
The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:

The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea.
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea.

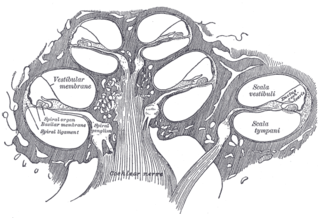
The basilar membrane is a stiff structural element within the cochlea of the inner ear which separates two liquid-filled tubes that run along the coil of the cochlea, the scala media and the scala tympani. The basilar membrane moves up and down in response to incoming sound waves, which are converted to traveling waves on the basilar membrane.

The organ of Corti, or spiral organ, is the receptor organ for hearing and is located in the mammalian cochlea. This highly varied strip of epithelial cells allows for transduction of auditory signals into nerve impulses' action potential. Transduction occurs through vibrations of structures in the inner ear causing displacement of cochlear fluid and movement of hair cells at the organ of Corti to produce electrochemical signals.

The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
Auditory neuropathy (AN) is a hearing disorder in which the outer hair cells of the cochlea are present and functional, but sound information is not transmitted sufficiently by the auditory nerve to the brain. The cause may be several dysfunctions of the inner hair cells of the cochlea or spiral ganglion neuron levels. Hearing loss with AN can range from normal hearing sensitivity to profound hearing loss.
The cochlear nerve is one of two parts of the vestibulocochlear nerve, a cranial nerve present in amniotes, the other part being the vestibular nerve. The cochlear nerve carries auditory sensory information from the cochlea of the inner ear directly to the brain. The other portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve is the vestibular nerve, which carries spatial orientation information to the brain from the semicircular canals, also known as semicircular ducts.

The vestibular membrane, vestibular wall or Reissner's membrane is a membrane inside the cochlea of the inner ear. It separates the cochlear duct from the vestibular duct. It helps to transmit vibrations from fluid in the vestibular duct to the cochlear duct. Together with the basilar membrane, it creates a compartment in the cochlea filled with endolymph, which is important for the function of the spiral organ of Corti. It allows nutrients to travel from the perilymph to the endolymph of the membranous labyrinth. It may be damaged in Ménière's disease. It is named after the German anatomist Ernst Reissner.

The internal auditory meatus is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear.

The cochlear nucleus (CN) or cochlear nuclear complex comprises two cranial nerve nuclei in the human brainstem, the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) and the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). The ventral cochlear nucleus is unlayered whereas the dorsal cochlear nucleus is layered. Auditory nerve fibers, fibers that travel through the auditory nerve carry information from the inner ear, the cochlea, on the same side of the head, to the nerve root in the ventral cochlear nucleus. At the nerve root the fibers branch to innervate the ventral cochlear nucleus and the deep layer of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. All acoustic information thus enters the brain through the cochlear nuclei, where the processing of acoustic information begins. The outputs from the cochlear nuclei are received in higher regions of the auditory brainstem.
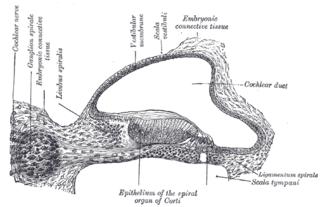
The spiral (cochlear) ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the modiolus, the conical central axis of the cochlea. These bipolar neurons innervate the hair cells of the organ of Corti. They project their axons to the ventral and dorsal cochlear nuclei as the cochlear nerve, a branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve.

The stria vascularis of the cochlear duct is a capillary loop in the upper portion of the spiral ligament. It produces endolymph for the scala media in the cochlea.

The osseous spiral lamina is a bony shelf or ledge which projects from the modiolus into the interior of the bony canal of the cochlea, and, like the canal, takes two-and-three-quarter turns around the modiolus.
Binaural fusion or binaural integration is a cognitive process that involves the combination of different auditory information presented binaurally, or to each ear. In humans, this process is essential in understanding speech as one ear may pick up more information about the speech stimuli than the other.

The vestibule is the central part of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear, and is situated medial to the eardrum, behind the cochlea, and in front of the three semicircular canals.
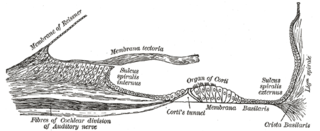
The spiral ligament is a fibrous cushion located between the stria vascularis and the bony otic capsule.

In the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), auditory nerve fibers enter the brain via the nerve root in the VCN. The ventral cochlear nucleus is divided into the anterior ventral (anteroventral) cochlear nucleus (AVCN) and the posterior ventral (posteroventral) cochlear nucleus (PVCN). In the VCN, auditory nerve fibers bifurcate, the ascending branch innervates the AVCN and the descending branch innervates the PVCN and then continue to the dorsal cochlear nucleus. The orderly innervation by auditory nerve fibers gives the AVCN a tonotopic organization along the dorsoventral axis. Fibers that carry information from the apex of the cochlea that are tuned to low frequencies contact neurons in the ventral part of the AVCN; those that carry information from the base of the cochlea that are tuned to high frequencies contact neurons in the dorsal part of the AVCN. Several populations of neurons populate the AVCN. Bushy cells receive input from auditory nerve fibers through particularly large endings called end bulbs of Held. They contact stellate cells through more conventional boutons.

The cochlear cupula is a structure in the cochlea. It is the apex of the cochlea. The bony canal of the cochlea takes two and three-quarter turns around the modiolus. The modiolus is about 35 mm in length, and diminishes gradually in diameter from the base to the summit, where it terminates in the cupula. The cupula points towards the anterosuperior area of the medial wall of the tympanic cavity.
Cochlea is Latin for “snail, shell or screw” and originates from the Greek word κοχλίας kokhlias. The modern definition, the auditory portion of the inner ear, originated in the late 17th century. Within the mammalian cochlea exists the organ of Corti, which contains hair cells that are responsible for translating the vibrations it receives from surrounding fluid-filled ducts into electrical impulses that are sent to the brain to process sound.













