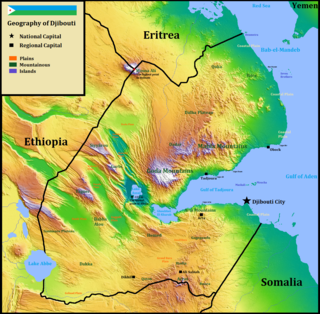
Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. To the east is its coastline on the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. Rainfall is sparse, and most of the territory has a semi-arid to arid environment. Lake Assal is a saline lake which lies 155 m (509 ft) below sea level, making it the lowest point on land in Africa and the third-lowest point on Earth after the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea. Djibouti's major settlements include the capital Djibouti City, the port towns of Tadjoura and Obock, and the southern cities of Ali Sabieh and Dikhil. It is the 147st largest country in the world by land area, covering a total of 23,200 km2, of which 23,180 km2 is land and 20 km2 is water.

A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water, generally on a planet's surface. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more rarely, puddles. A body of water does not have to be still or contained; rivers, streams, canals, and other geographical features where water moves from one place to another are also considered bodies of water.

Ali Sabieh Region is a region in southern Djibouti. With a mainland area of 2,400 square kilometres, it lies along the national border with Somalia and Ethiopia, bordering also the Dikhil Region to the west and the Arta Region to the north. Its capital is Ali Sabieh. The Arrei Mountains are the highest point in the region.

Wadi Mujib, which is also "almost certainly" known as the biblical Arnon Stream, is a river canyon in Jordan which enters the Dead Sea c 420 metres (1,380 ft) below sea level.

Djedi River or Djeddi River is a wadi in Algeria and one of the largest rivers of Sahara. It starts in the Saharan Atlas mountains, at elevation of about 1,400 meters (4,600 ft), flows for about 480 kilometers (300 mi) approximately from west to east, and discharges into Chott Melrhir lake at about –40 meters (130 ft) below mean sea level, which is the lowest point of Algeria. It is fed by rains and melting snow and has a permanent flow only in its upper part. The river rises on the southern slopes of Djebel Amour, near the town of Aflou, and feeds several date palm groves, such as the Laghouat oasis, which largely depend on this supply; water is also taken from numerous wells dug near the river. During the rain season in winter, the river helps to rise the water level of Chott Melrhir, and in summer, the lake and lower reaches of the river dry out. The river is up to several kilometers wide, but its banks are rarely covered with water. The river bed mostly consists of gypsum and mud and bears traces of erosion associated with the large variations of the flow. Although the soil in and around the river appears arable, it is barren due to the high concentration of salt. For the same reason, the soil absorbs much condensation overnight that keeps it partly humid during much of the day.

The Wildlife of Djibouti, consisting of flora and fauna, is in a harsh landscape with forest accounting for less than one percent of the total area of the country. The flora and fauna species are most found in the northern part of the country in the ecosystem of the Day Forest National Park at an average altitude 1,500 metres (4,900 ft), including the massif Goda, with a peak of 1,783 metres (5,850 ft). It covers an area of 3.5 square kilometres (1.4 sq mi) of Juniperus procera forest, with many of the trees rising to 20 metres (66 ft) height. This forest area is the main habitat of critically endangered and endemic Djibouti francolin, and another recently noted vertebrate, Platyceps afarensis. The area also contains many species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees, which account for sixty percent of the total identified species in the country.

Wadi Al-Rummah or ar-Rummah is one of the Arabian Peninsula's longest river valleys, at a length of almost 600 km (370 mi). Now mostly dry and partly blocked by encroaching sand dunes, the wadi arises near Medina at Jibāl al Abyaḑ. It heads towards the north-east, connecting to several smaller wadis, like Mohalla Wadi and Murghala Wadi to the north and Jifn Wadi and Jarir Wadi to the south. It ends at Thuayrat Dunes of the ad-Dahna Desert in Al-Qassim Province near Buraidah.

Djibouti participated in the 2010 Summer Youth Olympics in Singapore.










