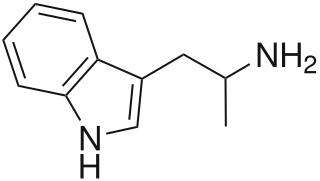
α-Methyltryptamine is a psychedelic, stimulant, and entactogen drug of the tryptamine class. It was originally developed as an antidepressant by workers at Upjohn in the 1960s, and was used briefly as an antidepressant in Russia under the trade name Indopan before being discontinued.

Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission.

5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

Iprindole, sold under the brand names Prondol, Galatur, and Tertran, is an atypical tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and Ireland for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. It was developed by Wyeth and was marketed in 1967. The drug has been described by some as the first "second-generation" antidepressant to be introduced. However, it was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.

Cyclopentamine is a sympathomimetic alkylamine, classified as a vasoconstrictor. Cyclopentamine was indicated in the past as an over-the-counter (OTC) medication for use as a nasal decongestant, notably in Europe and Australia, but has now been largely discontinued.

Desmetramadol (INN), also known as O-desmethyltramadol (O-DSMT), is an opioid analgesic and the main active metabolite of tramadol. Tramadol is demethylated by the liver enzyme CYP2D6 in the same way as codeine, and so similarly to the variation in effects seen with codeine, individuals who have a less active form of CYP2D6 will tend to get reduced analgesic effects from tramadol. This also results in a ceiling effect which limits tramadol's range of therapeutic benefits to the treatment of moderate pain.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptor, or 5-HT receptor, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarisation and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

8-OH-DPAT is a research chemical of the aminotetralin chemical class which was developed in the 1980s and has been widely used to study the function of the 5-HT1A receptor. It was one of the first major 5-HT1A receptor full agonists to be discovered.

Trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) is a trace amine-associated receptor (TAAR) protein that in humans is encoded by the TAAR1 gene. TAAR1 is an intracellular amine-activated Gs-coupled and Gq-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is primarily expressed in several peripheral organs and cells, astrocytes, and in the intracellular milieu within the presynaptic plasma membrane of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). TAAR1 was discovered in 2001 by two independent groups of investigators, Borowski et al. and Bunzow et al. TAAR1 is one of six functional human trace amine-associated receptors, which are so named for their ability to bind endogenous amines that occur in tissues at trace concentrations. TAAR1 plays a significant role in regulating neurotransmission in dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin neurons in the CNS; it also affects immune system and neuroimmune system function through different mechanisms.
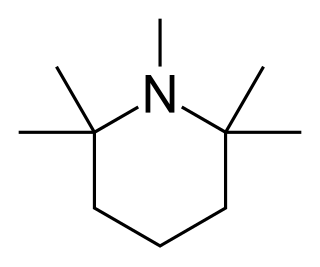
Pempidine is a ganglion-blocking drug, first reported in 1958 by two research groups working independently, and introduced as an oral treatment for hypertension.

BTS 74,398 is a centrally acting stimulant drug which was developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It inhibits the synaptic reuptake of dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline, making it a triple reuptake inhibitor. It was effective in animal models of Parkinson's disease, but was unsuccessful in human trials.

Ciclazindol (WY-23409) is an antidepressant and anorectic drug of the tetracyclic chemical class that was developed in the mid to late 1970s, but was never marketed. It acts as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, and to a lesser extent as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Ciclazindol has no effects on the SERT, 5-HT receptors, mACh receptors, or α-adrenergic receptors, and has only weak affinity for the H1 receptor. As suggested by its local anesthetic properties, ciclazindol may also inhibit sodium channels. It is known to block potassium channels as well.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a substituted amphetamine and monoamine releaser similar to MDMA, but with substantially higher neurotoxicity, thought to be due to the unrestrained release of both serotonin and dopamine by a metabolite. It is used as a neurotoxin by neurobiologists to selectively kill serotonergic neurons for research purposes, in the same way that 6-hydroxydopamine is used to kill dopaminergic neurons.

An adenosine reuptake inhibitor (AdoRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor for the purine nucleoside and neurotransmitter adenosine by blocking the action of one or more of the equilibrative nucleoside transporters (ENTs). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of adenosine and therefore an increase in adenosinergic neurotransmission.
A dopamine releasing agent (DRA) is a type of drug which induces the release of dopamine in the body and/or brain. No selective DRAs are currently known. Many releasing agents of both dopamine and norepinephrine and of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine are known, however. Serotonin–dopamine releasing agents are much rarer and are not selective for monoamine release. Examples of NDRAs include amphetamine and methamphetamine, and an example of an SNDRA is MDMA. The most selective dopamine releaser is 4-methylaminorex, but it also has considerable activity as a norepinephrine releaser. These drugs are frequently used for recreational purposes and encountered as drugs of abuse.

Mepiprazole is an anxiolytic drug of the phenylpiperazine group with additional antidepressant properties that is marketed in Spain. It acts as a 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist and inhibits the reuptake and induces the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine to varying extents, and has been described as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). Controlled clinical trials of mepiprazole in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) were also carried out and suggested some benefits of the drug in relieving symptoms of IBS in some patients. Similarly to other phenylpiperazines like trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone, mepiprazole produces mCPP as an active metabolite.
A monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI) is a drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor of one or more of the three major monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine by blocking the action of one or more of the respective monoamine transporters (MATs), which include the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT). This in turn results in an increase in the synaptic concentrations of one or more of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in monoaminergic neurotransmission.
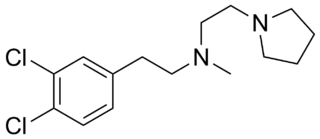
BD1008 or N-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-N-methyl-1-pyrrolidineethanamine is a selective sigma receptor antagonist, with a reported binding affinity of Ki = 2 ± 1 nM for the sigma-1 receptor and 4 times selectivity over the sigma-2 receptor.

para-Chloromethamphetamine is a stimulant that is the N-methyl derivative and prodrug of the neurotoxic drug para-chloroamphetamine (4-CA). It has been found to decrease serotonin in rats. Further investigation into the long-term effects of chloroamphetamines discovered that administration of 4-CMA caused a prolonged reduction in the levels of serotonin and the activity of tryptophan hydroxylase in the brain one month after injection of a single dose of the drug.

















