
The left and right brachiocephalic veins are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein.

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.
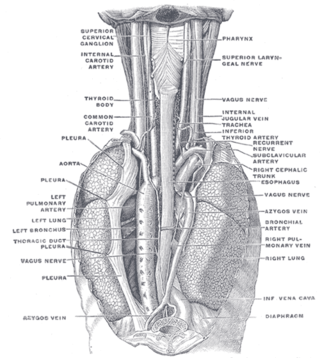
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.
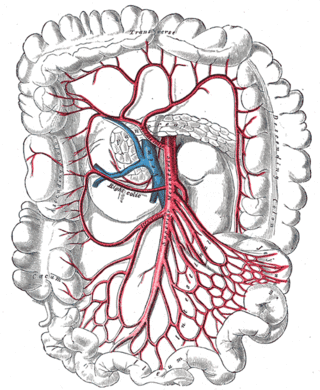
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the large intestine. It usually terminates when reaching the splenic vein, which goes on to form the portal vein with the superior mesenteric vein (SMV).

The superior sagittal sinus, within the human head, is an unpaired area along the attached margin of the falx cerebri. It allows blood to drain from the lateral aspects of anterior cerebral hemispheres to the confluence of sinuses. Cerebrospinal fluid drains through arachnoid granulations into the superior sagittal sinus and is returned to venous circulation.
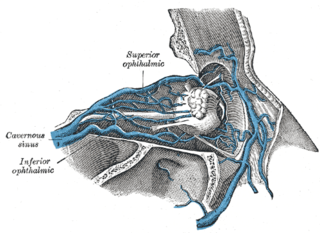
The superior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. It is formed by the union of the angular vein, and supraorbital vein. It passes backwards within the orbit alongside the ophthalmic artery, then exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to drain into the cavernous sinus.

The inferior thyroid veins appear two, frequently three or four, in number, and arise in the venous plexus on the thyroid gland, communicating with the middle and superior thyroid veins. While the superior and middle thyroid veins serve as direct tributaries to the internal jugular vein, the inferior thyroid veins drain directly to the brachiocephalic veins.

The inferior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. It begins from a venous network in the front of the orbit, then passes backwards through the lower orbit. It drains several structures of the orbit. It may end by splitting into two branches, one draining into the pterygoid venous plexus and the other ultimately into the cavernous sinus.

The supraorbital vein is a vein of the forehead. It communicates with the frontal branch of the superficial temporal vein. It passes through the supraorbital notch, and merges with the angular vein to form the superior ophthalmic vein. The supraorbital vein helps to drain blood from the forehead, eyebrow, and upper eyelid.

The rectal venous plexus is the venous plexus surrounding the rectum. It consists of an internal and an external rectal plexus. It is drained by the superior, middle, and inferior rectal veins. It forms a portosystemic (portocaval) anastomosis. This allows rectally administered medications to bypassing first pass metabolism.

The superior cerebral veins are several cerebral veins that drain the superolateral and superomedial surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres into the superior sagittal sinus. There are 8-12 cerebral veins. They are predominantly found in the sulci between the gyri, but can also be found running across the gyri.

The internal cerebral veins are two veins included in the group of deep cerebral veins that drain the deep parts of the hemispheres; each internal cerebral vein is formed near the interventricular foramina by the union of the superior thalamostriate vein and the superior choroid vein.

In human anatomy, the cerebral veins are blood vessels in the cerebral circulation which drain blood from the cerebrum of the human brain. They are divisible into external and internal groups according to the outer or inner parts of the hemispheres they drain into.

The cerebellar veins are veins which drain the cerebellum. They consist of the superior cerebellar veins and the inferior cerebellar veins. The superior cerebellar veins drain to the straight sinus and the internal cerebral veins. The inferior cerebellar veins drain to the transverse sinus, the superior petrosal sinus, and the occipital sinus.

The inferior mesenteric vein begins in the rectum as the superior rectal vein, which has its origin in the hemorrhoidal plexus, and through this plexus communicates with the middle and inferior hemorrhoidal veins.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries that supply the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space. The highest intercostal artery is an artery in the human body that usually gives rise to the first and second posterior intercostal arteries, which supply blood to their corresponding intercostal space. It usually arises from the costocervical trunk, which is a branch of the subclavian artery. Some anatomists may contend that there is no supreme intercostal artery, only a supreme intercostal vein.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The middle cerebral veins - the superficial middle cerebral vein and the deep middle cerebral vein - are two veins running along the lateral sulcus. The superficial middle cerebral vein is also known as the superficial Sylvian vein, and the deep middle cerebral vein is also known as the deep Sylvian vein. The lateral sulcus is also known as the Sylvian fissure.

















