
A histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To construct a histogram, the first step is to "bin" the range of values— divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals—and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping intervals of a variable. The bins (intervals) must be adjacent and are often of equal size.
A chart is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". A chart can represent tabular numeric data, functions or some kinds of quality structure and provides different info.

A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart.

In statistics, exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach of analyzing data sets to summarize their main characteristics, often using statistical graphics and other data visualization methods. A statistical model can be used or not, but primarily EDA is for seeing what the data can tell us beyond the formal modeling and thereby contrasts traditional hypothesis testing. Exploratory data analysis has been promoted by John Tukey since 1970 to encourage statisticians to explore the data, and possibly formulate hypotheses that could lead to new data collection and experiments. EDA is different from initial data analysis (IDA), which focuses more narrowly on checking assumptions required for model fitting and hypothesis testing, and handling missing values and making transformations of variables as needed. EDA encompasses IDA.

A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.

Scientific visualization is an interdisciplinary branch of science concerned with the visualization of scientific phenomena. It is also considered a subset of computer graphics, a branch of computer science. The purpose of scientific visualization is to graphically illustrate scientific data to enable scientists to understand, illustrate, and glean insight from their data. Research into how people read and misread various types of visualizations is helping to determine what types and features of visualizations are most understandable and effective in conveying information.
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word graph is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram.

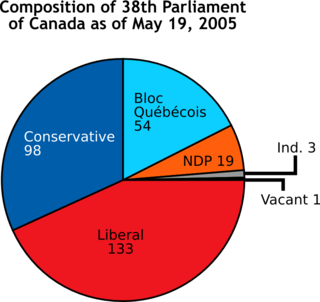
A pie chart is a circular statistical graphic which is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each slice is proportional to the quantity it represents. While it is named for its resemblance to a pie which has been sliced, there are variations on the way it can be presented. The earliest known pie chart is generally credited to William Playfair's Statistical Breviary of 1801.

Infographics are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly. They can improve cognition by using graphics to enhance the human visual system's ability to see patterns and trends. Similar pursuits are information visualization, data visualization, statistical graphics, information design, or information architecture. Infographics have evolved in recent years to be for mass communication, and thus are designed with fewer assumptions about the readers' knowledge base than other types of visualizations. Isotypes are an early example of infographics conveying information quickly and easily to the masses.

Flow diagram is a collective term for a diagram representing a flow or set of dynamic relationships in a system. The term flow diagram is also used as a synonym for flowchart, and sometimes as a counterpart of the flowchart.

Data and information visualization is the practice of designing and creating easy-to-communicate and easy-to-understand graphic or visual representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and information with the help of static, dynamic or interactive visual items. Typically based on data and information collected from a certain domain of expertise, these visualizations are intended for a broader audience to help them visually explore and discover, quickly understand, interpret and gain important insights into otherwise difficult-to-identify structures, relationships, correlations, local and global patterns, trends, variations, constancy, clusters, outliers and unusual groupings within data. When intended for the general public to convey a concise version of known, specific information in a clear and engaging manner, it is typically called information graphics.

Charles Joseph Minard was a French civil engineer recognized for his significant contribution in the field of information graphics in civil engineering and statistics. Minard was, among other things, noted for his representation of numerical data on geographic maps, especially his flow maps.
The Unistat computer program is a statistical data analysis tool featuring two modes of operation: The stand-alone user interface is a complete workbench for data input, analysis and visualization while the Microsoft Excel add-in mode extends the features of the mainstream spreadsheet application with powerful analytical capabilities.

The seven basic tools of quality are a fixed set of visual exercises identified as being most helpful in troubleshooting issues related to quality. They are called basic because they are suitable for people with little formal training in statistics and because they can be used to solve the vast majority of quality-related issues.
A dot chart or dot plot is a statistical chart consisting of data points plotted on a fairly simple scale, typically using filled in circles. There are two common, yet very different, versions of the dot chart. The first has been used in hand-drawn graphs to depict distributions going back to 1884. The other version is described by William S. Cleveland as an alternative to the bar chart, in which dots are used to depict the quantitative values associated with categorical variables.

Diagrammatic reasoning is reasoning by means of visual representations. The study of diagrammatic reasoning is about the understanding of concepts and ideas, visualized with the use of diagrams and imagery instead of by linguistic or algebraic means.
Statistical graphics, also known as statistical graphical techniques, are graphics used in the field of statistics for data visualization.
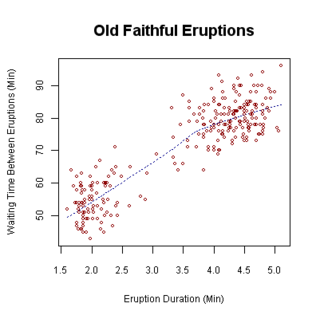
A plot is a graphical technique for representing a data set, usually as a graph showing the relationship between two or more variables. The plot can be drawn by hand or by a computer. In the past, sometimes mechanical or electronic plotters were used. Graphs are a visual representation of the relationship between variables, which are very useful for humans who can then quickly derive an understanding which may not have come from lists of values. Given a scale or ruler, graphs can also be used to read off the value of an unknown variable plotted as a function of a known one, but this can also be done with data presented in tabular form. Graphs of functions are used in mathematics, sciences, engineering, technology, finance, and other areas.

A motion chart is a dynamic bubble chart which allows efficient and interactive exploration and visualization of longitudinal multivariate data. Motion charts provide mechanisms for mapping ordinal, nominal and quantitative variables onto time, 2D coordinate axes, size, colors, glyphs and appearance characteristics, which facilitate the interactive display of multidimensional and temporal data.