
A steel guitar is any guitar played while moving a steel bar or similar hard object against plucked strings. The bar itself is called a "steel" and is the source of the name "steel guitar". The instrument differs from a conventional guitar in that it is played without using frets; conceptually, it is somewhat akin to playing a guitar with one finger. Known for its portamento capabilities, gliding smoothly over every pitch between notes, the instrument can produce a sinuous crying sound and deep vibrato emulating the human singing voice. Typically, the strings are plucked by the fingers of the dominant hand, while the steel tone bar is pressed lightly against the strings and moved by the opposite hand.

Sitting is a basic action and resting position in which the body weight is supported primarily by the bony ischial tuberosities with the buttocks in contact with the ground or a horizontal surface such as a chair seat, instead of by the lower limbs as in standing, squatting or kneeling. When sitting, the torso is more or less upright, although sometimes it can lean against other objects for a more relaxed posture.

A sex position is a positioning of the bodies that people use to engage in sexual intercourse or other sexual activities. Sexual acts are generally described by the positions the participants adopt in order to perform those acts. Though sexual intercourse generally involves penetration of the body of one person by another, sex positions commonly involve non-penetrative sexual activities.
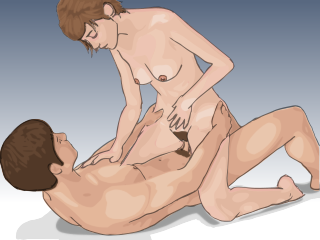
Woman on top is any sex position in which the woman is on top of her sexual partner during sexual activity. The position most commonly associated with the woman on top is often called the cowgirl or riding position, which derives its name from the image of the woman "riding" the man as a cowgirl rides a bucking horse. In that position, a man typically lies on his back with his legs closed, while the female partner straddles him, usually in a kneeling position facing either forward or back, and either the man or woman inserts the man's erect penis into the woman's vagina or anus. The cowgirl position is commonly cited as one of the more popular sex positions, especially by women, because it gives them control over the rhythm and pace of vaginal stimulation and the extent and duration of penetration and because of its ability to adequately stimulate the clitoris. There are other positions in which the woman may be on top, including the 69 position and the pompoir sex position.

A chair is a type of seat, typically designed for one person and consisting of one or more legs, a flat or slightly angled seat and a back-rest. It may be made of wood, metal, or synthetic materials, and may be padded or upholstered in various colors and fabrics.

The dholak is a two-headed hand drum, a folk percussion instrument. The dholak is most commonly recognised in countries such as India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka, but can also be found amongst the Indo-Diaspora in countries such as Guyana, Suriname, Fiji, Trinidad and Tobago, South Africa and Mauritius. The dholak can be anywhere about 16" to 24" in length. It is widely used in qawwali, kirtan, bhajan, bhangra, chutney, baithak gana, Bollywood film songs, lokgeet and various classical styles such as Hindustani, Carnatic and Trinidadian local classical / Guyanese taan. The drum has two different sized drumheads. There is a smaller drumhead that can be from 5.5 to 8 inches in diameter and is made for sharp notes while the bigger drumhead, which can be from 7.5 to 10 inches in diametre, is made for low pitch. The two drumheads allow a combination of bass and treble with rhythmic high and low pitches. The body or shell of the Dholak can made of sheesham or mango wood. The larger drum head has a compound of tar, clay and sand, called "masala" which is applied to lower the pitch and produce the sound. The smaller drumhead is played with the person's dominant hand, while the larger is played by the person's weaker hand. A dholak can either be fitted with a nuts and bolts or a rope and steel rings for tuning. Commonly in the Indian subcontinent, there are only one set of rings for tuning the treble side of the dholak, while in the Caribbean, hook screws are placed into the sides of the dholak to allow tuning of both the treble and the bass. Dholak can be played in three ways — on the player’s lap, while standing, or pressed down with one knee while sitting on the floor.

A desk or bureau is a piece of furniture with a flat table-style work surface used in a school, office, home or the like for academic, professional or domestic activities such as reading, writing, or using equipment such as a computer. Desks often have one or more drawers, compartments, or pigeonholes to store items such as office supplies and papers. Desks are usually made of wood or metal, although materials such as glass are sometimes seen.

