Related Research Articles
A political spectrum is a system to characterize and classify different political positions in relation to one another. These positions sit upon one or more geometric axes that represent independent political dimensions. The expressions political compass and political map are used to refer to the political spectrum as well, especially to popular two-dimensional models of it.

Theodor W. Adorno was a German philosopher, sociologist, psychologist, musicologist, and composer known for his critical theory of society.

A subculture is a group of people within a culture that differentiates itself from the parent culture to which it belongs, often maintaining some of its founding principles. Subcultures develop their own norms and values regarding cultural, political, and sexual matters. Subcultures are part of society while keeping their specific characteristics intact. Examples of subcultures include hippies, goths, bikers, and skinheads. The concept of subcultures was developed in sociology and cultural studies. Subcultures differ from countercultures.

Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behaviour of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behaviour.

The Frankfurt School was a school of social theory and critical philosophy associated with the Institute for Social Research, at Goethe University Frankfurt in 1929. Founded in the Weimar Republic (1918–1933), during the European interwar period (1918–1939), the Frankfurt School comprised intellectuals, academics, and political dissidents dissatisfied with the contemporary socio-economic systems of the 1930s. The Frankfurt theorists proposed that social theory was inadequate for explaining the turbulent political factionalism and reactionary politics occurring in 20th century liberal capitalist societies. Critical of both capitalism and of Marxism–Leninism as philosophically inflexible systems of social organization, the School's critical theory research indicated alternative paths to realizing the social development of a society and a nation.
The term culture industry was coined by the critical theorists Theodor Adorno (1903–1969) and Max Horkheimer (1895–1973), and was presented as critical vocabulary in the chapter "The Culture Industry: Enlightenment as Mass Deception", of the book Dialectic of Enlightenment (1947), wherein they proposed that popular culture is akin to a factory producing standardized cultural goods—films, radio programmes, magazines, etc.—that are used to manipulate mass society into passivity. Consumption of the easy pleasures of popular culture, made available by the mass communications media, renders people docile and content, no matter how difficult their economic circumstances. The inherent danger of the culture industry is the cultivation of false psychological needs that can only be met and satisfied by the products of capitalism; thus Adorno and Horkheimer especially perceived mass-produced culture as dangerous to the more technically and intellectually difficult high arts. In contrast, true psychological needs are freedom, creativity, and genuine happiness, which refer to an earlier demarcation of human needs, established by Herbert Marcuse.
In sociology, postmaterialism is the transformation of individual values from materialist, physical, and economic to new individual values of autonomy and self-expression.
In Marxist theory, interpellation—the process by which we encounter a culture's or ideology's values and internalize them—is an important concept regarding the notion of ideology. It is associated in particular with the work of French philosopher Louis Althusser. According to Althusser, every society is made up of ideological state apparatuses (ISAs) and repressive state apparatuses (RSAs) which are instrumental to constant reproduction of the relations to the production of that given society. While ISAs belong to the private domain and refer to private institutions, the RSA is one public institution (police/military) controlled by the government. Consequently, 'interpellation' describes the process by which ideology, embodied in major social and political institutions, constitutes the very nature of individual subjects' identities through the process of "hailing" them in social interactions.
In sociology, taste or palate is an individual or a demographic group's subjective preferences of dietary, design, cultural and/or aesthetic patterns. Taste manifests socially via distinctions in consumer choices such as delicacies/beverages, fashions, music, etiquettes, goods, styles of artwork, and other related cultural activities. The social inquiry of taste is about the arbitrary human ability to judge what is considered beautiful, good, proper and valuable.
VALS is a proprietary research methodology used for psychographic market segmentation. Market segmentation is designed to guide companies in tailoring their products and services in order to appeal to the people most likely to purchase them.
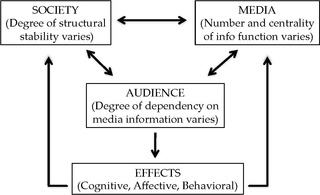
Media system dependency theory (MSD), or simply media dependency, was developed by Sandra Ball-Rokeach and Melvin Defleur in 1976. The theory is grounded in classical sociological literature positing that media and their audiences should be studied in the context of larger social systems.

