
The counties of Ireland are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number.

A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
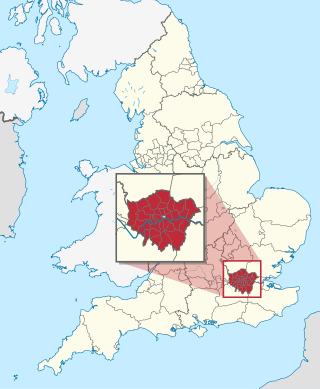
The London boroughs are the 32 local authority districts that together with the City of London make up the administrative area of Greater London, England; each is governed by a London borough council. The present London boroughs were all created at the same time as Greater London on 1 April 1965 by the London Government Act 1963 and are a type of local government district. Twelve were designated as Inner London boroughs and twenty as Outer London boroughs. The City of London, the historic centre, is a separate ceremonial county and sui generis local government district that functions quite differently from a London borough. However, the two counties together comprise the administrative area of Greater London as well as the London Region, all of which is also governed by the Greater London Authority.

Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically localised and has limited powers. While in some countries, "government" is normally reserved purely for a national administration (government), the term local government is always used specifically in contrast to national government – as well as, in many cases, the activities of sub-national, first-level administrative divisions. Local governments generally act only within powers specifically delegated to them by law and/or directives of a higher level of government. In federal states, local government generally comprises a third or fourth tier of government, whereas in unitary states, local government usually occupies the second or third tier of government.
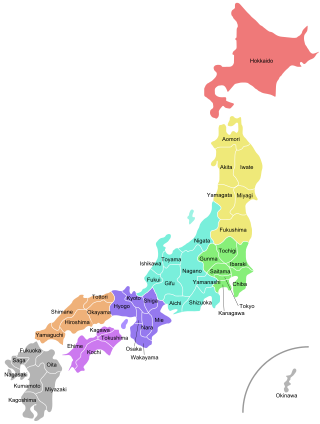
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one regional prefecture and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

This is a list of local government areas (LGAs) in Queensland, sorted by region. For the history and responsibilities of local government in that state, see Local government in Queensland. For former local government areas in Queensland, see List of former local government areas of Queensland.
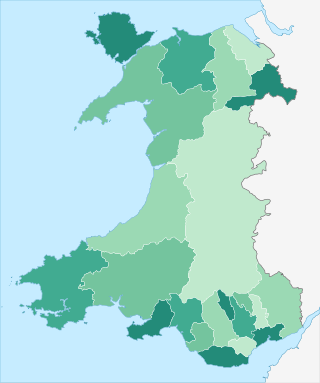
Since 1 April 1996, Wales has been divided into 22 single-tier principal areas, styled as counties or county boroughs for local government purposes. The elected councils of these areas are responsible for the provision of all local government services, including education, social work, environmental protection, and most highways. Below these there are also elected community councils to which responsibility for specific aspects of the application of local policy may be devolved. The last set of local elections in Wales took place in 2022, with the next due to take place in 2027.

An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. Widespread unincorporated communities and areas are a distinguishing feature of the United States and Canada. Most other countries of the world either have no unincorporated areas at all or these are very rare. They are typically remote, outlying, sparsely populated or uninhabited areas.

The districts of England are a level of subnational division of England used for the purposes of local government. As the structure of local government in England is not uniform, there are currently four principal types of district-level subdivision. There are a total of 294 districts made up of 36 metropolitan boroughs, 32 London boroughs, 164 two-tier non-metropolitan districts and 62 unitary authorities, as well as the City of London and Isles of Scilly which are also districts, but do not correspond to any of these categories. Some districts are styled as cities, boroughs or royal boroughs; these are purely honorific titles and do not alter the status of the district or the powers of their councils. All boroughs and cities are led by a mayor who in most cases is a ceremonial figure elected by the district council, but—after local government reform—is occasionally a directly elected mayor who makes most of the policy decisions instead of the council.

The counties of England are areas used for different purposes, which include administrative, geographical, cultural and political demarcation. The term "county" is defined in several ways and can apply to similar or the same areas used by each of these demarcation structures. These different types of county each have a more formal name but are commonly referred to as just "counties". The current arrangement is the result of incremental reform.
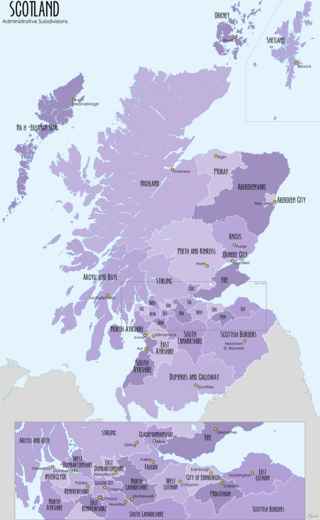
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas", which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1997 of being known as a "comhairle" when opting for a Gaelic name; only Comhairle nan Eilean Siar has chosen this option, whereas the Highland Council has adopted its Gaelic form alongside its English equivalent, informally.
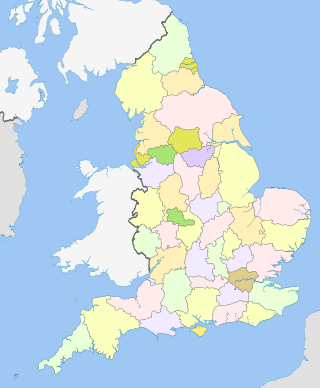
The counties for the purposes of the lieutenancies in England, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas in England, Wales and Scotland are defined by the Lieutenancies Act 1997 as "counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies in Great Britain", in contrast to the metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties of England used for local government. They are also informally known as "geographic counties", to distinguish them from other types of counties of England.

The preserved counties of Wales are the eight current areas used in Wales for the ceremonial purposes of lieutenancy and shrievalty. They are based on the counties which were used for local government and other purposes between 1974 and 1996. Each comprises one or more of the 22 single-tier principal areas which are used for administrative purposes.

In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of ecclesiastical parishes, which historically played a role in both secular and religious administration. Civil and religious parishes were formally differentiated in the 19th century and are now entirely separate. Civil parishes in their modern form came into being through the Local Government Act 1894, which established elected parish councils to take on the secular functions of the parish vestry.
Local government is the third level of government in Australia, administered with limited autonomy under the states and territories, and in turn beneath the federal government. Local government is not mentioned in the Constitution of Australia, and two referendums in 1974 and 1988 to alter the Constitution relating to local government were unsuccessful. Every state/territory government recognises local government in its own respective constitution. Unlike the two-tier local government system in Canada or the United States, there is only one tier of local government in each Australian state/territory, with no distinction between counties and cities.

The unitary authorities of England are those local authorities which are responsible for the provision of all local government services within a district. They are constituted under the Local Government Act 1992, which amended the Local Government Act 1972 to allow the existence of counties that do not have multiple districts. They typically allow large towns to have separate local authorities from the less urbanised parts of their counties and originally provided a single authority for small counties where division into districts would be impractical. However, the UK government has more recently created much larger unitary authority areas, including a single authority for North Yorkshire, the largest non-metropolitan county in England, previously divided into seven districts.
A local government area (LGA) is an administrative division of a country that a local government is responsible for. The size of an LGA varies by country but it is generally a subdivision of a state, province, division, or territory.

The regions, formerly known as the government office regions, are the highest tier of sub-national division in England. They were established in 1994 and follow the 1974–96 county borders. They are a continuation of the former 1940s standard regions which followed the 1889–1974 administrative county borders. Between 1994 and 2011, nine regions had partly devolved functions; they no longer fulfil this role, continuing to be used for limited statistical purposes.


















