
Zosuquidar is an experimental antineoplastic drug. Zosquidir inhibits P-glycoproteins. Other drugs with this mechanism include tariquidar and laniquidar. P-glycoproteins are trans-membrane proteins that pump foreign substances out of cells in an ATP dependent fashion. Cancers overexpressing P-glycoproteins are able to pump out therapeutic molecules before they are able to reach their target, effectively making the cancer multi-drug resistant. Zosuquidar inhibits P-glycoproteins, inhibiting the efflux pump and restoring sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents.
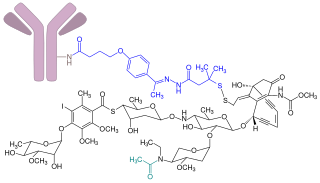
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Mylotarg, is an antibody-drug conjugate that is used to treat acute myeloid leukemia.

Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated.
The interleukin-3 receptor (CD123) is a molecule found on cells which helps transmit the signal of interleukin-3, a soluble cytokine important in the immune system.

Inotuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Besponsa, is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Epratuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody. Potential uses may be found in oncology and in treatment of inflammatory autoimmune disorders, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).

CD33 or Siglec-3 is a transmembrane receptor expressed on cells of myeloid lineage. It is usually considered myeloid-specific, but it can also be found on some lymphoid cells.

Lestaurtinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor structurally related to staurosporine. This semisynthetic derivative of the indolocarbazole K252a was investigated by Cephalon as a treatment for various types of cancer. It is an inhibitor of the kinases fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), tropomyosin receptor kinase (trk) A (TrkA), TrkB and TrkC.

Omacetaxine mepesuccinate, formerly named as homoharringtonine or HHT, is a pharmaceutical drug substance that is indicated for treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
Brentuximab vedotin, sold under the brand name Adcetris, is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), a type of T cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It selectively targets tumor cells expressing the CD30 antigen, a defining marker of Hodgkin lymphoma and ALCL. The drug is being jointly marketed by Millennium Pharmaceuticals outside the US and by Seagen in the US.

Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) is a synthetic antineoplastic agent. Because of its toxicity, it cannot be used as a drug itself; instead, it is linked to a monoclonal antibody (MAB) which directs it to the cancer cells. In International Nonproprietary Names for MMAE-MAB-conjugates, the name vedotin refers to MMAE plus its linking structure to the antibody. It is a potent antimitotic drug derived from peptides occurring in marine shell-less mollusc Dolabella auricularia called dolastatins which show potent activity in preclinical studies, both in vitro and in vivo, against a range of lymphomas, leukemia and solid tumors. These drugs show potency of up to 200 times that of vinblastine, another antimitotic drug used for Hodgkin lymphoma as well as other types of cancer.

Midostaurin, sold under the brand name Rydapt & Tauritmo both by Novartis, is a multi-targeted protein kinase inhibitor that has been investigated for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and advanced systemic mastocytosis. It is a semi-synthetic derivative of staurosporine, an alkaloid from the bacterium Streptomyces staurosporeus.
Vorsetuzumab mafodotin (SGN-75) is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) directed to the protein CD70 designed for the treatment of cancer. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody, vorsetuzumab, conjugated with noncleavable monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), a cytotoxic agent.

Vadastuximab talirine is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) directed to CD33 (siglec-3) which is a transmembrane receptor expressed on cells of myeloid lineage. The experimental drug, being developed by Seattle Genetics, was in clinical trials for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Seagen Inc. is an American biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing innovative, empowered monoclonal antibody-based therapies for the treatment of cancer. The company, headquartered in Bothell, Washington, is the industry leader in antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs, a technology designed to harness the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies to deliver cell-killing agents directly to cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugates are intended to spare non-targeted cells and thus reduce many of the toxic effects of traditional chemotherapy, while potentially enhancing antitumor activity.
FLAG is a chemotherapy regimen used for relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The acronym incorporates the three primary ingredients of the regimen:
- Fludarabine: an antimetabolite that, while not active toward AML, increases formation of an active cytarabine metabolite, ara-CTP, in AML cells;
- Arabinofuranosyl cytidine : an antimetabolite that has been proven to be the most active toward AML among various cytotoxic drugs in single-drug trials; and
- Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): a glycoprotein that shortens the duration and severity of neutropenia.

Venetoclax, sold under the brand names Venclexta and Venclyxto, is a medication used to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), or acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Denintuzumab mafodotin is a humanized monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of CD19-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It consists of an anti-CD19 mAb linked to monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), a cytotoxic agent. This drug was developed by Seattle Genetics.

Glasdegib, sold under the brand name Daurismo, is a medication for the treatment of newly-diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in adults older than 75 years or those who have comorbidities that preclude use of intensive induction chemotherapy. It is taken by mouth and is used in combination with low-dose cytarabine.
Camidanlumab tesirine is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) composed of a human antibody that binds to the protein CD25, conjugated to a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer toxin. The experimental drug, developed by ADC Therapeutics is being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of B-cell Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).










