Bassetlaw is a local government district in north Nottinghamshire, England. Its council is based in the town of Worksop; the other towns in the district are Retford, Tuxford and Harworth Bircotes. The district also contains numerous villages and surrounding rural areas.

Dudley Metropolitan Borough Council is the local authority for Dudley metropolitan borough. It is more commonly known as Dudley Council or Dudley MBC.

The Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley is a metropolitan borough in South Yorkshire, England; the main settlement is Barnsley and other notable towns include Penistone, Wombwell and Hoyland.

Newcastle City Council is the local authority for Newcastle upon Tyne, a metropolitan borough with city status in the ceremonial county of Tyne and Wear in North East England. The council consists of 78 councillors, three for each of the 26 wards in the city. It has been under Labour majority control since 2011. The council is a member of the North of Tyne Combined Authority.

The Borough of Darlington is a local government district with borough status in County Durham, England. Since 1997 Darlington Borough Council has been a unitary authority, with both district-level and county-level functions; it is independent from Durham County Council. It is named after its largest settlement, the town of Darlington, where the council is based. The borough also includes a rural area surrounding the town which contains several villages. The population of the borough at the 2021 census was 107,800, of which over 86% (93,015) lived in the built-up area of Darlington itself.

The Borough of Hartlepool is a local government district with borough status in County Durham, England. Since 1996 Hartlepool Borough Council has been a unitary authority, which gives it both district-level and county-level functions; it is independent of Durham County Council. It is named after its largest settlement, Hartlepool, where the council is based. The borough also includes a rural area to the west of the town. The population of the borough at the 2021 census was 92,571, of which over 95% (87,995) lived in the built-up area of Hartlepool itself.

Middlesbrough Council, also known as Middlesbrough Borough Council, is the local authority for Middlesbrough, in the ceremonial county of North Yorkshire, England. Since 1996 it has been a unitary authority, providing both district-level and county-level services. The council is led by the directly elected Mayor of Middlesbrough.
Rotherham Metropolitan Borough Council is the local authority for Rotherham in South Yorkshire, England. The council is elected every four years. Since the last boundary changes in 2004, 63 councillors have been elected from 21 wards.

City of Doncaster Council is the local authority of the City of Doncaster, a metropolitan borough with city status in South Yorkshire, England. Prior to being awarded city status in 2022 the council was called Doncaster Metropolitan Borough Council. The council is based at the Civic Office in Waterdale, central Doncaster. It is one of four local authorities in South Yorkshire and provides the majority of local government services in Doncaster. The council is a member of the South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority.

Kirklees Council is the local authority providing most local government services for the metropolitan borough of Kirklees in West Yorkshire, England. The council is one of five constituent members of the West Yorkshire Combined Authority.

Durham County Council is the local authority which governs the non-metropolitan county of County Durham in North East England. Since 2009 it has been a unitary authority, having taken over district-level functions when the county's districts were abolished. The non-metropolitan county is smaller than the ceremonial county of County Durham, which additionally includes Darlington, Hartlepool and the parts of Stockton-on-Tees north of the River Tees. The county council has its headquarters at County Hall in Durham.

City of Bradford Metropolitan District Council is the local authority of the City of Bradford in West Yorkshire, England. It is a metropolitan district council, one of five in West Yorkshire and one of 36 in the metropolitan counties of England, and provides the majority of local government services in Bradford. Since 2014 it has been a constituent member of the West Yorkshire Combined Authority.

City of York Council is the local authority for York, in Yorkshire, England. York has had a city council from medieval times, which has been reformed on numerous occasions. Since 1996 the council has been a unitary authority, performing both district-level and county-level functions. It is composed of 47 councillors and has been under Labour majority control since 2023. The council is based at West Offices on Station Rise.

Wakefield Council, formally the City of Wakefield Metropolitan District Council, is the local authority of the City of Wakefield in West Yorkshire, England. Wakefield is a metropolitan borough with city status. The council and provides a full range of local government services including Council Tax billing, libraries, social services, town planning, waste collection and disposal, and it is a local education authority. Wakefield is divided into 21 wards, electing 63 councillors. A third of the council is elected for three of every four years.

Barnsley Metropolitan Borough Council is the local authority of the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley in South Yorkshire, England. Barnsley is a metropolitan borough, one of four in South Yorkshire, and provides the majority of local government services in Barnsley. The council is a constituent member of the South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority.

Stockton-on-Tees Borough Council is the local authority of the Borough of Stockton-on-Tees, which straddles the ceremonial counties of County Durham and North Yorkshire in England. Since 1996 the council has been a unitary authority, providing both district-level and county-level services. It therefore provides services including Council Tax billing, libraries, social services, town planning, waste collection and disposal, and it is a local education authority. Since 2016 the council has been a member of the Tees Valley Combined Authority, which has been led by the directly elected Tees Valley Mayor since 2017.

Calderdale Metropolitan Borough Council is the local authority for the Metropolitan Borough of Calderdale in West Yorkshire, England. The council styles itself Calderdale Council. It is a metropolitan district council, one of five in West Yorkshire and one of 36 in the metropolitan counties of England. It provides the majority of local government services in Calderdale. Since 2014 the council has been a constituent member of the West Yorkshire Combined Authority.

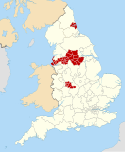
The South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority is the combined authority for South Yorkshire in England, with powers over transport, economic development and regeneration. It covers a total area of 3,484 km2 (1,345 sq mi) with a population of 1.8 million. The four metropolitan boroughs of South Yorkshire – Sheffield, Rotherham, Doncaster and Barnsley – are full members of the authority, while the Derbyshire Dales, North East Derbyshire, Chesterfield and Bolsover districts of Derbyshire, and the Bassetlaw district of Nottinghamshire, are non-constituent members.

The Mayor of West Yorkshire is a directly elected mayor responsible for the metropolitan county of West Yorkshire in England. The Mayor chairs and leads the West Yorkshire Combined Authority, and assumes the office and powers of the West Yorkshire Police and Crime Commissioner.

The Borough of Chesterfield is a non-metropolitan district with borough status in Derbyshire, England. It is named after the town of Chesterfield, its largest settlement, and also contains the town of Staveley and the large village of Brimington.