Related Research Articles
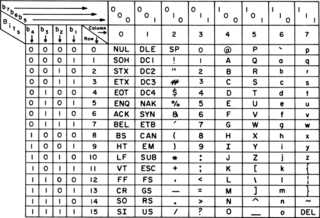
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are printable characters, which severely limited its scope. Many computer systems instead use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set.

Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using digital computers. The numerical values that make up a character encoding are known as "code points" and collectively comprise a "code space", a "code page", or a "character map".
In computing, AAP DTD is a set of three SGML Document Type Definitions for scientific documents, defined by the Association of American Publishers. It was ratified as a U.S. standard under the name ANSI/NISO Z39.59 in 1988, and evolved into the international ISO 12083 standard in 1993. It was supplanted as a U.S. standard by ANSI/ISO 12083 in 1995.
ISO/IEC 646 is a set of ISO/IEC standards, described as Information technology — ISO 7-bit coded character set for information interchange and developed in cooperation with ASCII at least since 1964. Since its first edition in 1967 it has specified a 7-bit character code from which several national standards are derived.
In computer programming, Base64 is a group of binary-to-text encoding schemes that represent binary data in sequences of 24 bits that can be represented by four 6-bit Base64 digits.

Windows-1252 or CP-1252 is a single-byte character encoding of the Latin alphabet that was used by default in Microsoft Windows for English and many Romance and Germanic languages including Spanish, Portuguese, French, and German. This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa. All modern operating systems, including Windows, now use Unicode code points and text encodings by default, which are portable across all of the world's major languages.
VISCII is an unofficially-defined modified ASCII character encoding for using the Vietnamese language with computers. It should not be confused with the similarly-named officially registered VSCII encoding. VISCII keeps the 95 printable characters of ASCII unmodified, but it replaces 6 of the 33 control characters with printable characters. It adds 128 precomposed characters. Unicode and the Windows-1258 code page are now used for virtually all Vietnamese computer data, but legacy VSCII and VISCII files may need conversion.
A technical report is a document that describes the process, progress, or results of technical or scientific research or the state of a technical or scientific research problem. It might also include recommendations and conclusions of the research. Unlike other scientific literature, such as scientific journals and the proceedings of some academic conferences, technical reports rarely undergo comprehensive independent peer review before publication. They may be considered as grey literature. Where there is a review process, it is often limited to within the originating organization. Similarly, there are no formal publishing procedures for such reports, except where established locally.
The C0 and C1 control code or control character sets define control codes for use in text by computer systems that use ASCII and derivatives of ASCII. The codes represent additional information about the text, such as the position of a cursor, an instruction to start a new line, or a message that the text has been received.
Windows code pages are sets of characters or code pages used in Microsoft Windows from the 1980s and 1990s. Windows code pages were gradually superseded when Unicode was implemented in Windows, although they are still supported both within Windows and other platforms, and still apply when Alt code shortcuts are used.
T.51 / ISO/IEC 6937:2001, Information technology — Coded graphic character set for text communication — Latin alphabet, is a multibyte extension of ASCII, or more precisely ISO/IEC 646-IRV. It was developed in common with ITU-T for telematic services under the name of T.51, and first became an ISO standard in 1983. Certain byte codes are used as lead bytes for letters with diacritics (accents). The value of the lead byte often indicates which diacritic that the letter has, and the follow byte then has the ASCII-value for the letter that the diacritic is on.
The phrase ANSI character set has no well-defined meaning and has been used to refer to the following, among other things:
ISO 2709 is an ISO standard for bibliographic descriptions, titled Information and documentation—Format for information exchange.
YUSCII is an informal name for several JUS standards for 7-bit character encoding. These include:

The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy. The Greek alphabet was adopted by the Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was adopted by the Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet.

Extended ASCII is a repertoire of character encodings that include the original 96 ASCII character set, plus up to 128 additional characters. There is no formal definition of "extended ASCII", and even use of the term is sometimes criticized, because it can be mistakenly interpreted to mean that the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) had updated its ANSI X3.4-1986 standard to include more characters, or that the term identifies a single unambiguous encoding, neither of which is the case.
The ISO basic Latin alphabet is an international standard for a Latin-script alphabet that consists of two sets of 26 letters, codified in various national and international standards and used widely in international communication. They are the same letters that comprise the current English alphabet. Since medieval times, they are also the same letters of the modern Latin alphabet. The order is also important for sorting words into alphabetical order.
The Vietnamese language is written with a Latin script with diacritics which requires several accommodations when typing on phone or computers. Software-based systems are a form of writing Vietnamese on phones or computers with software that can be installed on the device or from third-party software such as UniKey. Telex is the oldest input method devised to encode the Vietnamese language with its tones. Other input methods may also include VNI and VIQR. VNI input method is not to be confused with VNI code page.
ISO 12083 is an international SGML standard for document interchange between authors and publishers. It features separate Document Type Definitions for books, serials, articles, and math. Derived from AAP DTD, it was first published in 1993, revised in 1994, and last confirmed in 2016.
VSCII, also known as TCVN 5712, ISO-IR-180, .VN, ABC or simply the TCVN encodings, is a set of three closely related Vietnamese national standard character encodings for using the Vietnamese language with computers, developed by the TCVN Technical Committee on Information Technology (TCVN/TC1) and first adopted in 1993.
References
- 1 2 Extended Latin Alphabet Coded Character Set for Bibliographic Use (PDF) (National information standard specification). 1993 (R2003). Bethesda, Maryland: NISO Press. 3 May 1993. ISBN 1-880124-02-5. ISSN 1041-5653. OCLC 25546245. OL 12137795M. ANSI/NISO Z39.47-1993 (R2003). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- 1 2 "International Register Of Coded Character Sets To Be Used With Escape Sequences (Registration Listing Ordered By Registration Number)". International Register Of Coded Character Sets To Be Used With Escape Sequences. Information Technology Standards Commission of Japan. Archived from the original on 9 April 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- 1 2 "Project Overview: ANSI/NISO Z39.47-1993 (R2003) Extended Latin Alphabet Coded Character Set for Bibliographic Use (ANSEL) (Inactive)". National Information Standards Organization. Archived from the original on 14 March 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ↑ The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Family History Department (2 December 1995). "Appendix D: ANSEL Character Set". The GEDCOM Standard Release 5.5 (Information standard specification). Salt Lake City, Utah: The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. pp. 87–89.
- ↑ The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, Family History Department (4 November 1993). The GEDCOM Standard Release 5.3 (Information standard specification). Salt Lake City, Utah: The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. pp. 67–72.
- ↑ "MARC 21 Specifications for Record Structure, Character Sets, and Exchange Media: Code Table Extended Latin (ANSEL)". Library Standards at the Library of Congress. Library of Congress. December 2007.