narrow range of environmental conditions or has a limited diet. Most organisms do not all fit neatly into either group, however. Some species are highly specialized, others less so, and some can tolerate many different environments. In other words, there is a continuum from highly specialized to broadly generalist species.

Functional ecology is a branch of ecology that focuses on the roles, or functions, that species play in the community or ecosystem in which they occur. In this approach, physiological, anatomical, and life history characteristics of the species are emphasized. The term "function" is used to emphasize certain physiological processes rather than discrete properties, describe an organism's role in a trophic system, or illustrate the effects of natural selective processes on an organism. This sub-discipline of ecology represents the crossroads between ecological patterns and the processes and mechanisms that underlie them.

Competition is an interaction between organisms or species in which both require a resource that is in limited supply. Competition lowers the fitness of both organisms involved since the presence of one of the organisms always reduces the amount of the resource available to the other.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ecology:

Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of different species compete for the same resources in an ecosystem. This can be contrasted with mutualism, a type of symbiosis. Competition between members of the same species is called intraspecific competition.

In ecology, a community is a group or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time, also known as a biocoenosis, biotic community, biological community, ecological community, or life assemblage. The term community has a variety of uses. In its simplest form it refers to groups of organisms in a specific place or time, for example, "the fish community of Lake Ontario before industrialization".

Neuston, also called pleuston, are organisms that live at the surface of a body of water, such as an ocean, estuary, lake, river, wetland or pond. Neuston can live on top of the water surface or submersed just below the water surface. In addition, microorganisms can exist in the surface microlayer that forms between the top- and the under-side of the water surface. Neuston has been defined as "organisms living at the air/water interface of freshwater, estuarine, and marine habitats or referring to the biota on or directly below the water’s surface layer."
An operational taxonomic unit (OTU) is an operational definition used to classify groups of closely related individuals. The term was originally introduced in 1963 by Robert R. Sokal and Peter H. A. Sneath in the context of numerical taxonomy, where an "operational taxonomic unit" is simply the group of organisms currently being studied. Numerical taxonomy is a method in biological systematics that involves using numerical techniques to classify taxonomic units based on the states of their characteristics. In this sense, an OTU is a pragmatic definition to group individuals by similarity, equivalent to but not necessarily in line with classical Linnaean taxonomy or modern evolutionary taxonomy.

A microbiome is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps et al. as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably well-defined habitat which has distinct physio-chemical properties. The term thus not only refers to the microorganisms involved but also encompasses their theatre of activity". In 2020, an international panel of experts published the outcome of their discussions on the definition of the microbiome. They proposed a definition of the microbiome based on a revival of the "compact, clear, and comprehensive description of the term" as originally provided by Whipps et al., but supplemented with two explanatory paragraphs, the first pronouncing the dynamic character of the microbiome, and the second clearly separating the term microbiota from the term microbiome.
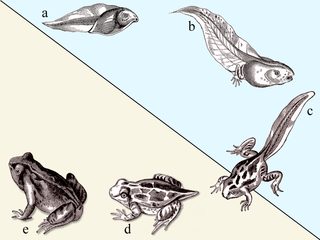
Ontogenetic niche shift is an ecological phenomenon where an organism changes its diet or habitat during its ontogeny (development). During the ontogenetic niche shifting an ecological niche of an individual changes its breadth and position. The best known representatives of taxa that exhibit some kind of the ontogenetic niche shift are fish, insects and amphibians. A niche shift is thought to be determined genetically, while also being irreversible. Important aspect of the ONS is the fact, that individuals of different stages of a population utilize different kind of resources and habitats. The term was introduced in a 1984 paper by biologists Earl E. Werner and James F. Gilliam.
In theoretical ecology and nonlinear dynamics, consumer-resource models (CRMs) are a class of ecological models in which a community of consumer species compete for a common pool of resources. Instead of species interacting directly, all species-species interactions are mediated through resource dynamics. Consumer-resource models have served as fundamental tools in the quantitative development of theories of niche construction, coexistence, and biological diversity. These models can be interpreted as a quantitative description of a single trophic level.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)