Related Research Articles

LaTeX is a software system for typesetting documents. LaTeX markup describes the content and layout of the document, as opposed to the formatted text found in WYSIWYG word processors like Microsoft Word, LibreOffice Writer and Apple Pages. The writer uses markup tagging conventions to define the general structure of a document, to stylise text throughout a document, and to add citations and cross-references. A TeX distribution such as TeX Live or MiKTeX is used to produce an output file suitable for printing or digital distribution.
V, or v, is the twenty-second letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is vee, plural vees.

Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, caucho, or caoutchouc, as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Cambodia are four of the leading rubber producers.
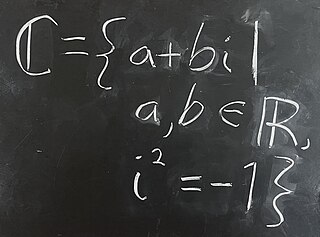
Blackboard bold is a style of writing bold symbols on a blackboard by doubling certain strokes, commonly used in mathematical lectures, and the derived style of typeface used in printed mathematical texts. The style is most commonly used to represent the number sets , (integers), , , and .

Leslie B. Lamport is an American computer scientist and mathematician. Lamport is best known for his seminal work in distributed systems, and as the initial developer of the document preparation system LaTeX and the author of its first manual.

The device independent file format (DVI) is the output file format of the TeX typesetting program, designed by David R. Fuchs and implemented by Donald E. Knuth in 1982. Unlike the TeX markup files used to generate them, DVI files are not intended to be human-readable; they consist of binary data describing the visual layout of a document in a manner not reliant on any specific image format, display hardware or printer. DVI files are typically used as input to a second program which translates DVI files to graphical data. For example, most TeX software packages include a program for previewing DVI files on a user's computer display; this program is a driver. Drivers are also used to convert from DVI to popular page description languages and for printing.

The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery.
In computer science, group coded recording or group code recording (GCR) refers to several distinct but related encoding methods for representing data on magnetic media. The first, used in 6250 bpi magnetic tape since 1973, is an error-correcting code combined with a run-length limited (RLL) encoding scheme, belonging into the group of modulation codes. The others are different mainframe hard disk as well as floppy disk encoding methods used in some microcomputers until the late 1980s. GCR is a modified form of a NRZI code, but necessarily with a higher transition density.

Hevea brasiliensis, the Pará rubber tree, sharinga tree, seringueira, or most commonly, rubber tree or rubber plant, is a flowering plant belonging to the spurge family Euphorbiaceae originally native to the Amazon basin, but is now pantropical in distribution due to introductions. It is the most economically important member of the genus Hevea because the milky latex extracted from the tree is the primary source of natural rubber.
In computing, Pic is a domain-specific programming language by Brian Kernighan for specifying line diagrams. The language contains predefined basic linear objects: line, move, arrow, and spline, the planar objects box, circle, ellipse, arc, and definable composite elements. Objects are placed with respect to other objects or absolute coordinates. A liberal interpretation of the input invokes default parameters when objects are incompletely specified. An interpreter translates this description into concrete drawing commands in a variety of possible output formats. Pic is a procedural programming language, with variable assignment, macros, conditionals, and looping. The language is an example of a little language originally intended for the comfort of non-programmers in the Unix environment.
xindy is a flexible program for sorting and formatting book indexes. It was written by Joachim Schrod as a successor to MakeIndex. xindy supports indexing for a variety of programs, including especially LaTeX and troff, and produces complex indices of the data.
In public-key cryptography, Edwards-curve Digital Signature Algorithm (EdDSA) is a digital signature scheme using a variant of Schnorr signature based on twisted Edwards curves. It is designed to be faster than existing digital signature schemes without sacrificing security. It was developed by a team including Daniel J. Bernstein, Niels Duif, Tanja Lange, Peter Schwabe, and Bo-Yin Yang. The reference implementation is public-domain software.

Sebastian Patrick Quintus Rahtz (SPQR) was a British digital humanities information professional.
The PostScript Standard Encoding is one of the character sets used by Adobe Systems' PostScript (PS) since 1984. In 1995, IBM assigned code page 1276 to this character set. NeXT based the character set for its NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP operating systems on this one.
OMS is a 7-bit TeX encoding developed by Donald E. Knuth. It encodes mathematical symbols with variable sizes like for capital Pi notation, brackets, braces and radicals.
OML is a 7-bit TeX encoding developed by Donald E. Knuth. It encodes italic Latin and Greek letters for mathematical formulas and various symbols.
OT1 is a 7-bit TeX encoding developed by Donald E. Knuth.
The PostScript Latin 1 Encoding is one of the character sets used by Adobe Systems' PostScript (PS) since 1984 (1982). In 1995, IBM assigned code page 1277 to this character set. It is a superset of ISO 8859-1.
References
- 1 2 Mittelbach, Frank; Fairbairns, Robin; Lemberg, Werner (2016-02-18) [1995]. "LATEX font encodings" (PDF). LATEX3 Project Team. pp. 11, 35. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-07-10. Retrieved 2017-07-10.
- ↑ Mittelbach, Frank; Goossens, Michel; Braams, Johannes; Carlisle, David; Rowley, Chris (2004). The LATEX Companion (2nd ed.). Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts, USA: Addison-Wesley. p. 416. ISBN 9780201362992.