The list of climate change controversies (or list of global warming controversies) concerns past or present public debates over certain aspects of climate change: whether it is occurring (climate change deniers dispute this), how much has occurred in modern times, what has caused it, what its effects will be, whether action should be taken to curb it now or later, and so forth. In the scientific literature, there is a very strong consensus that global surface temperatures have increased in recent decades and that the trend is caused by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases. [1]
The controversies are, by now, mostly political rather than scientific: there is a scientific consensus that global warming is happening and is caused by human activity. [2] Public debates that also reflect scientific debate include estimates of how responsive the climate system might be to any given level of greenhouse gases (climate sensitivity). Disputes over the key scientific facts of global warming are more prevalent in the media than in the scientific literature, where such issues are treated as resolved, and such disputes are more prevalent in the United States and Australia than globally. [3] [4] [5]
There have been many debates around the details of climate change science. Climate change deniers and "skeptics" tend to cherry-pick data or studies, and then trump up any scientific discussions or apparent discrepancies that match with their agenda.[ citation needed ] Many of those apparent discrepancies have been reconciled in the meantime, climate models have become more accurate, the scientific consensus on climate change has strengthened and so forth. For example, climatologist Kevin E. Trenberth has published widely on the topic of climate variability and has exposed flaws in the publications of other scientists. [6] [7] [8]
For past debates and controversies on scientific details see for example:
There have been debates on the best responses to slow global warming, and their timing. The debates are around the specific actions for climate change mitigation and climate change adaptation, or climate action in general. See for example:

The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) established the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts to prepare IPCC reports. It draws the experts from nominations by governments and observer organizations. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work.

The temperature record of the last 2,000 years is reconstructed using data from climate proxy records in conjunction with the modern instrumental temperature record which only covers the last 170 years at a global scale. Large-scale reconstructions covering part or all of the 1st millennium and 2nd millennium have shown that recent temperatures are exceptional: the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report of 2007 concluded that "Average Northern Hemisphere temperatures during the second half of the 20th century were very likely higher than during any other 50-year period in the last 500 years and likely the highest in at least the past 1,300 years." The curve shown in graphs of these reconstructions is widely known as the hockey stick graph because of the sharp increase in temperatures during the last century. As of 2010 this broad pattern was supported by more than two dozen reconstructions, using various statistical methods and combinations of proxy records, with variations in how flat the pre-20th-century "shaft" appears. Sparseness of proxy records results in considerable uncertainty for earlier periods.

There is a strong scientific consensus that the Earth has been consistently warming since the start of the Industrial Revolution, and the rate of recent warming is largely unprecedented. This warming is mainly caused by the rapid increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) since 1750 from human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, cement production, and land use changes such as deforestation, with a significant supporting role from the other greenhouse gases such as methane and nitrous oxide. This human role in climate change is now considered "unequivocal" and "incontrovertible".

Kevin Edward Trenberth worked as a climate scientist in the Climate Analysis Section at the US National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). He was a lead author of the 1995, 2001 and 2007 IPCC assessment reports. He also played major roles in the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), for example in its Tropical Oceans Global Atmosphere program (TOGA), the Climate Variability and Predictability (CLIVAR) program, and the Global Energy and Water Exchanges (GEWEX) project.
The Summary for policymakers (SPM) is a summary of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports intended to aid policymakers. The form is approved line by line by governments: "Negotiations occur over wording to ensure accuracy, balance, clarity of message, and relevance to understanding and policy."

The IPCC Third Assessment Report (TAR), Climate Change 2001, is an assessment of available scientific and socio-economic information on climate change by the IPCC. Statements of the IPCC or information from the TAR were often used as a reference showing a scientific consensus on the subject of global warming. The Third Assessment Report (TAR) was completed in 2001 and consists of four reports, three of them from its Working Groups: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis; Working Group II: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; Working Group III: Mitigation; Synthesis Report. A number of the TAR's conclusions are given quantitative estimates of how probable it is that they are correct, e.g., greater than 66% probability of being correct. These are "Bayesian" probabilities, which are based on an expert assessment of all the available evidence.

False balance, known colloquially as bothsidesism, is a media bias in which journalists present an issue as being more balanced between opposing viewpoints than the evidence supports. Journalists may present evidence and arguments out of proportion to the actual evidence for each side, or may omit information that would establish one side's claims as baseless. False balance has been cited as a cause of misinformation.
The iris hypothesis was a hypothesis proposed by Richard Lindzen and colleagues in 2001 that suggested increased sea surface temperature in the tropics would result in reduced cirrus clouds and thus more infrared radiation leakage from Earth's atmosphere. His study of observed changes in cloud coverage and modeled effects on infrared radiation released to space as a result seemed to support the hypothesis. This suggested infrared radiation leakage was hypothesized to be a negative feedback in which an initial warming would result in an overall cooling of the surface.

