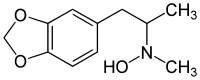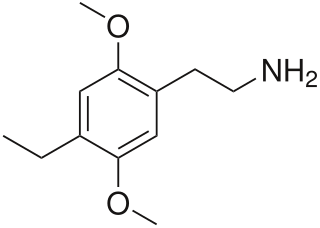
2C-E is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and documented in his book PiHKAL. Like the other substances in its family, it produces sensory and cognitive effects in its physical reactions with living organisms.

Dimethoxybromoamphetamine (DOB), also known as brolamfetamine (INN) and bromo-DMA, is a psychedelic drug and substituted amphetamine of the phenethylamine class of compounds. DOB was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1967. Its synthesis and effects are documented in Shulgin's book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story.

2C-N (2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenethylamine) is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.
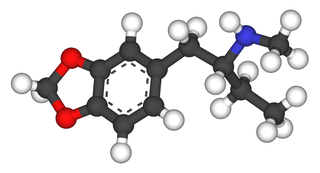
1,3-Benzodioxolyl-N-methylbutanamine (N-methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylbutanamine, MBDB, 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methyl-α-ethylphenylethylamine) is an entactogen of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is known by the street names Eden and Methyl-J. MBDB is a ring substituted amphetamine and an analogue of MDMA. Like MDMA, it has a methylene dioxy substitution at the 3 and 4 position on the aromatic ring; this is perhaps the most distinctive feature that structurally define analogues of MDMA, in addition to their unique effects, and as a class they are often referred to as "entactogens" to differentiate between typical psychostimulant amphetamines that (as a general rule) are not ring substituted. MBDB differs from MDMA by having an ethyl group instead of a methyl group attached to the alpha carbon; all other parts are identical. Modification at the alpha carbon is uncommon for substituted amphetamines. It has IC50 values of 784 nM against 5-HT, 7825 nM against dopamine, and 1233 nM against norepinephrine. Its metabolism has been described in scientific literature.

2C-T-15 or 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(β-cyclopropylthio)phenethylamine is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was presumably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book PiHKAL .
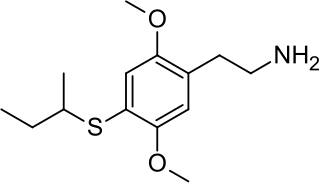
2C-T-17 or 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(β-secbutylthio)phenethylamine is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was presumably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book PiHKAL .
MDMEOET, or 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methoxyethylamphetamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. It is also the N-methoxyethyl analogue of MDA. MDMEOET was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the minimum dosage is listed as 180 mg. MDMEOET produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MDMEOET.

3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-methylphentermine is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. MDMP was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 110 mg, and the duration is listed as approximately 6 hours. MDMP produces few to no effects, and is slightly similar to MDMA. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MDMP.

3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-hydroxyamphetamine is an entactogen, psychedelic, and stimulant of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It is the N-hydroxy homologue of MDA, and the N-desmethyl homologue of MDHMA. MDOH was first synthesized and assayed by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, Shulgin listed the dosage range as 100–160 mg, and the duration as approximately 3–6 hours. He describes MDOH as being very psychedelic and producing increased pleasure in beauty and nature. He also mentioned several negative side effects also seen with MDMA ("Ecstasy") such as difficulty urinating and internal dryness.

2C-H (2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known substituted phenethylamine of the 2C family.

BOD (4-methyl-2,5,β-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the beta-methoxy analog of 2C-D and was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 15–25 mg with a duration of 8–16 hours. Its reported effects include mild open-eye and moderate closed-eye alterations in visual perception, enhancement of conversation and sense of humor, and unpleasant physical effects such as nausea and lethargy. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of BOD.

BOH, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-β-methoxyphenethylamine, is a drug of the phenethylamine class. It is the β-methoxy analog of methylenedioxyphenethylamine (MDPEA) and is also more distantly related to methylone. On account of its similarity to norepinephrine, the effects of BOH may be of a purely adrenergic nature.

BOHD (4-methyl-2,5-dimethoxy-beta-hydroxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the beta-hydroxy derivative of 2C-D. BOHD was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 50 mg, and the duration unknown. BOHD produces a marked drop in blood pressure. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of BOHD.

BOM (3,4,5,beta-tetramethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the beta-methoxy derivative of mescaline. BOM was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 200 mg, and the duration unknown. BOM produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about its pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity.

MDHOET, or 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-hydroxyethylamphetamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. It is also the N-hydroxyethyl analogue of MDA. MDHOET was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the minimum dosage is listed as 50 mg. MDHOET produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, effects, and toxicity of MDHOET.

N-Ethyl-1,3-benzodioxolylpentanamine is a psychoactive drug and member of the phenethylamine chemical class which acts as an entactogen, psychedelic, and stimulant. It is the N-ethyl analog of 1,3-benzodioxolylpentanamine. Ethyl-K was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 40 mg and the duration is unknown. Very little is known about the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, effects, and toxicity of Ethyl-K.

N-Methyl-2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine is a psychedelic drug of the amphetamine class. It is the N-methylated derivative of MMDA-2, and it is also an analog of MDMA and 6-methyl-MDA.
MDCPM, or 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-cyclopropylmethylamphetamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is the N-cyclopropylmethyl derivative of MDMA. MDCPM was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin; it is also one of the compounds delineated in a patent by Horrom in 1972. In his book PiHKAL , the minimum dosage is listed as 10 mg, and the duration unknown. MDCPM produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MDCPM.

3,4-Methylenedioxy-N,N-dimethylamphetamine (MDDM) is a lesser-known research chemical. It is also the N,N-dimethyl analog of 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA). MDDM was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL , the dosage is unspecified and the duration unknown. MDDM produces only mild effects that are not well characterized in PiHKAL. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of MDDM. This compound is however occasionally encountered as an impurity in 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine (MDMA) which has been synthesized by methylation of MDA using methylating reagents such as methyl iodide. An excess of reagent or a reaction temperature that is too high results in some double methylation of the amine nitrogen, yielding MDDM as well as MDMA. The presence of MDDM as an impurity can thus reveal which synthetic route was used to manufacture seized samples of MDMA.

N-Methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylpentanamine, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-α-propyl-N-methylphenethylamine, is a psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is the N-methyl analogue of 1,3-benzodioxolylpentanamine. Methyl-K was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the minimum dosage is listed as 100 mg, and the duration is unknown. Very little is known about the pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, effects, and toxicity of Methyl-K.