
The Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the Firth of Clyde between Argyll and Bute in the west and Inverclyde, North Ayrshire and South Ayrshire in the east. There are about forty islands and skerries. Only four are inhabited, and only nine are larger than 40 hectares. The largest and most populous are Arran and Bute. They are served by dedicated ferry routes, as are Great Cumbrae and Holy Island. Unlike the isles in the four larger Scottish archipelagos, none of the isles in this group are connected to one another or to the mainland by bridges.
Firth is a word in the English and Scots languages used to denote various coastal waters in the United Kingdom, predominantly within Scotland. In the Northern Isles, it more often refers to a smaller inlet. It is linguistically cognate to Scandinavian fjord and fjard, with the original meaning of "sailable waterway". The word has a more constrained sense in English. Bodies of water named "firths" tend to be more common on the Scottish east coast, or in the southwest of the country, although the Firth of Clyde is an exception to this. The Highland coast contains numerous estuaries, straits, and inlets of a similar kind, but not called "firth" ; instead, these are often called sea lochs. Before about 1850, the spelling "Frith" was more common.

The Isle of Mull or simply Mull is the second-largest island of the Inner Hebrides and lies off the west coast of Scotland in the council area of Argyll and Bute.
Argyll, sometimes called Argyllshire, is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland. The county ceased to be used for local government purposes in 1975 and most of the area now forms part of the larger Argyll and Bute council area.

Cowal is a rugged peninsula in Argyll and Bute, on the west coast of Scotland. It is connected to the mainland to the north, and is bounded by Loch Fyne to the west, by Loch Long and the Firth of Clyde to the east, and by the Kyles of Bute to the south.

The Rhinsof Galloway is a double-headed peninsula in southwestern Scotland. It takes the form of a hammerhead projecting into the Irish Sea, terminating in the north at Corsewall and Milleur Points and in the south at the Mull of Galloway. It is connected to the rest of Wigtownshire by an isthmus, washed on the north by Loch Ryan and on the south by Luce Bay. From end to end, the peninsula measures 28 miles. It takes its name from the Gaelic word rinn, meaning "point".

Loch Katrine is a freshwater loch in the Trossachs area of the Scottish Highlands, east of Loch Lomond, within the historic county and registration county of Perthshire and the contemporary district of Stirling. The loch is about 8 miles (13 km) long and 1 mile (1.6 km) wide at its widest point, and runs the length of Strath Gartney. It is within the drainage basins of the River Teith and River Forth.

Loch Maree is a loch in Wester Ross in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. At 21.7 km (13.46 mi) long and with a maximum width of four kilometres, it is the fourth-largest freshwater loch in Scotland; it is the largest north of Loch Ness. Its surface area is 28.7 km2 (11.08 sq mi).

Corrour railway station is on the West Highland Line, near Loch Ossian on the Corrour Estate, in the Highland Region of Scotland. It is the highest mainline railway station in the United Kingdom at an elevation of 1,340 feet (410 m) above sea level. It is located between Rannoch and Tulloch, and is sited 71 miles 54 chains (115.3 km) from Craigendoran Junction, near Helensburgh. ScotRail manage the station and provide most services, along with Caledonian Sleeper.

Loch Tummel is a long, narrow loch, seven kilometres northwest of Pitlochry in the council area of Perth and Kinross, Scotland. It is fed and drained by the River Tummel, which flows into the River Tay about 13 km (8 mi) south-east of the Clunie Dam at the loch's eastern end.

Loch Striven is a sea loch in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The loch meets the Firth of Clyde and the Kyles of Bute just north of the Isle of Bute, and forms a narrow inlet about 8 miles (13 km) long extending north into the Cowal Peninsula.

Carna or Càrna is an island in Loch Sunart, an arm of the sea, close to the Ardnamurchan peninsula, on the west coast of Scotland.

Gruinard Bay is a large remote coastal embayment, located 12 miles north of Poolewe, in northwestern Ross and Cromarty, and is in the former parish of Lochbroom, in the west coast of Scotland.

Loch na Keal, meaning Loch of the Kyle, or Narrows, also Loch of the Cliffs, is the principal sea loch on the western, or Atlantic coastline of the island of Mull, in the Inner Hebrides, Argyll and Bute, Scotland. Loch na Keal extends over 20 kilometres (12 mi) inland, almost bisecting Mull, and extending to within 5 km (3 mi) of the eastern shore. The loch gives its name to the Loch na Keal National Scenic Area, one of forty national scenic areas in Scotland.

Tiroran is hamlet on the Isle of Mull in Argyll and Bute, Scotland.
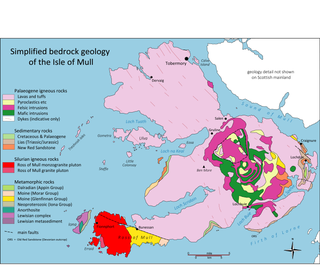
The geology of the Isle of Mull in Scotland is dominated by the development during the early Palaeogene period of a ‘volcanic central complex’ associated with the opening of the Atlantic Ocean. The bedrock of the larger part of the island is formed by basalt lava flows ascribed to the Mull Lava Group erupted onto a succession of Mesozoic sedimentary rocks during the Palaeocene epoch. Precambrian and Palaeozoic rocks occur at the island's margins. A number of distinct deposits and features such as raised beaches were formed during the Quaternary period.

Loch Spelve is a sea loch on the southeast coast of the Isle of Mull, off the west coast of Scotland. It is almost landlocked with a relatively narrow opening onto the Firth of Lorn. The A849 road runs past the northern arm of the loch and a minor road runs south from it and around the shore of the western arm via Kinlochspelve as far as the settlement of Croggan. Raised beaches are notable features of the loch, particularly on the shores of the narrows through which it enters the open waters of the firth. There are a few rocky islets within the loch, the largest of which is Eilean Amalaig on which are the ruins of a castle.
Loch Don is a sea loch on the east coast of the Isle of Mull, off the west coast of Scotland. It is an intricately shaped loch opening onto the Firth of Lorn near the easternmost point of Mull. Its waters are shallow and the loch dries almost completely at low tide. The community of Lochdon sits on the A849 at the head of the loch. A minor road runs south from Lochdon and around to Grass Point at the point where the loch meets the open waters of the firth. There are both a terminal moraine and deltaic sand deposits around the northern end of the loch, a product of meltwater flow at the end of the last ice age. The shores of the outer part of the loch are formed from basalt lava flows of Palaeogene age whilst the inner parts of the loch extend across Palaeozoic basalt and also Mesozoic sedimentary rocks including Triassic sandstones and Jurassic Lias strata.

The River Dionard is a river in the historic county of Sutherland in northwest Scotland. It arises as the outflow from Loch Dionard which lies below the eastern side of Foinaven and flows north-northwest through Strath Dionard below that mountain's eastern flanks for 7 km before turning north and then northeast towards the head of the Kyle of Durness. Its winding channel is exposed at low tide within the sands of this shallow firth which connects with the Atlantic Ocean on the north coast. The principal headwater stream feeding Loch Dionard is the Allt an Easain Ghill which passes through two lochans beneath Meall Horn; the upper Lochan Ulbha and the lower An Dubh-loch. The nearby Allt Eilidh a' Chleirich flows from a third lochan, Lochan Sgeireach. There are numerous other streams and lochans in the upper catchment. The Gualin National Nature Reserve has been established within the catchment.



















