Longdendale is a valley in the Peak District of England, north of Glossop and southwest of Holmfirth. The name means "long wooded valley" and the valley is mostly in the counties of Derbyshire and Greater Manchester.

The River Etherow is a river in northern England, and a tributary of the River Goyt. Although now passing through South Yorkshire, Derbyshire and Greater Manchester, it historically formed the ancient county boundary between Cheshire and Derbyshire. The upper valley is known as Longdendale. The river has a watershed of approximately 30 square miles (78 km2), and the area an annual rainfall of 52.5 inches (1,330 mm).

The M67 is a 5-mile (8.0 km) urban motorway in Greater Manchester, England, which heads east from the M60 motorway passing through Denton and Hyde before ending near Mottram. The road was originally conceived as the first section of a trans-Pennine motorway between Manchester and Sheffield that would connect the A57(M) motorway with the M1 motorway; however, the motorway became the only part to be built.

Thirlmere is a reservoir in the Borough of Allerdale in Cumbria and the English Lake District. The Helvellyn ridge lies to the east of Thirlmere. To the west of Thirlmere are a number of fells; for instance, Armboth Fell and Raven Crag both of which give views of the lake and of Helvellyn beyond. It runs roughly south to north and is bordered on the eastern side for much of its length by the A591 road and on the western side by a minor road. It occupies the site of a former natural lake: this had a fordable waist so narrow that it was sometimes regarded as two lakes. In the 19th century Manchester Corporation constructed a dam at the northern end, raising the water level, flooding the valley bottom, and creating a reservoir to provide the growing industrial city of Manchester with water supplies via the 96 mile-long Thirlmere Aqueduct. The reservoir and the aqueduct still provide water to the Manchester area, but under the Water Act 1973 ownership passed to the North West Water Authority; as a result of subsequent privatisation and amalgamation they are now owned and managed by United Utilities, a private water and waste water company.

Woodhead is a small and scattered settlement at the head of the Longdendale valley in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the trans-Pennine A628 road connecting Greater Manchester and South Yorkshire, 6 miles (10 km) north of Glossop, 19 miles (31 km) east of Manchester and 18 miles (29 km) west of Barnsley. It is close to the River Etherow and the Trans Pennine Trail. Although part of Derbyshire since 1974, like nearby Tintwistle and Crowden, the hamlet was in the historic county of Cheshire.

The Woodhead line was a railway line linking Sheffield, Penistone and Manchester in the north of England. A key feature of the route is the passage under the high moorlands of the northern Peak District through the Woodhead Tunnels. The line was electrified in 1953 and closed between Hadfield and Penistone in 1981.

Woodhead reservoir is a man-made lake near the hamlet of Woodhead in Longdendale in north Derbyshire, England. It was constructed by John Frederick Bateman between 1847 and June 1877 as part of the Longdendale Chain of reservoirs to supply water from the River Etherow to the urban areas of Greater Manchester. It is at the top of the chain of reservoirs and was the first to be started, though, due to construction problems, it was the last to be completed.

Torside Reservoir is the largest man-made lake in Longdendale in north Derbyshire, England. It was constructed by John Frederick Bateman between April 1849 and July 1864 as part of the Longdendale Chain of reservoirs to supply water from the River Etherow to the urban areas of Greater Manchester.

ValehouseReservoir is a man-made lake in Longdendale in north Derbyshire, England. It was built between 1865 and 1869 as part of the Longdendale Chain of reservoirs, which was built to supply water from the River Etherow to the urban areas of Greater Manchester, while maintaining a constant flow into the river. The upper reservoirs supply the drinking water, while Vale House and Bottoms are compensation reservoirs which guarantee the flow of water to water-powered mills downstream. Valehouse, with a crest elevation of 503 metres (1,650 ft), is too low to supply water under gravity to the Mottram Tunnel, so could not be used as an impounding reservoir. Today 45 megalitres of compensation water are released each day into the River Etherow.

Bottoms Reservoir is a man-made lake in Longdendale in north Derbyshire, England. It was constructed between 1865 and 1877, by John Frederick Bateman as part of the Longdendale Chain of reservoirs to supply water from the River Etherow to the urban areas of Greater Manchester. The upper reservoirs supplied the drinking water, while Bottoms and Vale House reservoirs regulated the flow downstream for the benefit of local water-powered mills.

Arnfield Reservoir is a man-made lake in Longdendale in north Derbyshire, England. It was constructed in 1854 as part of the Longdendale chain to supply water from the River Etherow to the urban areas of Greater Manchester. Unlike the other reservoirs in the chain, Arnfield and Hollingworth Reservoir are not in the Etherow valley but lie in the valley of tributary brooks to the north and above. From Arnfield the water is extracted to pass through the Mottram Tunnel to Godley.

The Longdendale Chain is a sequence of six reservoirs on the River Etherow in the Longdendale Valley, in northern Derbyshire. They were constructed between 1848 and 1884 to a design by John Frederick Bateman to supply the growing population of Manchester and Salford with fresh water.

The A628 is a major road connecting Greater Manchester and South Yorkshire in northern England. It crosses the Pennine hills by way of Longdendale and the Woodhead Pass in the Peak District National Park. The road's altitude and exposure to bad weather create problems in winter and the road is sometimes closed due to snow or high winds.

Swallows Wood

The Thirlmere Aqueduct is a 95.9-mile-long (154.3-kilometre-long) pioneering section of water supply system in England, built by the Manchester Corporation Water Works between 1890 and 1925. Often incorrectly thought of as one of the longest tunnels in the world, the aqueduct's tunnel section is not continuous.
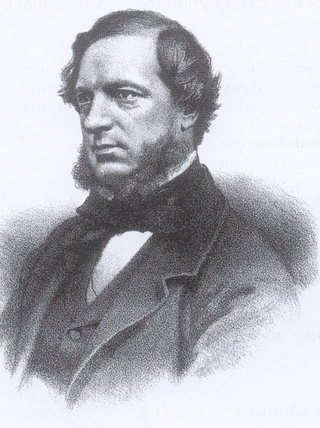
John Frederick La Trobe Bateman was an English civil engineer whose work formed the basis of the modern United Kingdom water supply industry. For more than 50 years from 1835 he designed and constructed reservoirs and waterworks. His largest project was the Longdendale Chain system that has supplied Manchester with much of its water since the 19th century. The construction of what was in its day the largest chain of reservoirs in the world began in 1848 and was completed in 1877. Bateman became "the greatest dam-builder of his generation".

Hurst Reservoir is a former, now disused, reservoir near Glossop, north Derbyshire.

The Godley Reservoir is a reservoir in Godley, Hyde, Greater Manchester. It was completed in 1851, as a critical part of the Longdendale Chain project that brings fresh water to Manchester.
The Mottram Tunnel is a tunnel carrying drinking water by gravity from Arnfield Reservoir, Tintwistle, Derbyshire, in the valley of the River Etherow, to Godley, Greater Manchester, in the valley of the River Tame. It was essential to the construction of the Longdendale Chain of reservoirs constructed by John Frederick Bateman. The tunnel was built between August 1848 and October 1850, and the Godley Reservoir was finished in 1851 to receive and filter the water.
The Grand Contour Canal in England and Wales was intended to enhance and upgrade the British canal system, but was never built. This canal was proposed in 1943, and again ten years later, by J F Pownall. Pownall observed that there was a natural 'contour' down the spine of England, around the 300 ft level that connected several of the most populated areas. He put forward the idea that this contour could be used to define the course of a large European sized canal which contained no locks except at its entry and exit points. It would also serve as a water grid capable of distributing domestic water supply around England as need arises.