The pedal steel guitar is a console-type of steel guitar with pedals and knee levers that change the pitch of certain strings to enable playing more varied and complex music than other steel guitar designs. Like all steel guitars, it can play unlimited glissandi and deep vibrati—characteristics it shares with the human voice. Pedal steel is most commonly associated with Country music and Hawaiian music.

The lap steel guitar, also known as a Hawaiian guitar or Lap Slide Guitar, is a type of steel guitar without pedals that is typically played with the instrument in a horizontal position across the performer's lap. Unlike the usual manner of playing a traditional acoustic guitar, in which the performer's fingertips press the strings against frets, the pitch of a steel guitar is changed by pressing a polished steel bar against plucked strings. Though the instrument does not have frets, it displays markers that resemble them. Lap steels may differ markedly from one another in external appearance, depending on whether they are acoustic or electric, but in either case, do not have pedals, distinguishing them from pedal steel guitars.
To assume a brace position or crash position is an instruction that can be given to prepare for a crash, such as on an aircraft; the instruction to "Brace for impact!" or "Brace! Brace!" is often given if the aircraft must make an emergency landing on land or water. There are many different ways to adopt the brace position, with many countries adopting their own version based on research performed by their own aviation authority or that of other countries. The most common in passenger airliners being the forward-facing seat version, in which the person bracing places their head against or as close as possible to the surface it is likely to strike, placing their feet firmly on the floor, and their hands either on their head or the seat in front.

English saddles are used to ride horses in English riding disciplines throughout the world. The discipline is not limited to England, the United Kingdom in general or other English-speaking countries. This style of saddle is used in all of the Olympic and International Federation for Equestrian Sports (FEI) equestrian disciplines, except for the newly approved FEI events of equestrian vaulting and reining. Most designs were specifically developed to allow the horse freedom of movement, whether jumping, running, or moving quickly across rugged, broken country with fences. Unlike the western saddle or Australian Stock Saddle, there is no horn or other design elements that stick out above the main tree of the saddle.

A child safety seat, sometimes called an infant safety seat, child restraint system, child seat, baby seat, car seat, or a booster seat, is a seat designed specifically to protect children from injury or death during vehicle collisions. Most commonly these seats are purchased and installed by car owners, but car manufacturers may integrate them directly into their vehicle's design and generally are required to provide anchors and ensure seat belt compatibility. Many jurisdictions require children defined by age, weight, and/or height to use a government-approved child safety seat when riding in a vehicle. Child safety seats provide passive restraints and must be properly used to be effective. However, research indicates that many child safety restraints are often not installed or used properly. To tackle this negative trend, health officials and child safety experts produce child safety videos to teach proper car seat installation to parents and caregivers.

Static trapeze, also known as fixed trapeze, is a type of circus apparatus. In contrast to the other forms of trapeze, static trapeze the bars and ropes mainly stay in place.
Child development stages are the theoretical milestones of child development, some of which are asserted in nativist theories. This article discusses the most widely accepted developmental stages in children. There exists a wide variation in terms of what is considered "normal", caused by variations in genetic, cognitive, physical, family, cultural, nutritional, educational, and environmental factors. Many children reach some or most of these milestones at different times from the norm.

'Twas the Night is a 2001 American Christmas fantasy comedy film that was released as a Disney Channel Original Movie It was directed by Nick Castle and stars Josh Zuckerman, Brenda Grate, Bryan Cranston and Jefferson Mappin. It was first aired in December 2001 for the Christmas holiday.

Playground slides are found in parks, schools, playgrounds and backyards. The slide is an example of the simple machine known as the inclined plane, which makes moving objects up and down easier, or in this case more fun. The slide may be flat, or half cylindrical or tubular to prevent falls. Slides are usually constructed of plastic or metal and they have a smooth surface that is either straight or wavy. The user, typically a child, climbs to the top of the slide via a ladder or stairs and sits down on the top of the slide and slides down the chute.

Squatting is a versatile posture where the weight of the body is on the feet but the knees and hips are bent. In contrast, sitting involves supporting the weight of the body on the ischial tuberosities of the pelvis, with the lower buttocks in contact with the ground or a horizontal object. The angle between the legs when squatting can vary from zero to widely splayed out, flexibility permitting. Another variable may be the degree of forward tilt of the upper body from the hips. Squatting may be either full or partial.
Kniereitvers is a nursery rhyme that is recited while two people play. Usually an older person plays with a younger one, with the child sitting on the older person's knee.















