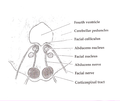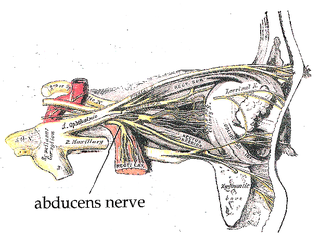
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocular muscles responsible for outward gaze. It is a somatic efferent nerve.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The pons is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.

The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that interconnects the cerebrum and diencephalon with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.
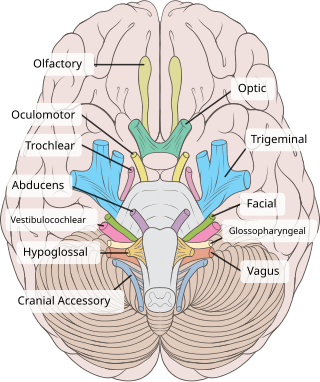
The trochlear nerve, also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates a single muscle - the superior oblique muscle of the eye. Unlike most other cranial nerves, the trochlear nerve is exclusively a motor nerve.
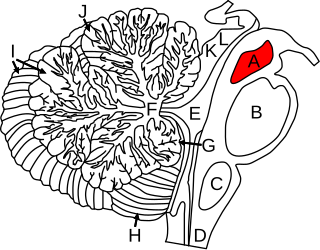
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the rostral-most portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
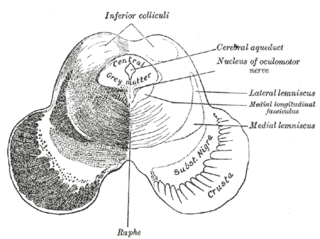
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is an area of crossed over tracts, on each side of the brainstem. These bundles of axons are situated near the midline of the brainstem. They are made up of both ascending and descending fibers that arise from a number of sources and terminate in different areas, including the superior colliculus, the vestibular nuclei, and the cerebellum. It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement.

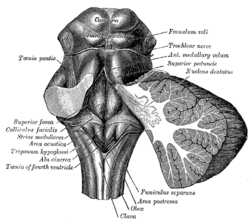
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The pontine tegmentum, or dorsal pons, is located within the brainstem, and is one of two parts of the pons, the other being the ventral pons or basilar part of the pons. The pontine tegmentum can be defined in contrast to the basilar pons: basilar pons contains the corticospinal tract running craniocaudally and can be considered the rostral extension of the ventral medulla oblongata; however, basilar pons is distinguished from ventral medulla oblongata in that it contains additional transverse pontine fibres that continue laterally to become the middle cerebellar peduncle. The pontine tegmentum is all the material dorsal from the basilar pons to the fourth ventricle. Along with the dorsal surface of the medulla, it forms part of the rhomboid fossa – the floor of the fourth ventricle.

The Edinger–Westphal nucleus is one of two nuclei of the oculomotor nerve and is located in the midbrain. It receives afferents from the both pretectal nuclei. It contains parasympathetic pre-ganglionic neuron cell bodies that synapse in the ciliary ganglion. It contributes the autonomic, parasympathetic component to the oculomotor nerve, ultimately providing innervation to the iris sphincter muscle and ciliary muscle to mediate the pupillary light reflex and accommodation, respectively.

The abducens nucleus is the originating nucleus from which the abducens nerve (VI) emerges—a cranial nerve nucleus. This nucleus is located beneath the fourth ventricle in the caudal portion of the pons near the midline, medial to the sulcus limitans.

The greater petrosal nerve is a nerve of the head mainly containing pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres which ultimately synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion. It branches from the facial nerve and is derived from the parasympathetic part of the nervus intermedius component of CN VII, with its cell bodies located in the superior salivary nucleus. In the connective tissue substance of the foramen lacerum, the greater petrosal nerve unites with the (sympathetic) deep petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal which proceeds to the pterygopalatine ganglion.

The nucleus of the trochlear nerve is a motor nucleus in the medial midbrain giving rise to the trochlear nerve.

The vestibular nuclei (VN) are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve located in the brainstem.

The rhomboid fossa is a rhombus-shaped depression that is the anterior part of the fourth ventricle. Its anterior wall, formed by the back of the pons and the medulla oblongata, constitutes the floor of the fourth ventricle.
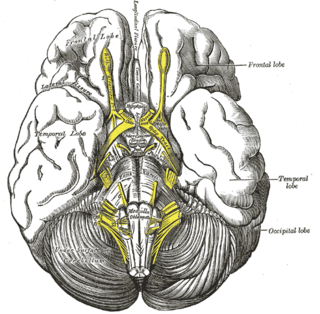
The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression of the ventral surface of the midbrain between the two crura cerebri.

The sulcus limitans is a groove on either side of the midline in the rhomboid fossa. It separates the cranial nerve motor nuclei, and the sensory nuclei. It is parallel to the median sulcus.

The vagal trigone is a triangular eminence upon the rhomboid fossa produced by the underlying dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve.

In the human brain, the rhomboid fossa is divided into symmetrical halves by a median sulcus which reaches from the upper to the lower angles of the fossa and is deeper below than above. On either side of this sulcus is an elevation, the medial eminence, bounded laterally by a sulcus, the sulcus limitans.
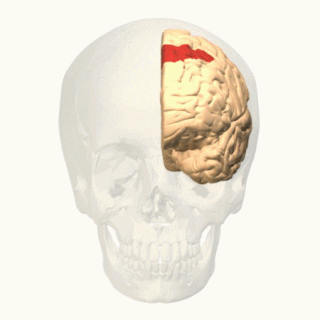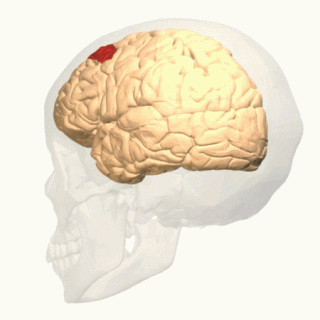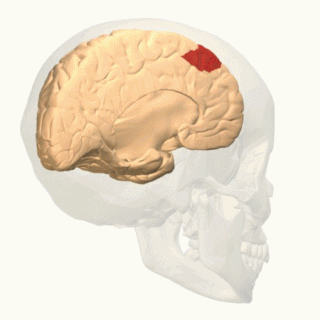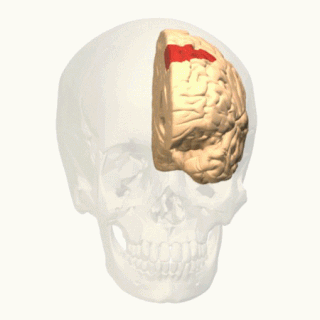
In neuroanatomy, corticomesencephalic tract is a descending nerve tract that originates in the frontal eye field and terminate in the midbrain. Its fibers mediate conjugate eye movement.