Related Research Articles
ISO/IEC 8859-6:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 6: Latin/Arabic alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. It is informally referred to as Latin/Arabic. It was designed to cover Arabic. Only nominal letters are encoded, no preshaped forms of the letters, so shaping processing is required for display. It does not include the extra letters needed to write most Arabic-script languages other than Arabic itself.

Code page 850 is a code page used under DOS operating systems in Western Europe. Depending on the country setting and system configuration, code page 850 is the primary code page and default OEM code page in many countries, including various English-speaking locales, whilst other English-speaking locales default to the hardware code page 437.

Code page 855 is a code page used under DOS to write Cyrillic script.
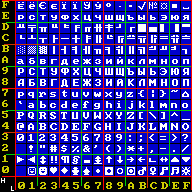
Code page 866 is a code page used under DOS and OS/2 in Russia to write Cyrillic script. It is based on the "alternative code page" developed in 1984 in IHNA AS USSR and published in 1986 by a research group at the Academy of Science of the USSR. The code page was widely used during the DOS era because it preserves all of the pseudographic symbols of code page 437 and maintains alphabetic order of Cyrillic letters. Initially this encoding was only available in the Russian version of MS-DOS 4.01 (1990), but with MS-DOS 6.22 it became available in any language version.
Windows-1255 is a code page used under Microsoft Windows to write Hebrew. It is an almost compatible superset of ISO-8859-8 – most of the symbols are in the same positions, but Windows-1255 adds vowel-points and other signs in lower positions.
Code page 852 is a code page used under DOS to write Central European languages that use Latin script.
Mac OS Central European is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in Central European and Southeastern European languages that use the Latin script. This encoding is also known as Code Page 10029. IBM assigns code page/CCSID 1282 to this encoding. This codepage contains diacritical letters that ISO 8859-2 does not have, and vice versa.
Code page 865 is a code page used under DOS in Denmark and Norway to write Nordic languages.
Code page 860 is a code page used under DOS in Portugal to write Portuguese and it is also suitable to write Spanish and Italian. In Brazil, however, the most widespread codepage – and that which DOS in Brazilian Portuguese used by default – was code page 850.
Code page 863 is a code page used under DOS in Canada to write French although it lacks the letters Æ, æ, Œ, œ, Ÿ and ÿ.
Code page 857 is a code page used under DOS in Turkey to write Turkish.

Code page 737 is a code page used under DOS to write the Greek language. It was much more popular than code page 869 although it lacks the letters ΐ and ΰ.
Code page 869 is a code page used under DOS to write Greek and may also be used to get Greek letters for other uses such as math. It is also called DOS Greek 2. It was designed to include all characters from ISO 8859-7.
Code page 861 is a code page used under DOS in Iceland to write the Icelandic language.
Windows code pages are sets of characters or code pages used in Microsoft Windows from the 1980s and 1990s. Windows code pages were gradually superseded when Unicode was implemented in Windows, although they are still supported both within Windows and other platforms, and still apply when Alt code shortcuts are used.
Code page 775 is a code page used under DOS to write the Estonian, Lithuanian and Latvian languages. In Lithuania, this code page is standardised as LST 1590-1, alongside the related Code page 778.
Code page 720 is a code page used under DOS to write Arabic in Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. The Windows (ANSI) code page for Arabic is Windows-1256.
Code page 851 is a code page used under DOS to write Greek language although it lacks the letters Ϊ and Ϋ. It covers the German language as well. It also covers some accented letters of the French language, but it lacks most of the accented capital letters required for French. It is also called MS-DOS Greek 1.
Code page 856, is a code page used under DOS for Hebrew in Israel.
Mac OS Croatian is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent Gaj's Latin alphabet. It is a derivative of Mac OS Roman. The three digraphs, Dž, Lj, and Nj, are not encoded.
References
- ↑ Character Sets, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), 2018-12-12
- ↑ "CCSID 862 information document". Archived from the original on 2016-03-28.
- 1 2 "OEM 862". Go Global Developer Center. Microsoft. Retrieved 25 Nov 2011.
- ↑ "Code Pages Supported by Windows: OEM Code Pages". Go Global Developer Center. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2 November 2011. Retrieved 11 Oct 2011.
- ↑ "Code Page 862 MS-DOS Hebrew". Developing International Software. Microsoft. Retrieved 25 Nov 2011.
- ↑ "Code page 862 information document". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04.
- ↑ "cp862_DOSHebrew to Unicode table" (TXT). The Unicode Consortium. Retrieved 25 Nov 2011.
- ↑ Code Page CPGID 00862 (pdf) (PDF), IBM[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Code Page CPGID 00862 (txt), IBM[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-862_P100-1995.ucm, 2002-12-03