Articles related to anatomy include:

The occipital bone is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput. It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of the skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord.

The scalp is the area of the head where head hair grows. It is made up of skin, layers of connective and fibrous tissues, and the membrane of the skull. Anatomically, the scalp is part of the epicranium, a collection of structures covering the cranium. The scalp is bordered by the face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. The scientific study of hair and scalp is called trichology.
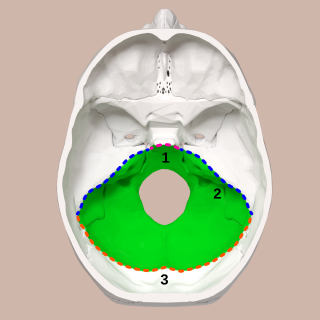
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone. It lodges the cerebellum, and parts of the brainstem.
The emissary veins connect the extracranial venous system with the intracranial venous sinuses. They connect the veins outside the cranium to the venous sinuses inside the cranium. They drain from the scalp, through the skull, into the larger meningeal veins and dural venous sinuses. They may also connect to diploic veins within the skull.

The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

The confluence of sinuses, torcular Herophili, or torcula is the connecting point of the superior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, and occipital sinus. It is below the internal occipital protuberance of the skull. It drains venous blood from the brain into the transverse sinuses. It may be affected by arteriovenous fistulas, a thrombus, major trauma, or surgical damage, and may be imaged with many radiology techniques.

The superior sagittal sinus, within the human head, is an unpaired area along the attached margin of the falx cerebri. It allows blood to drain from the lateral aspects of anterior cerebral hemispheres to the confluence of sinuses. Cerebrospinal fluid drains through arachnoid granulations into the superior sagittal sinus and is returned to venous circulation.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The transverse sinuses, within the human head, are two areas beneath the brain which allow blood to drain from the back of the head. They run laterally in a groove along the interior surface of the occipital bone. They drain from the confluence of sinuses to the sigmoid sinuses, which ultimately connect to the internal jugular vein. See diagram : labeled under the brain as "SIN. TRANS.".
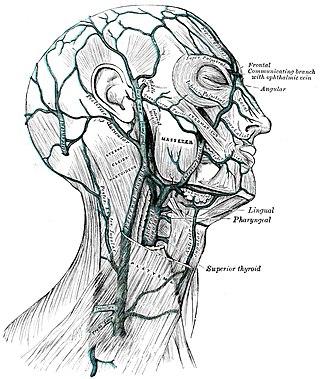
The pterygoid plexus is a fine venous plexus upon and within the lateral pterygoid muscle. It drains by a short maxillary vein.

The posterior auricular vein is a vein of the head. It begins from a plexus with the occipital vein and the superficial temporal vein, descends behind the auricle, and drains into the external jugular vein.
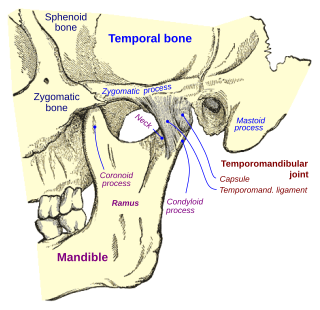
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, the mastoid part articulates with two other bones.

The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word petrosus, meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. In other mammals, it is a separate bone, the petrosal bone.

The squamous part of occipital bone is situated above and behind the foramen magnum, and is curved from above downward and from side to side.

The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to the dura mater.

The mastoid cells are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium. The mastoid cells are a form of skeletal pneumaticity. Infection in these cells is called mastoiditis.

The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
















