This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
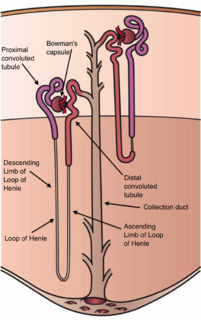
The 'nephron is the microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and an encompassing Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 0.8 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the foot processes of the podocytes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged ; first with the interstitial fluid outside the tubules, and then into the plasma in the adjacent peritubular capillaries through the endothelial cells lining that capillary. This process regulates the volume of body fluid as well as levels of many body substances. At the end of the tubule, the remaining fluid—urine—exits: it is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.
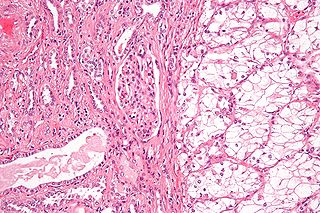
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases.
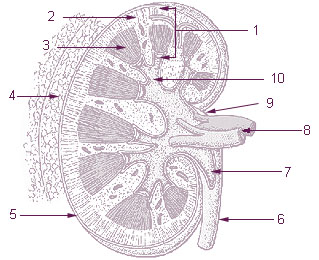
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the Loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter.

The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. In humans, the renal pelvis is the point where the two or three major calyces join together. It has a mucous membrane is covered with transitional epithelium, and an underlying lamina propria of loose to dense connective tissue.

The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.
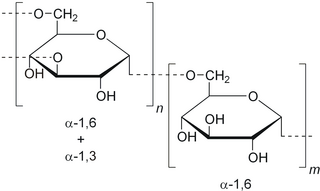
Dextran is a complex branched glucan. IUPAC defines dextrans as "Branched poly-α-d-glucosides of microbial origin having glycosidic bonds predominantly C-1 → C-6". Dextran chains are of varying lengths.

Aesculus hippocastanum is a species of flowering plant in the soapberry and lychee family Sapindaceae. It is a large deciduous, synoecious (hermaphroditic-flowered) tree, commonly known as horse-chestnut or conker tree.

The renal arteries normally arise off the left interior side of the abdominal aorta, immediately below the superior mesenteric artery, and supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.

The renal veins are veins that drain the kidney. They connect the kidney to the inferior vena cava. They carry the blood filtered by the kidney.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.

The afferent arterioles are a group of blood vessels that supply the nephrons in many excretory systems. They play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure as a part of the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism.

The middle suprarenal arteries are two small vessels which arise, one from either side of the abdominal aorta, opposite the superior mesenteric artery.

The renal plexus is formed by filaments from the celiac ganglia and plexus, aorticorenal ganglia, lower thoracic splanchnic nerves and first lumbar splanchnic nerve and aortic plexus.

Interlobular arteries are renal blood vessels given off at right angles from the side of the arcuate arteries looking toward the cortical substance. The interlobular arteries pass directly outward between the medullary rays to reach the fibrous tunic, where they end in the capillary network of this part.
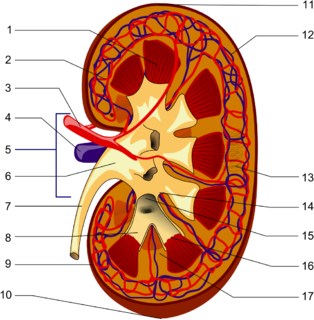
The interlobar arteries are vessels of the renal circulation which supply the renal lobes. The interlobar arteries branch from the lobar arteries which branch from the segmental arteries, from the renal artery. They give rise to arcuate arteries.
The segmental arteries are branches of the renal arteries.
The ureteral branches of renal artery are small branches which supply the ureter.
Lachiewicz–Sibley syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by preauricular pits and renal disease. Persons with this disease may have hypoplasic kidneys or proteinuria. This disease was first described in a Caucasian family of British and Irish descent that emigrated to Ohio in the 19th century before settling in Nebraska. Many of the members of this family still live in Nebraska, although the relatives are now scattered throughout the country.
The Kidney Foundation of Canada promotes organ donor awareness, and fundraises for kidney/renal research at various hospitals across Canada. They have offices in most major cities in Canada.