The sociology of literature is a subfield of the sociology of culture. It studies the social production of literature and its social implications. A notable example is Pierre Bourdieu's 1992 Les Règles de L'Art: Genèse et Structure du Champ Littéraire, translated by Susan Emanuel as Rules of Art: Genesis and Structure of the Literary Field (1996). For a concise overview of the "state-of-the-art" of the sociology of literature, look at Váňa (2020).
Popular culture is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of the practices, beliefs, and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a society at a given point in time. Popular culture also encompasses the activities and feelings produced as a result of interaction with these dominant objects. The primary driving force behind popular culture is mass appeal, and it is produced by what cultural analyst Theodor Adorno refers to as the "culture industry". Heavily influenced in modern times by mass media, this collection of ideas permeates the everyday lives of people in a given society. Therefore, popular culture has a way of influencing an individual's attitudes towards certain topics. However, there are various ways to define pop culture. Because of this, popular culture is something that can be defined in a variety of conflicting ways by different people across different contexts. It is generally viewed in contrast to other forms of culture such as folk cults, working-class culture, or high culture, and also through different high praised perspectives such as psychoanalysis, structuralism, postmodernism, and more. The common pop-culture categories are: entertainment, sports, news, politics, fashion, technology, and slang.
Values scales are psychological inventories used to determine the values that people endorse in their lives. They facilitate the understanding of both work and general values that individuals uphold. In addition, they assess the importance of each value in people's lives and how the individual strives toward fulfillment through work and other life roles, such as parenting. Most scales have been normalized and can therefore be used cross-culturally for vocational, marketing, and counseling purposes, yielding unbiased results. Psychologists, political scientists, economists, and others interested in defining values, use values scales to determine what people value, and to evaluate the ultimate function or purpose of values.

Augusto Ponzio is an Italian semiologist and philosopher.
In cultural studies, media culture refers to the current Western capitalist society that emerged and developed from the 20th century, under the influence of mass media. The term alludes to the overall impact and intellectual guidance exerted by the media, not only on public opinion but also on tastes and values.

Lynn R Kahle is an American consumer psychologist and Professor Emeritus at the University of Oregon's Lundquist College of Business. From 2018-2020 he taught at the Lubin School of Business, Pace University in New York as a Visiting Scholar and Professor.
Ethnosemiotics is a disciplinary perspective which links semiotics concepts to ethnographic methods.

