| Sublingual fovea | |
|---|---|
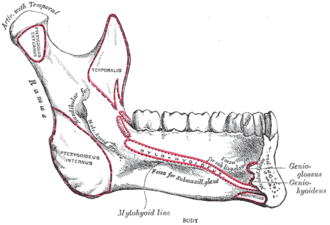 Mandible. Inner surface. Side view. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fovea sublingualis |
| TA98 | A02.1.15.014 |
| TA2 | 850 |
| FMA | 59434 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The sublingual fovea (or sublingual fossa) is a fovea in the mandible for the sublingual gland.
