
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly known as ecstasy, and molly or mandy, is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant and minor psychedelic properties, primarily used for recreational purposes. The purported pharmacological effects that may be prosocial include altered sensations, increased energy, empathy, and pleasure. When taken by mouth, effects begin in 30 to 45 minutes and last three to six hours.

PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story is a book by Dr. Alexander Shulgin and Ann Shulgin, published in 1991. The subject of the work is psychoactive phenethylamine chemical derivatives, notably those that act as psychedelics and/or empathogen-entactogens. The main title, PiHKAL, is an acronym that stands for "Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved."
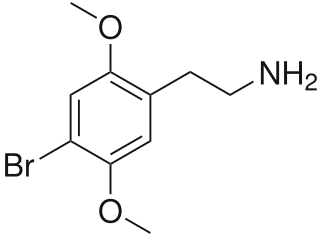
2C-B (4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a synthetic psychedelic drug of the 2C family, initially synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1974 and commonly used as a recreational drug. There is limited scientific information regarding the drug's pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects in humans. The existing studies primarily classify 2C-B as a stimulant, and hallucinogen, and less commonly as an entactogen, and empathogen.

2,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine is a psychedelic and a substituted amphetamine. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, and later reported in his book PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. DOM is classified as a Schedule I substance in the United States, and is similarly controlled in other parts of the world. Internationally, it is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. It is generally taken orally.

3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine is an empathogen-entactogen, psychostimulant, and psychedelic drug of the amphetamine family that is encountered mainly as a recreational drug. In its pharmacology, MDA is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). In most countries, the drug is a controlled substance and its possession and sale are illegal.

para-Methoxyamphetamine (PMA), also known as 4-methoxyamphetamine (4-MA), is a designer drug of the amphetamine class with serotonergic effects. Unlike other similar drugs of this family, PMA does not produce stimulant, euphoriant, or entactogen effects, and behaves more like an antidepressant in comparison, though it does have some psychedelic properties.
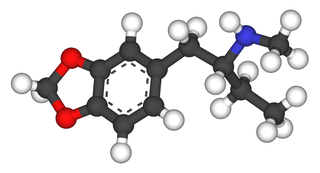
1,3-Benzodioxolyl-N-methylbutanamine (N-methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylbutanamine, MBDB, 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methyl-α-ethylphenylethylamine) is an entactogen of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is known by the street names Eden and Methyl-J. MBDB is a ring substituted amphetamine and an analogue of MDMA. Like MDMA, it has a methylene dioxy substitution at the 3 and 4 position on the aromatic ring; this is perhaps the most distinctive feature that structurally define analogues of MDMA, in addition to their unique effects, and as a class they are often referred to as "entactogens" to differentiate between typical psychostimulant amphetamines that (as a general rule) are not ring substituted. MBDB differs from MDMA by having an ethyl group instead of a methyl group attached to the alpha carbon; all other parts are identical. Modification at the alpha carbon is uncommon for substituted amphetamines. It has IC50 values of 784 nM against 5-HT, 7825 nM against dopamine, and 1233 nM against norepinephrine. Its metabolism has been described in scientific literature.
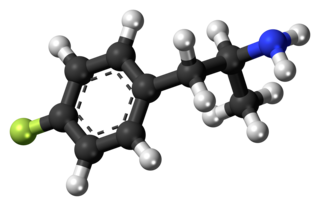
4-Fluoroamphetamine, also known as para-fluoroamphetamine (PFA) is a psychoactive research chemical of the phenethylamine and substituted amphetamine chemical classes. It produces stimulant and entactogenic effects. As a recreational drug, 4-FA is sometimes sold along with related compounds such as 2-fluoroamphetamine and 4-fluoromethamphetamine.

MMDA is a psychedelic and entactogen drug of the amphetamine class. It is an analogue of lophophine, MDA, and MDMA.

4-Methylthioamphetamine (4-MTA) is a designer drug of the substituted amphetamine class developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols, an American pharmacologist and medical chemist, at Purdue University. It acts as a non-neurotoxic highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) in animals. 4-MTA is the methylthio derivative of amphetamine.

1,3-Benzodioxolylbutanamine is an entactogenic drug of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is the α-ethyl analog of MDPEA and MDA and the methylenedioxy analogue of α-ethylphenethylamine.

4'-Methoxy-α-pyrrolidinopropiophenone (MOPPP) is a stimulant designer drug of the pyrrolidinophenone class. It has the potential to produce euphoria, an effect shared with other classical stimulants.

MDAI (5,6-methylenedioxy-2-aminoindane) is a drug developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It acts as a non-neurotoxic and highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) in vitro and produces entactogen effects in humans.

3-Methoxy-4-methylamphetamine (MMA) is an entactogen and psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes. It was first synthesized in 1970 and was encountered as a street drug in Italy in the same decade. MMA was largely forgotten until being reassayed by David E. Nichols as a non-neurotoxic MDMA analogue in 1991, and has subsequently been sold as a designer drug on the internet since the late 2000s (decade).
A serotonin releasing agent (SRA) is a type of drug that induces the release of serotonin into the neuronal synaptic cleft. A selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) is an SRA with less significant or no efficacy in producing neurotransmitter efflux at other types of monoamine neurons.
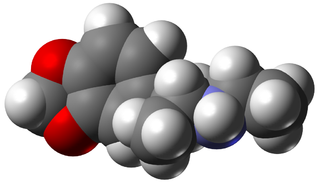
3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-ethylamphetamine is an empathogenic psychoactive drug. MDEA is a substituted amphetamine and a substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamine. MDEA acts as a serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine releasing agent and reuptake inhibitor.

meta-Methoxyamphetamine (MMA), also known as 3-methoxyamphetamine (3-MA), is a stimulant drug from the amphetamine family. It has similar effects in animal drug discrimination tests to the more widely known derivative 4-methoxyamphetamine (PMA), although with a slightly different ratio of monoamine release, being a combined serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine releasing agent rather than a fairly selective serotonin releaser like PMA. 3-Methoxyamphetamine has similarly appeared on the illicit market as a designer drug alternative to MDMA, although far more rarely than its infamous positional isomer. It produces gepefrine, a cardiac stimulant, as one of its major metabolites.
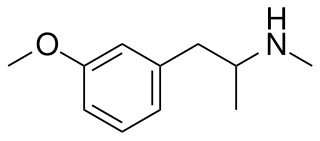
3-Methoxymethamphetamine, which is most closely related to 3-methoxyamphetamine and PMMA and shares similar monoamine releasing effects, although its effects have not been studied so extensively as other related drugs. It is an agonist of human TAAR1.
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, tranylcypromine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP).


