Marxist cultural analysis is a form of cultural analysis and anti-capitalist cultural critique, which assumes the theory of cultural hegemony and from this specifically targets those aspects of culture which are profit driven and mass-produced under capitalism.
References
Notes
- ↑ Lifestyle from Merriam-Webster's Dictionary
- ↑ Lynn R. Kahle; Angeline G. Close (2011). Consumer Behavior Knowledge for Effective Sports and Event Marketing. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-87358-1.
- 1 2 Online Etymology Dictionary
- ↑ Spaargaren, G., and B. VanVliet (2000) "Lifestyle, Consumption and the Environment: The Ecological Modernisation of Domestic Consumption", Environmental Politics9(1): 50-75.
- ↑ Giddens, A. (1991) Modernity and self-identity: self and society in the late modern age, Cambridge: Polity Press
- ↑ Lynn R. Kahle, Eda Gurel-Atay, Eds (2014). Communicating Sustainability for the Green Economy. New York: M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 978-0-7656-3680-5.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ↑ Ropke, I. (1999) "The Dynamics of Willingness to Consume", Ecological Economics 28: 399-420.
- ↑ Giuffrâe, K., & DiGeronimo, T. (1999) Care and Feeding of Your Brain : How Diet and Environment Affect What You Think and Feel, Career Press.
- ↑ Berzano L., Genova C., Lifestyles and Subcultures. History and a New Perspective, Routledge, London, 2015 (Part I).
- ↑ Ponthiere G. (2011) "Mortality, Family and Lifestyles", Journal of Family and Economic Issues32 (2): 175-190
- ↑ Case, A., Lubotsky D. & Paxson C. (2002) "Economic Status and Health in Childhood: The Origins of the Gradient", The American Economic Review 92(5): 1308-1334
- ↑ William Dufty (1975) Sugar Blues , page 204
- ↑ Bögenhold, Dieter (2001). "Social Inequality and the Sociology of Life Style: Material and Cultural Aspects of Social Stratification". American Journal of Economics and Sociology. 60 (4): 829–847. doi:10.1111/1536-7150.00125.
- 1 2 Bernstein (1991) p.23
- ↑ Adorno [1963] p.98
Bibliography
- Adorno, Th., "Culture Industry Reconsidered," in Adorno (1991).
- Adorno, The Culture Industry - Selected essays on mass culture, Routledge, London, 1991.
- Amaturo E., Palumbo M., Classi sociali. Stili di vita, coscienza e conflitto di classe. Problemi metodologici, Ecig, Genova, 1990.
- Ansbacher H. L., Life style. A historical and systematic review, in “Journal of individual psychology”, 1967, vol. 23, n. 2, pp. 191–212.
- Bell D., Hollows J., Historicizing lifestyle. Mediating taste, consumption and identity from the 1900s to 1970s, Asghate, Aldershot-Burlington, 2006.
- Bénédicte Châtel (Auteur), Jean-Luc Dubois (Auteur), Bernard Perret (Auteur), Justice et Paix-France (Auteur), François Maupu (Postface), Notre mode de vie est-il durable ? : Nouvel horizon de la responsabilité, Karthala Éditions, 2005
- Bernstein, J. M. (1991) "Introduction," in Adorno (1991)
- Berzano L., Genova C., Lifestyles and Subcultures. History and a New Perspective, Routledge, London, 2015.
- Burkle, F. M. (2004)
- Calvi G. (a cura di), Indagine sociale italiana. Rapporto 1986, Franco Angeli, Milano, 1987.
- Calvi G. (a cura di), Signori si cambia. Rapporto Eurisko sull’evoluzione dei consumi e degli stili di vita, Bridge, Milano, 1993.
- Calvi G., Valori e stili di vita degli italiani, Isedi, Milano, 1977.
- Cathelat B., Les styles de vie des Français 1978–1998, Stanké, Parigi, 1977.
- Cathelat B., Socio-Styles-Système. Les “styles de vie”. Théorie, méthodes, applications, Les éditions d’organisation, Parigi, 1990.
- Cathelat B., Styles de vie, Les éditions d’organisation, pàgiri, 1985.
- Chaney D., Lifestyles, Routledge, Londra, 1996.
- Fabris G., Mortara V., Le otto Italie. Dinamica e frammentazione della società italiana, Mondadori, Milano, 1986.
- Faggiano M. P., Stile di vita e partecipazione sociale giovanile. Il circolo virtuoso teoria-ricerca-teoria, Franco Angeli, Milano, 2007.
- Gonzalez Moro V., Los estilos de vida y la cultura cotidiana. Un modelo de investigacion, Baroja, [San Sebastian, 1990].
- Kahle L., Attitude and social adaption. A person-situation interaction approach, Pergamon, Oxford, 1984.
- Kahle L., Social values and social change. Adaptation to life in America, Praeger, Santa Barbara, 1983.
- Leone S., Stili di vita. Un approccio multidimensionale, Aracne, Roma, 2005.
- Mitchell A., Consumer values. A tipology, Values and lifestyles program, SRI International, Stanford, 1978.
- Mitchell A., Life ways and life styles, Business intelligence program, SRI International, Stanford, 1973.
- Mitchell A., The nine American lifestyles. Who we are and where we’re going, Macmillan, New York, 1983.
- Mitchell A., Ways of life, Values and lifestyles program, SRI International, Stanford, 1982.
- Negre Rigol P., El ocio y las edades. Estilo de vida y oferta lúdica, Hacer, Barcellona, 1993.
- Parenti F., Pagani P. L., Lo stile di vita. Come imparare a conoscere sé stessi e gli altri, De Agostini, Novara, 1987.
- Patterson M. Consumption and Everyday Life, 2006
- Ragone G., Consumi e stili di vita in Italia, Guida, Napoli, 1985.
- Ramos Soler I., El estilo de vida de los mayores y la publicidad, La Caixa, Barcellona, [2007].
- Rokeach M., Beliefs, attitudes and values, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, 1968.
- Rokeach M., The nature of human values, Free Press, New York, 1973.
- Shields R., Lifestyle shopping. The subject of consumption, Routledge, Londra, 1992.
- Shulman B. H., Mosak H. H., Manual for life style assessment, Accelerated Development, Muncie, 1988 (trad. it. Manuale per l’analisi dello stile di vita, Franco Angeli, Milano, 2008).
- Sobel M. E., Lifestyle and social structure. Concepts, definitions and analyses, Academic Press, New York, 1981.
- Soldevilla Pérez C., Estilo de vida. Hacia una teoría psicosocial de la acción, Entimema, Madrid, 1998.
- Valette-Florence P., Les styles de vie. Bilan critique et perspectives. Du mythe à la réalité, Nathan, Parigi, 1994.
- Valette-Florence P., Les styles de vie. Fondements, méthodes et applications, Economica, Parigi, 1989.
- Valette-Florence P., Jolibert A., Life-styles and consumption patterns, Publications de recherche du CERAG, École supériore des affaires de Grenoble, 1988.
- Veal A. J., The concept of lifestyle. A review, in “Leisure studies”, 1993, vol. 12, n. 4, pp. 233–252.
- Vergati S., Stili di vita e gruppi sociali, Euroma, Roma, 1996.
- Walters G. D., Beyond behavior. Construction of an overarching psychological theory of lifestyles, Praeger, Westport, 2000.
- Wells W. (a cura di), Life-style and psycographics, American marketing association, Chicago, 1974.
- Yankelovich D., New criteria for market segmentation, in “Harvard Business Review”, 1964, vol. 42, n. 2, pp. 83–90.
- Yankelovich D., Meer D., Rediscovering market segmentation, in “Harvard Business Review”, 2006, febbraio, pp. 1–10.