PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story is a book by Alexander Shulgin and Ann Shulgin, published in 1991. The subject of the work is psychoactive phenethylamine chemical derivatives, notably those that act as psychedelics and/or empathogen-entactogens. The main title, PiHKAL, is an acronym that stands for "Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved".

Dimethoxybromoamphetamine (DOB), also known as brolamfetamine and bromo-DMA, is a psychedelic drug and substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine class of compounds. DOB was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1967. Its synthesis and effects are documented in Shulgin's book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story.

ALD-52, also known as 1-acetyl-LSD, has chemical structural features similar to lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), a known psychedelic drug. Similarly, ALD-52 has been reported to produce psychoactive effects, but its pharmacological effects on humans are poorly understood. Given its psychoactive properties, it has been reported to be consumed as a recreational drug, and the purported first confirmed detection of the substance on the illicit market occurred in April 2016.
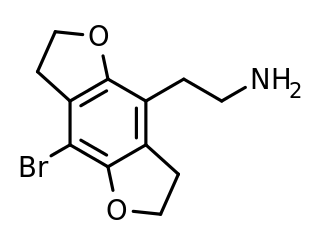
2C-B-FLY is a psychedelic phenethylamine and designer drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized in 1996 by Aaron Monte, Professor of Chemistry at UW-La Crosse.
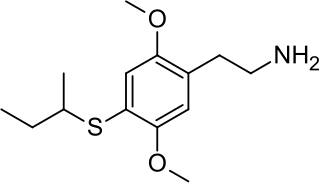
2C-T-17 or 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(β-secbutylthio)phenethylamine is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was presumably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book PiHKAL .

The substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines represent a diverse chemical class of compounds derived from phenethylamines. This category encompasses numerous psychoactive substances with entactogenic, psychedelic, and/or stimulant properties, in addition to entheogens. These compounds find application as research chemicals, designer drugs, and recreational substances.

3C-BZ (4-benzyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. 3C-BZ was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 25–200 mg and the duration as 18–24 hours. According to anecdotal reports from the substance's entry in PiHKAL, 3C-BZ's effects can vary significantly, ranging from intensified emotions and strange dreams, to effects similar to those of LSD or TMA. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 3C-BZ.
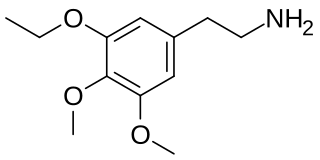
Metaescaline (3,4-dimethoxy-5-ethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. Metaescaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 200–350 mg, and the duration listed as 8–12 hours. Metaescaline produces mental insights, entactogenic, MDMA-like effects, and TOMSO-like activation. Little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of metaescaline, though it has been studied to a limited extent in comparison with other related compounds.

Ariadne, also known chemically as 4C-D or 4C-DOM, by its developmental code name BL-3912, and by its former tentative brand name Dimoxamine, is a little-known psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and phenylisobutylamine families. It is a homologue of the psychedelics 2C-D and DOM.

2,5-Dimethoxy-4-propylamphetamine (DOPR) is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, and was described in his book PiHKAL. Shulgin described DOPR as a "heavy duty psychedelic", complete with alterations of the thought process and visual distortion. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of DOPR.
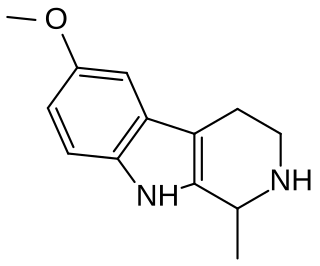
6-MeO-THH, or 6-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroharman, is a β-carboline derivative and a structural isomer of tetrahydroharmine (7-MeO-THH). 6-MeO-THH is mentioned in Alexander Shulgin's book TiHKAL, stating that 6-MeO-THH is very similar to the other carbolines. Limited testing suggests that it possesses mild psychoactive effects at 1.5 mg/kg and is said to be about one-third as potent as 6-methoxyharmalan. It has been isolated from certain plants of the Virola family.

