Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.

Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes.

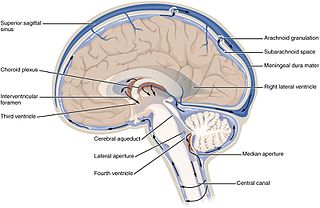
In neuroanatomy, the ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate.
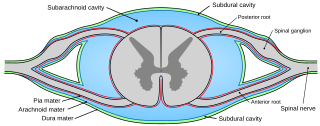
Pia mater, often referred to as simply the pia, is the delicate innermost layer of the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Pia mater is medieval Latin meaning "tender mother". The other two meningeal membranes are the dura mater and the arachnoid mater. Both the pia and arachnoid mater are derivatives of the neural crest while the dura is derived from embryonic mesoderm. The pia mater is a thin fibrous tissue that is permeable to water and small solutes. The pia mater allows blood vessels to pass through and nourish the brain. The perivascular space between blood vessels and pia mater is proposed to be part of a pseudolymphatic system for the brain. When the pia mater becomes irritated and inflamed the result is meningitis.

The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid.

The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
The aperture of an optical system is the opening that limits the amount of light that can pass through.

The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid. Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively.

In the brain, the interventricular foramina are channels that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain. As channels, they allow cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) produced in the lateral ventricles to reach the third ventricle and then the rest of the brain's ventricular system. The walls of the interventricular foramina also contain choroid plexus, a specialized CSF-producing structure, that is continuous with that of the lateral and third ventricles above and below it.
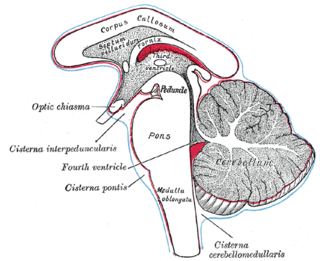
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The cisterna magna is the largest of the subarachnoid cisterns. It occupies the space created by the angle between the caudal/inferior surface of the cerebellum, and the dorsal/posterior surface of the medulla oblongata. The fourth ventricle communicates with the cistern via the unpaired midline median aperture. It is continuous inferiorly with the subarachnoid space of the spinal canal.

The arachnoid mater is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural crest mesoectoderm in the embryo.

The lateral aperture of the fourth ventricle or foramen of Luschka is an opening at the lateral extremity of either lateral recess of the fourth ventricle opening anteriorly into the pontine cistern/lateral cerebellomedullary cistern at cerebellopontine angle. A tuft of choroid plexus commonly extends into the lateral aperture, partially obstructing CSF flow through this aperture.

The tela choroidea is a region of meningeal pia mater that adheres to the underlying ependyma, and gives rise to the choroid plexus in each of the brain’s four ventricles. Tela is Latin for woven and is used to describe a web-like membrane or layer. The tela choroidea is a very thin part of the loose connective tissue of pia mater overlying and closely adhering to the ependyma. It has a rich blood supply. The ependyma and vascular pia mater – the tela choroidea, form regions of minute projections known as a choroid plexus that projects into each ventricle. The choroid plexus produces most of the cerebrospinal fluid of the central nervous system that circulates through the ventricles of the brain, the central canal of the spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space. The tela choroidea in the ventricles forms from different parts of the roof plate in the development of the embryo.

The superior medullary velum is a thin, transparent lamina of white matter which - together with the inferior medullary velum - forms the roof of the fourth ventricle. It extends between the two superior cerebellar peduncles. The lingula of cerebellum covers - and adheres to - its dorsal surface.
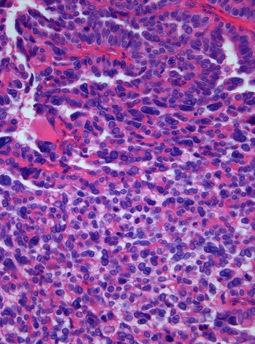
A choroid plexus carcinoma is a type of choroid plexus tumor that affects the choroid plexus of the brain. It is considered the worst of the three grades of chord plexus tumors, having a much poorer prognosis than choroid atypical plexus papilloma and choroid plexus papilloma. The disease creates lesions in the brain and increases cerebrospinal fluid volume, resulting in hydrocephalus.
The choroid glomus or glomus choroideum, is an enlargement of the choroid plexus located in the atrium of each lateral ventricle. They are commonly calcified in adults and can easily be seen as a bright tufts on CT imaging. Their main purpose is for the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Bobble-head doll syndrome is a rare neurological movement disorder in which patients, usually children around age 3, begin to bob their head and shoulders forward and back, or sometimes side-to-side, involuntarily, in a manner reminiscent of a bobblehead doll. The syndrome is related to cystic lesions and swelling of the third ventricle in the brain.















