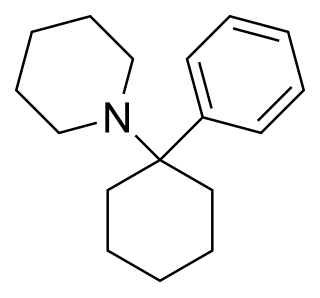
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known in its use as a street drug as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco.

NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for humans and animals; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia.
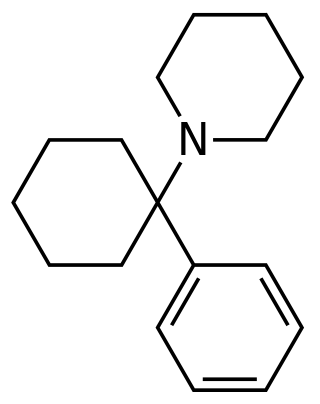
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.

3-Methoxyphencyclidine (3-MeO-PCP) is a dissociative hallucinogen of the arylcyclohexylamine class related to phencyclidine (PCP) which has been sold online as a designer drug. It has been used across Europe and the United States. In some cases, consumption has been known to be fatal. It acts mainly as an NMDA receptor antagonist, though it has also been found to interact with the sigma σ1 receptor and the serotonin transporter. The drug does not possess any opioid activity nor does it act as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor.

4-Methoxyphencyclidine is a dissociative anesthetic drug that has been sold online as a research chemical. The synthesis of 4-MeO-PCP was first reported in 1965 by the Parke-Davis medicinal chemist Victor Maddox. A 1999 review published by a chemist using the pseudonym John Q. Beagle suggested the potency of 4-MeO-PCP in man was reduced relative to PCP, two years later Beagle published a detailed description of the synthesis and qualitative effects of 4-MeO-PCP, which he said possessed 70% the potency of PCP. 4-MeO-PCP was the first arylcyclohexylamine research chemical to be sold online, it was introduced in late 2008 by a company trading under the name CBAY and was followed by several related compounds such as 3-MeO-PCP and methoxetamine. 4-MeO-PCP has lower affinity for the NMDA receptor than PCP, but higher affinity than ketamine, it is orally active in a dosage range similar to ketamine, with some users requiring doses in excess of 100 mg for desired effects. Users have reported substantial differences in active dose, these discrepancies can be partially explained by the presence of unreacted PCC and other impurities in samples sold on the grey market. 4-MeO-PCP has Ki values of 404 nM for the NMDA receptor, 713 nM for the norepinephrine transporter, 844 nM for the serotonin transporter, 296 nM for the σ1 receptor and 143 nM for the σ2 receptor.

Methoxetamine (MXE) is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociatives such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP) that were developed as pharmaceutical drugs for use as general anesthetics in that it was designed specifically to increase the antidepressant effects of ketamine.
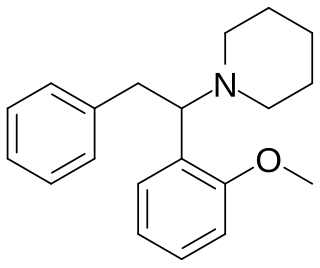
Methoxphenidine is a dissociative of the diarylethylamine class that has been sold online as a designer drug. Methoxphenidine was first reported in a 1989 patent where it was tested as a treatment for neurotoxic injury. Shortly after the 2013 UK ban on arylcyclohexylamines methoxphenidine and the related compound diphenidine became available on the gray market, where it has been encountered as a powder and in tablet form. Though diphenidine possesses higher affinity for the NMDA receptor, anecdotal reports suggest methoxphenidine has greater oral potency. Of the three isomeric anisyl-substituents methoxphenidine has affinity for the NMDA receptor that is higher than 4-MeO-diphenidine but lower than 3-MeO-diphenidine, a structure–activity relationship shared by the arylcyclohexylamines.

Ephenidine is a dissociative anesthetic that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is illegal in some countries as a structural isomer of the banned opioid drug lefetamine, but has been sold in countries where it is not yet banned.

