Cancer immunotherapy is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology and a growing subspecialty of oncology.
Adecatumumab (MT201) is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody which is used to target tumor cells. It binds to the epithelial cell adhesion molecule, with the intent to trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. It was developed by Micromet Inc, which was acquired by Amgen.

Bivatuzumab mertansine is a combination of bivatuzumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, and mertansine, a cytotoxic agent. It is designed for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma.
Cantuzumab is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancers. Also known as huC242 it binds the CanAg antigen.
Epratuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody. Potential uses may be found in oncology and in treatment of inflammatory autoimmune disorders, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Etaracizumab, also known as MEDI-522, trade name Abegrin, is a humanized monoclonal antibody which is being investigated for the treatment of metastatic melanoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer and various other types of cancer. It is manufactured by MedImmune.

Mertansine, also called DM1, is a thiol-containing maytansinoid that for therapeutic purposes is attached to a monoclonal antibody through reaction of the thiol group with a linker structure to create an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC).

Maitansine (INN), or maytansine (USAN), is a cytotoxic agent. It inhibits the assembly of microtubules by binding to tubulin at the rhizoxin binding site.
Glembatumumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) that targets cancer cells expressing transmembrane glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB).
Peptide-based synthetic vaccines are subunit vaccines made from peptides. The peptides mimic the epitopes of the antigen that triggers direct or potent immune responses. Peptide vaccines can not only induce protection against infectious pathogens and non-infectious diseases but also be utilized as therapeutic cancer vaccines, where peptides from tumor-associated antigens are used to induce an effective anti-tumor T-cell response.

Trastuzumab emtansine, sold under the brand name Kadcyla, is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) covalently linked to the cytotoxic agent DM1. Trastuzumab alone stops growth of cancer cells by binding to the HER2 receptor, whereas trastuzumab emtansine undergoes receptor-mediated internalization into cells, is catabolized in lysosomes where DM1-containing catabolites are released and subsequently bind tubulin to cause mitotic arrest and cell death. Trastuzumab binding to HER2 prevents homodimerization or heterodimerization (HER2/HER3) of the receptor, ultimately inhibiting the activation of MAPK and PI3K/AKT cellular signalling pathways. Because the monoclonal antibody targets HER2, and HER2 is only over-expressed in cancer cells, the conjugate delivers the cytotoxic agent DM1 specifically to tumor cells. The conjugate is abbreviated T-DM1.

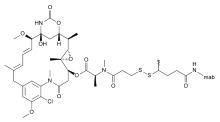
Lorvotuzumab mertansine (IMGN901) is an antibody-drug conjugate. It comprises the CD56-binding antibody, lorvotuzumab (huN901), with a maytansinoid cell-killing agent, DM1, attached using a disulfide linker, SPP.
Urelumab is a fully human, non‐ligand binding, CD137 agonist immunoglobulin‐γ 4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody. It was developed utilizing Medarex's UltiMAb(R) technology by Bristol-Myers Squibb for the treatment of cancer and solid tumors. Urelumab promotes anti-tumor immunity, or an immune response against tumor cells, via CD137 activation. The application of Urelumab has been limited due to the fact that it can cause severe liver toxicity.

Cantuzumab ravtansine (huC242-SPDB-DM4) is an antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of cancers. The humanized monoclonal antibody cantuzumab (huC242) is linked to a cytotoxic agent, ravtansine (DM4). It uses a more hindered disulfide linkage than cantuzumab mertansine.
ImmunoGen, Inc. is a biotechnology company focused on the development of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) therapeutics for the treatment of cancer. ImmunoGen was founded in 1981 and is headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts.

Isatuximab, sold under the brand name Sarclisa, is a monoclonal antibody (mAb) medication for the treatment of multiple myeloma.

Immune checkpoints are regulators of the immune system. These pathways are crucial for self-tolerance, which prevents the immune system from attacking cells indiscriminately. However, some cancers can protect themselves from attack by stimulating immune checkpoint targets.
The immune-related response criteria (irRC) is a set of published rules that define when tumors in cancer patients improve ("respond"), stay the same ("stabilize"), or worsen ("progress") during treatment, where the compound being evaluated is an immuno-oncology drug. Immuno-oncology, part of the broader field of cancer immunotherapy, involves agents which harness the body's own immune system to fight cancer. Traditionally, patient responses to new cancer treatments have been evaluated using two sets of criteria, the WHO criteria and the response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST). The immune-related response criteria, first published in 2009, arose out of observations that immuno-oncology drugs would fail in clinical trials that measured responses using the WHO or RECIST Criteria, because these criteria could not account for the time gap in many patients between initial treatment and the apparent action of the immune system to reduce the tumor burden.
Stable isotope standards and capture by anti-peptide antibodies (SISCAPA) is a mass spectrometry method for measuring the amount of a protein in a biological sample.
Dostarlimab, sold under the brand name Jemperli, is a monoclonal antibody used as an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of endometrial cancer. Dostarlimab is a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)–blocking monoclonal antibody.