An antiseptic is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from antibiotics by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from disinfectants, which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects.

Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for human consumption, but water purification may also be carried out for a variety of other purposes, including medical, pharmacological, chemical, and industrial applications. The history of water purification includes a wide variety of methods. The methods used include physical processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and distillation; biological processes such as slow sand filters or biologically active carbon; chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination; and the use of electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light.
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a slightly different definition for biocides as "a diverse group of poisonous substances including preservatives, insecticides, disinfectants, and pesticides used for the control of organisms that are harmful to human or animal health or that cause damage to natural or manufactured products". When compared, the two definitions roughly imply the same, although the US EPA definition includes plant protection products and some veterinary medicines.

Chlorine dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula ClO2 that exists as yellowish-green gas above 11 °C, a reddish-brown liquid between 11 °C and −59 °C, and as bright orange crystals below −59 °C. It does not hydrolyze when it enters water, and is usually handled as an aqueous solution. Potential hazards with chlorine dioxide include poisoning and the risk of spontaneous ignition or explosion on contact with flammable materials. It is also commonly used as a bleach.

A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than sterilization, which is an extreme physical or chemical process that kills all types of life. Disinfectants are generally distinguished from other antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue. Disinfectants are also different from biocides—the latter are intended to destroy all forms of life, not just microorganisms. Disinfectants work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with their metabolism. It is also a form of decontamination, and can be defined as the process whereby physical or chemical methods are used to reduce the amount of pathogenic microorganisms on a surface.
ATC code D08Antiseptics and disinfectants is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup D08 is part of the anatomical group D Dermatologicals.
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals are used against fungi. They can also be classified according to their function. Agents that kill microbes are microbicides, while those that merely inhibit their growth are called bacteriostatic agents. The use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy, while the use of antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis.

In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure NR+4, R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule.

Dettol is a cleaning disinfectant and antiseptic. It was introduced in 1932 by the British company Reckitt. In Germany, it is sold under the name Sagrotan.

Organomercury refers to the group of organometallic compounds that contain mercury. Typically the Hg–C bond is stable toward air and moisture but sensitive to light. Important organomercury compounds are the methylmercury(II) cation, CH3Hg+; ethylmercury(II) cation, C2H5Hg+; dimethylmercury, (CH3)2Hg, diethylmercury and merbromin ("Mercurochrome"). Thiomersal is used as a preservative for vaccines and intravenous drugs.
A mode of action (MoA) describes a functional or anatomical change, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance. In comparison, a mechanism of action (MOA) describes such changes at the molecular level.

Lysol is a brand of American cleaning and disinfecting products distributed by Reckitt, which markets the similar Dettol or Sagrotan in other markets. The line includes liquid solutions for hard and soft surfaces, air treatment, and hand washing. The active ingredient in many Lysol products is benzalkonium chloride, but the active ingredient in the Lysol "Power and Free" line is hydrogen peroxide. Lysol has been used since its invention in the late 19th century as a household and industrial cleaning agent, and previously as a medical disinfectant.
The Rideal–Walker coefficient, now only of historical interest, is a figure expressing the disinfecting power of any disinfectant. It is the ratio of the dilution of the disinfectant that kills a microorganism to the dilution of phenol that kills the organism in the same time under identical conditions. The Rideal–Walker coefficient determines the phenol coefficient utilizing the method (test) described by English chemists Samuel Rideal (1863–1929) and J. T. Ainslie Walker (1868–1930).
Didecyldimethylammonium chloride (DDAC) is a quaternary ammonium compound used as antiseptic/disinfectant. It causes the disruption of intermolecular interactions and the dissociation of lipid bilayers. The bacteriostatic or bactericide activity of DDAC depends on its concentration and the growth phase of the microbial population. It is a broad spectrum biocidal against bacteria and fungi and can be used as disinfectant cleaner for linen, recommended for use in hospitals, hotels and industries. It is also used in gynaecology, surgery, ophthalmology, pediatrics, OT, and for the sterilization of surgical instruments, endoscopes and surface disinfection.

Benzoxonium chloride (Absonal) is an antiseptic and disinfectant.

Phenylmercuric acetate is an organomercury compound. This compound was formerly used as a preservative in paints, and as a disinfectant. When applied to the leaves of plants, it is an antitranspirant.
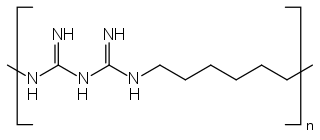
Polyhexanide is a polymer used as a disinfectant and antiseptic. In dermatological use, it is spelled polihexanide (INN) and sold under the names Lavasept, Serasept, Prontosan, and Omnicide. PHMB has been shown to be effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Candida albicans, Aspergillus brasiliensis, enterococci, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Nitromersol (metaphen) is a mercury-containing organic compound that is primarily used as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is a brown-yellow solid that has no odor or taste, does not irritate the skin or mucous membranes, and has no impact on rubber or metallic instruments, including surgical and dental tools.
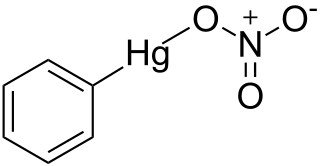
Phenylmercuric nitrate is an organomercury compound with powerful antiseptic and antifungal effects. It was once commonly used as a topical solution for disinfecting wounds, but as with all organomercury compounds it is highly toxic, especially to the kidneys, and is no longer used in this application. However it is still used in low concentrations as a preservative in eye drops for ophthalmic use, making it one of the few organomercury derivatives remaining in current medical use.
Diving equipment may be exposed to contamination in use and when this happens it must be decontaminated. This is a particular issue for hazmat diving, but incidental contamination can occur in other environments. Personal diving equipment shared by more than one user requires disinfection before use. Shared use is common for expensive commercial diving equipment, and for rental recreational equipment, and some items such as demand valves, masks, helmets and snorkels which are worn over the face or held in the mouth are possible vectors for infection by a variety of pathogens. Diving suits are also likely to be contaminated, but less likely to transmit infection directly.