3-Methoxyeticyclidine (3-MeO-PCE), also known as methoxieticyclidine, is a dissociative anesthetic that is qualitatively similar to PCE and PCP and has been sold online as a designer drug.
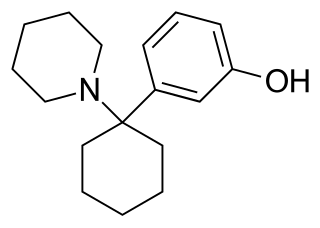
3-Hydroxyphencyclidine (3-HO-PCP) is a dissociative of the arylcyclohexylamine class related to phencyclidine (PCP) that has been sold online as a designer drug.
2-Fluorodeschloroketamine is a dissociative anesthetic related to ketamine. Its sale and use as a designer drug has been reported in various countries. It is an analogue of ketamine where the chlorine group has been replaced by fluorine. Due to its recent emergence, the pharmacological specifics of the compound are mostly unclear, but effects are reported to be similar to its parent compound, ketamine.
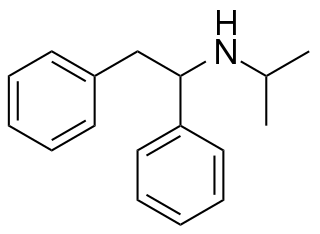
NPDPA is a dissociative anesthetic that has been sold online as a designer drug. It was first identified in Germany in 2008, and while it has never been as widely sold as related compounds such as diphenidine and ephenidine, it has continued to show up in seized drug samples occasionally, and was banned in Sweden in 2015.
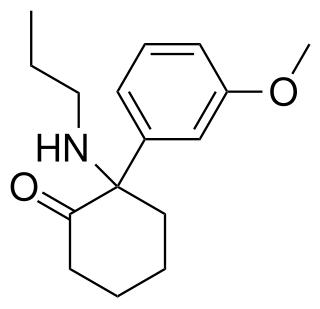
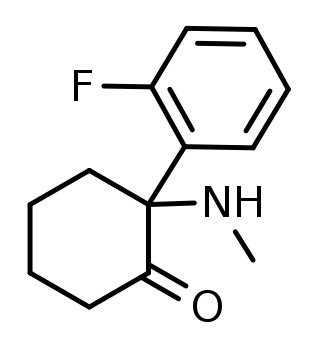
Methoxpropamine is a dissociative anesthetic drug of the arylcyclohexylamine class and NMDA receptor antagonist that is closely related to substances such as methoxetamine and PCPr. It has been sold online as a designer drug, first being identified in Denmark in October 2019, and is illegal in Finland.

MXiPr is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as ketamine and methoxetamine. It was first identified in Slovenia in December 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021.

3-Methyl-PCP is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as 3'-MeO-PCP and 3'-Me-PCPy. It was first synthesised in the 1960s, but was only identified on the illicit market in Hungary in September 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021.
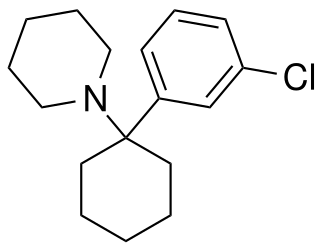
3-Chloro-PCP (3'-Cl-PCP) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It has comparable potency to phencyclidine but with a slightly different effects profile, being somewhat more potent as an NMDA antagonist but around the same potency as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It was first identified in Slovenia in December 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021.
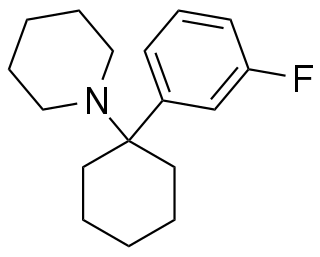
3-Fluoro-PCP is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It was first identified in Slovenia in October 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021.

4-Keto-PCP is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It has potency in between that of ketamine and phencyclidine but with somewhat more sedating effects in animal studies.
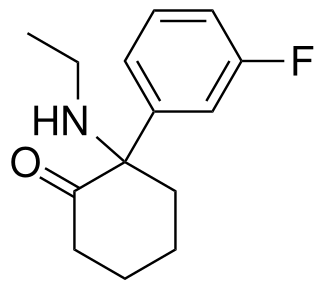
Fluorexetamine is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It has reportedly been sold over the internet since around 2017, though has remained relatively uncommon.

Deoxymethoxetamine is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It is an analogue of methoxetamine where the 3-methoxy group has been replaced by methyl. It has been sold online since around October 2020, and was first definitively identified by a forensic laboratory in Denmark in February 2021.




















