
This is a list of barrages and headworks in Pakistan .

This is a list of barrages and headworks in Pakistan .
| Picture | Name | River | Year completed | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Munda Headworks | Swat | 1931 | [1] |
| Picture | Name | River | Year completed | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Balloki Headworks | Ravi | 1915 1966 (remodeling) | [2] |
 | Chashma Barrage | Indus | 1971 | [3] |
 | Ghazi Brotha Barrage | Indus | 2004 | [4] |
 | Islam Headworks | Sutlej | 1927 | [5] |
 | Jinnah Barrage | Indus | 1946 | [6] [7] |
 | Khanki Headworks | Chenab | 1892 2017 (replaced by the New Khanki Barrage) | [8] [9] [10] |
| Marala Headworks | Chenab | 1912 (as Marala weir) 1968 (replaced by Marala Barrage) | [11] | |
| Mohammadwala Headworks | Chenab | |||
 | Panjnad Headworks | Chenab | 1932 | [12] |
 | Qadirabad Headworks | Chenab | 1967 | [13] |
 | Rasul Barrage | Jhelum | 1968 | [14] |
 | Sidhnai Headworks | Ravi | 1965 | |
 | Sulemanki Headworks | Sutlej | 1927 | |
 | Taunsa Barrage | Indus | 1958 | [15] [16] |
 | Trimmu Barrage | Chenab | 1939 | [17] |
| Picture | Name | River | Year completed | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Guddu Barrage | Indus | 1962 | [18] |
 | Kotri Barrage | 1955 | [19] [18] | |
 | Sukkur Barrage | 1932 | [18] | |
| Sindh Barrage | December 2024 (expected) | [20] [21] |

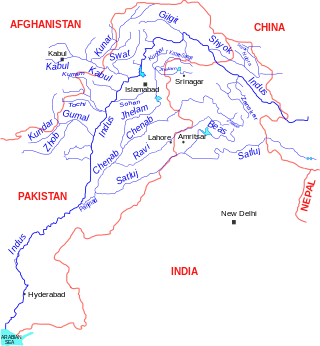
The Indus is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The 3,120 km (1,940 mi) river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, bends sharply to the left after the Nanga Parbat massif, and flows south-by-southwest through Pakistan, before emptying into the Arabian Sea near the port city of Karachi.


The Chenab River is a major river that flows in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul region of Himachal Pradesh, India. The Chenab flows through the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, India into the plains of Punjab, Pakistan, before ultimately flowing into the Indus River.

Panjnad Headworks is located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is a beautiful picnic spot and an agricultural area near Uch, Bahawalpur and it is where all the five rivers of Punjab merge.

Sukkur Barrage is a barrage on the River Indus near the city of Sukkur in the Sindh province of Pakistan. The barrage was built during the British Raj from 1923 to 1932 and was named Lloyd Barrage. The Sukkur Barrage, is the pride of Pakistan's irrigation system as it is the largest single irrigation network of its kind in the world. It irrigates from Sukkur district in the north, to Mirpurkhas/Tharparkar and Hyderabad districts in the south of Sindh, almost all parts of the province. It is situated about 500 kilometres northeast of Karachi, 5 kilometres below the railway bridge, or the Sukkur Gorge. The introduction of barrage-controlled irrigation system resulted in more timely water supplies for the existing cultivated areas of Sindh province of Pakistan.
The Indus Water Treaty (IWT) is a water-distribution treaty between India and Pakistan, arranged and negotiated by the World Bank, to use the water available in the Indus River and its tributaries. It was signed in Karachi on 19 September 1960 by then Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and then Pakistani president Ayub Khan.

Guddu Barrage is a barrage on the Indus River near Kashmore in the Sindh province of Pakistan. President Iskander Mirza laid the foundation-stone of Guddu Barrage on 2 February 1957. The barrage was completed in 1962 at a cost of 474.8 million rupees and inaugurated by Field Marshal Ayub Khan in 1962.

Head Taunsa Barrage is a barrage on the River Indus in Taunsa district of previously Dera Ghazi Khan District, Punjab province of Pakistan. It is situated 20 kilometres southeast of Taunsa Sharif and 16 kilometres from district Kot Addu. This barrage controls water flow in the River Indus for irrigation and flood control purposes. Taunsa Barrage was designated a Ramsar site on 22 March 1996.

Trimmu Barrage is a barrage on the River Chenab in the Jhang District of the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is situated downstream of the confluence of the River Jhelum and River Chenab. It is situated some 25 km from the city of Jhang near the city of Atharan Hazari where the River Jhelum flows into the River Chenab. It was one of the 7 link canals to be built under the Indus Water Plan of Pakistan. Pakistan created this plan after Indus Water Treaty
Khanki Headworks is a headworks situated on the River Chenab in Gujranwala District of the Punjab province of Pakistan. The construction of this headworks was completed in 1889 and was one of the oldest headworks in Pakistan.
The Lower Chenab Canal is a canal in Pakistan. It was dug in 1892 and originates from Khanki Headworks, which is situated on the River Chenab in Gujranwala District.

Marala Headworks is a headworks situated on the Chenab River near the city of Sialkot in Punjab, Pakistan. A weir was first built during 1906–1912 in the British India to feed the Upper Chenab Canal, as part of the 'Triple Canals Project'. A new Marala Barrage was constructed in 1968 to feed the Marala–Ravi Link Canal in addition to the original Upper Chenab Canal.

The Islam Headworks, commonly known as Head Islam, is a headworks on the River Sutlej in Hasilpur Tehsil of the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is used for irrigation and flood control.
Rasul Barrage is a barrage on the River Jehlum between Jhelum District and Mandi Bahauddin District of the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is situated 72 km downstream of Mangla Dam.
Sulemanki Headworks is a headworks on the River Sutlej near Okara, in the Punjab province of Pakistan.

Kotri Barrage, also known as the Ghulam Muhammad Barrage, is a barrage on the Indus River between Jamshoro and Hyderabad in the Sindh province of Pakistan. The barrage was completed in 1955 and was inaugurated by Ghulam Muhammad. It is used to control water flow in the Indus for irrigation and flood control purposes.
Madhopur Headworks is a barrage on the Ravi River, just 14km from Pathankot city in Pathankot district in the Indian state of Punjab. It is located on the border with Jammu and Kashmir. The Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC) off-taking from Madhopur irrigates agricultural lands in Punjab and provides water to the cities of Pathankot, Gurdaspur, Batala and Amritsar.
Jalalpur Canal or Jalalpur Irrigation Project (JIP) جلالپور آبپاشی منصوبہ is proposed for the northern bank of the Jhelum River from Rasul Barrage / Rasul Headworks to up until Khushāb. It will also irrigate the uncultivated lands of Pind Dadan Khan.

Punjab Irrigation Department, Pakistan, is a provincial irrigation department in the Punjab province of Pakistan. Punjab Irrigation Department irrigates 21 million acres (8,500,000 ha) of agricultural land in Punjab. Rai Manzoor Nasir, Secretary to the government of the Punjab, is the administrative head of the department.