Substituted phenethylamines are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure; the class is composed of all the derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents.

5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole is an indole and phenethylamine derivative with empathogenic effects. Its preparation was first reported by Albert Hofmann in 1962. It is a designer drug that has been openly sold as a recreational drug by online vendors since 2011.
Substituted amphetamines, or simply amphetamines, are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, tranylcypromine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).

2,5-Dimethoxy-4-fluoroamphetamine (DOF) is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes. Alexander Shulgin briefly describes DOF in his book PiHKAL:
Animal studies that have compared DOF to the highly potent DOI and DOB imply that the human activity will be some four to six times less than these two heavier halide analogues.

4-Substituted-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamines (DOx) is a chemical class of substituted amphetamine derivatives featuring methoxy groups at the 2- and 5- positions of the phenyl ring, and a substituent such as alkyl or halogen at the 4- position of the phenyl ring. Most compounds of this class are potent and long-lasting psychedelic drugs, and act as highly selective 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptor partial agonists. A few bulkier derivatives such as DOAM have similarly high binding affinity for 5-HT2 receptors but instead act as antagonists, and so do not produce psychedelic effects though they retain amphetamine-like stimulant effects.

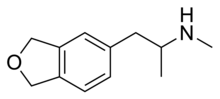
5-MAPDB (1-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-N-methylpropan-2-amine) is a chemical compound which acts as an entactogenic drug. It is structurally related to drugs like 5-APDB and 5-MAPB, which have similar effects to MDMA and have been used as recreational drugs. 5-MAPDB has been studied to determine its pharmacological activity, and was found to be a relatively selective serotonin releaser, though with weaker actions as a releaser of other monoamines and 5-HT2 receptor family agonist, similar to older compounds such as 5-APDB.
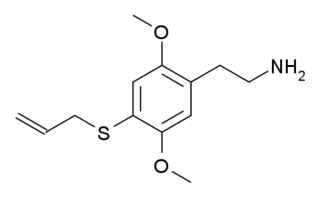
2C-T-16 is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It was originally named by Alexander Shulgin as described in his book PiHKAL, however while Shulgin began synthesis of this compound he only got as far as the nitrostyrene intermediate, and did not complete the final synthetic step. Synthesis of 2C-T-16 was finally achieved by Daniel Trachsel some years later, and it was subsequently reported as showing similar psychedelic activity to related compounds, with a dose range of 10–25 mg and a duration of 4–6 hours, making it around the same potency as the better-known saturated analogue 2C-T-7, but with a significantly shorter duration of action. Binding studies in vitro showed 2C-T-16 to have a binding affinity of 44 nM at 5-HT2A and 15 nM at 5-HT2C. 2C-T-16 and related derivatives are potent partial agonists of the 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors and induce a head-twitch response in mice.
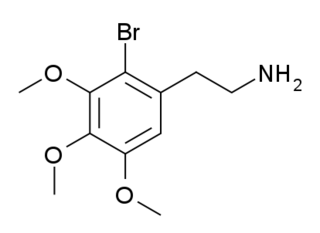
2-Bromomescaline (2-Br-M) is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen mescaline which has an unusual 2-bromo substitution. It is an agonist for serotonin receptors, with a binding affinity of 215 nM at 5-HT1A, 513 nM at 5-HT2A and 379 nM at 5-HT2C, so while it is around ten times more tightly binding than mescaline at 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors, it is over twenty times more potent at 5-HT2C. It has been reported as a designer drug, first identified in Austria in January 2023.

5-MAPDI is an entactogenic amphetamine derivative which is structurally related to MDMA as well as to dihydrobenzofuran derivatives such as 5-MAPDB and 6-MAPDB, and has been sold as a designer drug. It has reportedly been sold over grey-market websites since around 2014, although the first definitive identification was not made until September 2016 by a forensic laboratory in Slovenia.