In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices add to greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming.

The First Assessment Report (FAR) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was completed in 1990. It served as the basis of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). This report had effects not only on the establishment of the UNFCCC, but also on the first session of the Conference of the Parties (COP), held in Berlin in 1995. The executive summary of the WG I Summary for Policymakers report that said they were certain that emissions resulting from human activities are substantially increasing the atmospheric concentrations of the greenhouse gases, resulting on average in an additional warming of the Earth's surface. They calculated with confidence that CO2 had been responsible for over half the enhanced greenhouse effect.

Climate change denial is a form of science denial characterized by rejecting, refusing to acknowledge, disputing, or fighting the scientific consensus on climate change. Those promoting denial commonly use rhetorical tactics to give the appearance of a scientific controversy where there is none. Climate change denial includes unreasonable doubts about the extent to which climate change is caused by humans, its effects on nature and human society, and the potential of adaptation to global warming by human actions. To a lesser extent, climate change denial can also be implicit when people accept the science but fail to reconcile it with their belief or action. Several studies have analyzed these positions as forms of denialism, pseudoscience, or propaganda.

Willard Anthony Watts is an American blogger who runs Watts Up With That?, a climate change denial blog that opposes the scientific consensus on climate change. A former television meteorologist and current radio meteorologist, he is also founder of the Surface Stations project, a volunteer initiative to document the condition of U.S. weather stations. The Heartland Institute helped fund some of Watts' projects, including publishing a report on the Surface Stations project, and invited him to be a paid speaker at its International Conference on Climate Change from 2008 to 2014.
This is a list of climate change topics.
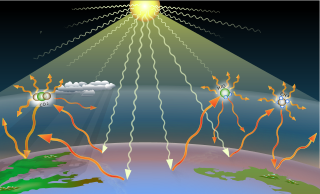
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. What distinguishes them from other gases is that they absorb the wavelengths of radiation that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F).

The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect was first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change Earth's energy balance and climate. The existence of the greenhouse effect, while not named as such, was proposed as early as 1824 by Joseph Fourier. The argument and the evidence were further strengthened by Claude Pouillet in 1827 and 1838. In 1856 Eunice Newton Foote demonstrated that the warming effect of the sun is greater for air with water vapour than for dry air, and the effect is even greater with carbon dioxide.

Climatic Research Unit documents including thousands of e-mails and other computer files were stolen from a server at the Climatic Research Unit of the University of East Anglia in a hacking incident in November 2009. The documents were redistributed first through several blogs of global warming deniers, who alleged that the documents indicated misconduct by leading climate scientists. A series of investigations rejected these allegations, while concluding that CRU scientists should have been more open with distributing data and methods on request. Precisely six committees investigated the allegations and published reports, finding no evidence of fraud or scientific misconduct. The scientific consensus that global warming is occurring as a result of human activity remained unchanged by the end of the investigations.
Watts Up With That? (WUWT) is a blog promoting climate change denial that was created by Anthony Watts in 2006.

Media coverage of climate change has had effects on public opinion on climate change, as it conveys the scientific consensus on climate change that the global temperature has increased in recent decades and that the trend is caused by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases.

Several factors cause the ocean temperature to vary. These are depth, geographical location and season. Both the temperature and salinity of ocean water differ. Warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters. In polar regions, the upper layers of ocean water are cold and fresh. Deep ocean water is cold, salty water found deep below the surface of Earth's oceans. This water has a uniform temperature of around 0-3 °C. The ocean temperature also depends on the amount of solar radiation falling on its surface. In the tropics, with the Sun nearly overhead, the temperature of the surface layers can rise to over 30 °C (86 °F). Near the poles the temperature in equilibrium with the sea ice is about −2 °C (28 °F). There is a continuous circulation of water in the oceans. Thermohaline circulation (THC) is part of the large-scale ocean circulation. It is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. Warm surface currents cool as they move away from the tropics. This happens as the water becomes denser and sinks. Changes in temperature and density move the cold water back towards the equator as a deep sea current. Then it eventually wells up again towards the surface.

The effects of climate change on the water cycle are profound and have been described as an intensification or a strengthening of the water cycle. This effect has been observed since at least 1980. One example is the intensification of heavy precipitation events. This has important negative effects on the availability of freshwater resources, as well as other water reservoirs such as oceans, ice sheets, atmosphere and land surface. The water cycle is essential to life on Earth and plays a large role in the global climate and the ocean circulation. The warming of our planet is expected to be accompanied by changes in the water cycle for various reasons. For example, a warmer atmosphere can contain more water vapor which has effects on evaporation and rainfall.